The 8 Parts of Speech: Examples and Rules

- The 8 parts of speech are nouns , pronouns , adjectives , verbs , adverbs , prepositions , conjunctions , and articles .
- Every word in English can be classified as one of these 8 parts of speech.
- The term part of speech refers to a word’s role in a sentence.
- Some words can be different parts of speech depending on how they’re used in a sentence, such as work ( noun and verb ) and well ( adverb , adjective , and noun ).
- The parts of speech fall into two word classes : open (parts of speech that regularly acquire new words) and closed (parts of speech that don’t readily acquire new words).
Mastering the parts of speech is essential for clear communication, strong writing, and learning other languages. Here, we’ll explore the rules behind the different parts of speech and how to use them together in grammatically correct sentences, with examples.
Work smarter with Grammarly The AI writing assistant for anyone with work to do Get Grammarly

Table of contents
What are the 8 parts of speech, how to identify parts of speech, when a word can be different parts of speech, open vs. closed word classes, the 8 parts of speech faqs.
A noun is a word that names a person, place, concept, or object. Basically, anything that names a “thing” is a noun.
basketball court
San Francisco
self-preservation
Nouns fall into two categories: common nouns and proper nouns . Common nouns are general names for things, such as:
Proper nouns are names or titles for specific things, such as:
2 Pronouns
Pronouns are words you substitute for specific nouns when the reader or listener already knows which specific noun you’re referring to.
You might say, “Jennifer was supposed to be here at eight,” then follow it with “ She’s always late; next time I’ll tell her to be here a half hour earlier.”
Instead of saying Jennifer’s name three times in a row, you substituted she and her , and your sentences remained grammatically correct.
3 Adjectives
Adjectives are the words that describe nouns. Think about your favorite movie. How would you describe it to a friend who’s never seen it?
“That movie movie was funny , engaging , and well-written .
When describing the movie with these words, you’re using adjectives. An adjective can go right before the noun it’s describing:
“I have a black dog.”
But it doesn’t have to. Sometimes, adjectives are at the end of a sentence:
“My dog is black. ”
Verbs are words that describe specific actions, whether physical or mental.
“ Go ! Be amazing!”
“ Run as fast as you can .”
“The coach congratulated every participant who put in the work and competed .”
Not all verbs refer to literal actions, though. Verbs that refer to feelings or states of being, like to love and to be , are known as nonaction verbs .
“She seems happy.”
The verb seems is a non-action verb, describing a state of being rather than an action. Conversely, the verbs that refer to literal actions are known as action verbs .
“He runs every morning.”
The verb runs is an action verb describing what he does .
5 Adverbs
An adverb is a word that describes an adjective, a verb, or another adverb.
“ I entered the room quietly .”
Quietly describes how you entered (verb) the room.
“ A cheetah is always faster than a lion.”
Always describes how frequently a cheetah is faster (adjective) than a lion.
6 Prepositions
Prepositions tell you the relationships between other words in a sentence.
“I left my bike leaning against the garage.”
Against is the preposition because it tells us where you left your bike.
“She put the pizza in the oven.”
Without the preposition in , we don’t know where the pizza is.
7 Conjunctions
Conjunctions make it possible to build complex sentences that express multiple ideas.
“ I like marinara sauce. I like alfredo sauce. I don’t like puttanesca sauce.”
Each of these three sentences expresses a clear idea. There’s nothing wrong with listing your preferences like this, but it’s not the most efficient way to do it. Consider instead:
“I like marinara sauce and alfredo sauce, but I don’t like puttanesca sauce.”
In this sentence, and and but are the two conjunctions linking your ideas.
8 Articles
Articles are words that appear before nouns to indicate whether the noun is specific or general.
The brick house
An exciting experience
A , the , and an are all examples of articles. Articles come in two types: definite articles and indefinite articles . Similarly to the two types of nouns, the type of article you use depends on how specific you need to be about the thing you’re discussing.
A definite article, like the or this , describes one specific noun.
“ Did you buy the car?”
From the above sentence, we understand that the speaker is referring to a specific previously discussed car.
Now swap in an indefinite article:
“ Did you buy a car?”
The implication that you’re referring back to something specific is gone, and it becomes a more general question.
Sometimes, it’s difficult to tell which part of speech a word is. Here are a few easy tips for quickly figuring out what part of speech you’re dealing with:
- If it’s an adjective plus the ending –ly , it’s an adverb . Examples: commonly , quickly .
- If you can swap it out for a noun and the sentence still makes sense, it’s a pronoun . Examples: “ He played basketball.” / “ Steve played basketball.”
- If it’s something you do and you can modify the sentence to include the word do , it’s a verb . Examples: “I have an umbrella.” / “I do have an umbrella.”
- If you can remove the word and the sentence still makes sense, but you lose a detail, the word is most likely an adjective . Examples: “She drives a red van.” / “She drives a van.”
And if you’re ever really stumped, just look the word up. Dictionaries typically list a word’s part of speech in its entry. If it has multiple forms with different parts of speech, they are all listed with examples.
Here’s a tip: Want to make sure you’re using parts of speech correctly in your writing ? Grammarly can check your spelling and save you from grammar and punctuation mistakes. It even proofreads your text, so your work is extra polished wherever you write.
Just like y is sometimes a vowel and sometimes a consonant , some words are sometimes one part of speech and other times another.
Let’s use the example of the word work .
“I went to work. ” (noun)
“I work in the garden.” (verb)
Now, let’s use the word well as another example.
“She paints very well. ” (adverb)
“They are finally well now, after weeks of illness.” (adjective)
“I dropped a penny into the well .” (noun)
Finally, let’s use the word but as an example.
“I cooked breakfast and lunch, but Steve cooked dinner.” (conjunction)
“I brought everything but the pens you asked for.” (preposition)
Sometimes, words evolve to add forms that are new parts of speech. One recent example is the word adult . Before the 2010s, adult was primarily a noun that referred to a fully grown person. It could also be used as an adjective to refer to specific types of media, like adult contemporary music. At the turn of the 2010s, the word adulting , a brand-new verb, appeared in the internet lexicon. As a verb, adulting refers to the act of doing tasks associated with adulthood, like paying bills and grocery shopping.
The parts of speech fall into two word classes : open and closed .
Open word classes are the parts of speech that regularly acquire new words. Language evolves, and that evolution usually takes place in nouns, adjectives, adverbs, and verbs.
In 2022, new words added to the Merriam-Webster dictionary included dumbphone (noun), greenwash (verb), and cringe (adjective).
Closed word classes are the parts of speech that don’t readily acquire new words. These parts of speech are more set in stone and include pronouns, conjunctions, articles, and prepositions.
“The cat is under the table.”
The word under is a closed class preposition that indicates a relationship between the cat and the table.
Nouns, pronouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and articles.
How do you tell what part of speech a word is?
Look at its role in the sentence. For example, does it describe an action (verb) or a thing (noun)?
Can a word be more than one part of speech?
Yes, words like well and work can function as different parts of speech depending on context.
What’s the difference between open and closed word classes?
Open class words can evolve, while closed class words remain fixed.

Parts of Speech
What are the parts of speech, a formal definition.
Table of Contents
The Part of Speech Is Determined by the Word's Function
Are there 8 or 9 parts of speech, the nine parts of speech, (1) adjective, (3) conjunction, (4) determiner, (5) interjection, (7) preposition, (8) pronoun, why the parts of speech are important, video lesson.

- You need to dig a well . (noun)
- You look well . (adjective)
- You dance well . (adverb)
- Well , I agree. (interjection)
- My eyes will well up. (verb)
- red, happy, enormous
- Ask the boy in the red jumper.
- I live in a happy place.
- I caught a fish this morning! I mean an enormous one.
- happily, loosely, often
- They skipped happily to the counter.
- Tie the knot loosely so they can escape.
- I often walk to work.
- It is an intriguingly magic setting.
- He plays the piano extremely well.
- and, or, but
- it is a large and important city.
- Shall we run to the hills or hide in the bushes?
- I know you are lying, but I cannot prove it.
- my, those, two, many
- My dog is fine with those cats.
- There are two dogs but many cats.
- ouch, oops, eek
- Ouch , that hurt.
- Oops , it's broken.
- Eek! A mouse just ran past my foot!
- leader, town, apple
- Take me to your leader .
- I will see you in town later.
- An apple fell on his head .
- in, near, on, with
- Sarah is hiding in the box.
- I live near the train station.
- Put your hands on your head.
- She yelled with enthusiasm.
- she, we, they, that
- Joanne is smart. She is also funny.
- Our team has studied the evidence. We know the truth.
- Jack and Jill went up the hill, but they never returned.
- That is clever!
- work, be, write, exist
- Tony works down the pit now. He was unemployed.
- I will write a song for you.
- I think aliens exist .
Are you a visual learner? Do you prefer video to text? Here is a list of all our grammar videos .
Video for Each Part of Speech
The Most Important Writing Issues
The top issue related to adjectives, the top issue related to adverbs.
- Extremely annoyed, she stared menacingly at her rival.
- Infuriated, she glared at her rival.
The Top Issue Related to Conjunctions
- Burger, Fries, and a shake
- Fish, chips and peas
The Top Issue Related to Determiners
The Top Issue Related to Interjections
The top issue related to nouns, the top issue related to prepositions, the top issue related to pronouns, the top issue related to verbs.
- Crack the parts of speech to help with learning a foreign language or to take your writing to the next level.

This page was written by Craig Shrives .
You might also like...
Help us improve....

Was something wrong with this page?

Use #gm to find us quicker .

Create a QR code for this, or any, page.
mailing list
grammar forum
teachers' zone
Confirmatory test.
This test is printable and sendable
expand to full page
show as slides
download as .doc
print as handout
send as homework
display QR code

All Parts of speech with their types, definition and example
All parts of speech are fundamental building blocks of language that help structure sentences and convey meaning. They define the function of each word in a sentence, making communication clearer and more effective. There are eight main parts of speech in English: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection. Each part serves a unique role, whether it’s naming things, describing actions, or showing relationships. Understanding the types and examples of each part is essential for mastering grammar and improving writing skills. Let’s explore these components in detail.
All Parts of speech
- Common Noun
- Proper Noun
- Abstract Noun
- Concrete Noun
- Collective Noun
- Personal Pronoun
- Possessive Pronoun
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Interrogative Pronoun
- Relative Pronoun
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Action Verb
- Linking Verb
- Helping Verb
- Transitive Verb
- Intransitive Verb
- Descriptive Adjective
- Quantitative Adjective
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Possessive Adjective
- Interrogative Adjective
- Comparative Adjective
- Superlative Adjective
- Adverb of Manner
- Adverb of Time
- Adverb of Place
- Adverb of Frequency
- Adverb of Degree
- Preposition
- Simple Preposition
- Compound Preposition
- Complex Preposition
- Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Subordinating Conjunction
- Correlative Conjunction
- Interjection
- Primary Interjection
- Secondary Interjection

All Parts of speech with their types
A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea.
- Common Noun : Names general things.
- Example Words : dog, city, book
- Sentence : The dog ran in the city .
- Proper Noun : Names specific people, places, or organizations.
- Example Words : Michael, London, Microsoft
- Sentence : Michael lives in London .
- Abstract Noun : Names ideas or concepts that cannot be seen or touched.
- Example Words : happiness, freedom, love
- Sentence : Happiness is important to everyone.
- Concrete Noun : Names things that can be seen or touched.
- Example Words : apple, car, chair
- Sentence : She ate an apple while sitting on the chair .
- Collective Noun : Names a group of people, animals, or things.
- Example Words : team, flock, bunch
- Sentence : The team won the game.
A pronoun is a word used instead of a noun to avoid repetition.
- Personal Pronoun : Refers to specific people or things.
- Example Words : I, you, he, she
- Sentence : She is going to the store.
- Possessive Pronoun : Shows ownership.
- Example Words : mine, yours, his
- Sentence : This book is mine .
- Reflexive Pronoun : Refers back to the subject of the sentence.
- Example Words : myself, yourself, himself
- Sentence : I made this cake myself .
- Demonstrative Pronoun : Points to specific things.
- Example Words : this, that, these, those
- Sentence : This is my pen.
- Interrogative Pronoun : Used to ask questions.
- Example Words : who, what, which
- Sentence : Who is at the door?
- Relative Pronoun : Connects a clause or phrase to a noun or pronoun.
- Example Words : who, which, that
- Sentence : The book that I read was interesting.
- Indefinite Pronoun : Refers to non-specific things or people.
- Example Words : anyone, someone, everything
- Sentence : Someone left a message for you.
A verb is a word that expresses an action or a state of being.
- Action Verb : Describes an action.
- Example Words : run, jump, write
- Sentence : She runs every morning.
- Linking Verb : Connects the subject to additional information.
- Example Words : am, is, are
- Sentence : The sky is blue.
- Helping Verb : Assists the main verb to form different tenses.
- Example Words : have, will, can
- Sentence : She will eat lunch later.
- Transitive Verb : Requires an object to complete its meaning.
- Example Words : give, send, eat
- Sentence : I give her a gift.
- Intransitive Verb : Does not require an object.
- Example Words : sleep, arrive, fall
- Sentence : He arrived late.
4. Adjective
An adjective is a word that describes or modifies a noun.
- Descriptive Adjective : Describes the qualities of a noun.
- Example Words : red, tall, happy
- Sentence : She has a red car.
- Quantitative Adjective : Shows the quantity of a noun.
- Example Words : some, few, many
- Sentence : There are many apples in the basket.
- Demonstrative Adjective : Points to specific nouns.
- Example Words : this, that, these
- Sentence : This book is new.
- Possessive Adjective : Shows ownership.
- Example Words : my, your, his
- Sentence : My cat is very cute.
- Interrogative Adjective : Used in questions to describe nouns.
- Example Words : which, what
- Sentence : Which color do you prefer?
- Comparative Adjective : Compares two nouns.
- Example Words : better, taller, more beautiful
- Sentence : This book is taller than that one.
- Superlative Adjective : Compares more than two nouns, showing the highest degree.
- Example Words : best, tallest, most beautiful
- Sentence : She is the best singer.
An adverb is a word that modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb. It often tells us how, when, where, how often, or to what extent something happens.
- Adverb of Manner : Describes how an action is done.
- Example Words : quickly, softly, carefully
- Sentence : She writes carefully to avoid mistakes.
- Adverb of Time : Indicates when an action occurs.
- Example Words : now, yesterday, soon
- Sentence : We will start the meeting soon .
- Adverb of Place : Shows the location of an action.
- Example Words : here, there, everywhere
- Sentence : Please put the box there .
- Adverb of Frequency : Describes how often an action happens.
- Example Words : always, rarely, often
- Sentence : He rarely eats fast food.
- Adverb of Degree : Indicates the intensity or degree of an action or quality.
- Example Words : very, too, quite
- Sentence : The movie was too loud.
6. Preposition
A preposition is a word that shows the relationship between a noun (or pronoun) and other words in a sentence. It often indicates location, direction, time, or manner.
- Simple Preposition : Single words that show relationships.
- Example Words : in, on, at
- Sentence : The cat is under the table.
- Compound Preposition : Made up of more than one word.
- Example Words : in front of, next to, out of
- Sentence : She sat next to her friend.
- Complex Preposition : A preposition that includes a more complex structure.
- Example Words : because of, due to, in spite of
- Sentence : The flight was delayed because of the weather.
7. Conjunction
A conjunction is a word that connects words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence. It helps in creating more complex and fluid sentences.
- Coordinating Conjunction : Connects words or groups of words that are similar.
- Example Words : and, but, or
- Sentence : I want to go to the beach, but it is raining.
- Subordinating Conjunction : Connects a dependent clause to an independent clause, showing a relationship between them.
- Example Words : because, although, if
- Sentence : I stayed home because it was raining.
- Correlative Conjunction : Pairs of conjunctions that work together to connect equal parts.
- Example Words : either…or, neither…nor
- Sentence : Either you come with us, or you stay here
8. Interjection
An interjection is a word or phrase that expresses strong emotion.
- Primary Interjection : Simple words that express emotion.
- Example Words : wow, oh, ouch
- Sentence : Wow , that’s amazing!
- Secondary Interjection : More complex expressions that show emotion.
- Example Words : hey, hooray, alas
- Sentence : Hooray for the winning team!
Parts of speech —FAQS
1: What are the parts of speech in English?
Answer: The parts of speech in English are categories of words based on their function in a sentence. The main parts of speech are:
FAQ 2: How can I identify a noun in a sentence?
Answer: Nouns are words that name people, places, things, or ideas. To identify a noun, look for words that refer to entities like “dog,” “city,” “happiness,” or “John.” They often act as the subject or object in a sentence.
FAQ 3: What is the difference between a verb and an adverb?
Answer: A verb is a word that expresses an action or state of being, such as “run,” “is,” or “think.” An adverb modifies verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, indicating how, when, where, how often, or to what extent something occurs. For example, in “She runs quickly,” “runs” is the verb, and “quickly” is the adverb modifying the verb.
FAQ 4: Can you explain the different types of pronouns?
Answer: Yes! There are several types of pronouns:
- Personal Pronouns : Refer to specific people or things (e.g., I, you, he, she).
- Possessive Pronouns : Show ownership (e.g., mine, yours, his).
- Reflexive Pronouns : Refer back to the subject (e.g., myself, yourself).
- Demonstrative Pronouns : Point to specific things (e.g., this, that).
- Interrogative Pronouns : Used to ask questions (e.g., who, what).
- Relative Pronouns : Connect clauses or phrases (e.g., who, which).
- Indefinite Pronouns : Refer to non-specific things (e.g., anyone, everything).
FAQ 5: What are adjectives and how do they differ from adverbs?
Answer: Adjectives describe or modify nouns, giving more detail about them (e.g., “happy,” “blue”). Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, providing information about how, when, where, or to what extent something happens (e.g., “quickly,” “very”). For example, in “The quick runner,” “quick” is an adjective describing “runner,” while in “She runs quickly,” “quickly” is an adverb modifying the verb “runs.”
FAQ 6: How do prepositions function in a sentence?
Answer: Prepositions are words that show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence, often indicating location, time, or direction (e.g., “in,” “on,” “before”). For example, in the sentence “The book is on the table,” the preposition “on” shows the relationship between “book” and “table.”
FAQ 7: What is the role of conjunctions?
Answer: Conjunctions connect words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence. They help to create complex sentences and show the relationships between different parts of the sentence. There are three main types:
- Coordinating Conjunctions : Connect similar words or clauses (e.g., “and,” “but”).
- Subordinating Conjunctions : Connect dependent clauses to independent clauses (e.g., “because,” “although”).
- Correlative Conjunctions : Work in pairs to connect equal parts (e.g., “either…or,” “neither…nor”).
FAQ 8: What is an interjection and how is it used?
Answer: An interjection is a word or phrase that expresses strong emotion or sudden exclamation (e.g., “Wow!”, “Ouch!”). It often stands alone and is typically followed by an exclamation mark. Interjections are used to convey emotions or reactions quickly and directly.
FAQ 9: Can parts of speech overlap or function differently?
Answer: Yes, some words can function as different parts of speech depending on their use in a sentence. For example, “run” can be a verb (“I run every day”) or a noun (“I went for a run”). Similarly, “fast” can be an adjective (“a fast car”) or an adverb (“He runs fast”).
FAQ 10: Why is it important to understand parts of speech?
Answer: Understanding parts of speech is crucial for constructing grammatically correct sentences, improving writing clarity, and enhancing communication skills. It helps learners identify and use words correctly and understand how words interact in a sentence.
Recent Posts
Examples of past continuous tense, examples of future continuous tense, 100 examples of present perfect tense, essay on environment conservation, write an essay on conservation of our environment 100-300 words, 100 examples of present continuous tense, mood in english grammar: definition, types, and examples, number in english grammar: definition, types, rules, and examples.
- Abbreviation
- active / Passive
- American Vs British
- Another Ways to Say
- Basic Grammar for beginner
- Brain Teasers
- Business English
- Business Words
- Collective Nouns
- Collocations
- Common Mistakes
- Communication
- Complex Sentences
- Compound Sentences
- Conditionals
- conjunctions
- Contractions
- Determiners
- Direct and Indirect
- English Exercises
- English Phrases
- English Riddles
- English Speaking
- Expressions
- Knowledge Base
- Miscellaneous
- Opposite Word
- Parts of Speech
- Personal Questions
- Phrasal Verbs
- Prepositions
- Punctuation
- Question Words
- Reading comprehension worksheet
- Reported Speech
- Right form of verbs
- Spoken English
- Synonyms – Antonyms
- Tag Question
- WH Question Words
- Word Family list

Welcome to English Grammar Zone, your trusted guide for mastering English grammar. Learn grammar easily with our simple explanations and practical examples. Start your journey today!
Top Categories
Quick links.
English Grammar Zone Copyright © 2024
- English Grammar Free Course
- English Grammar Tutorial
- Parts of Speech
- Figure of Speech
- Tenses Chart
- Essay Writing
- Email Writing
- NCERT English Solutions
- English Difference Between
- SSC CGL English Syllabus
- SBI PO English Syllabus
- SBI Clerk English Syllabus
- IBPS PO English Syllabus
- IBPS CLERK English Syllabus
Parts of Speech: Definitions, Examples & 8 Types
Every word is a part of speech playing a specific role in sentences or paragraphs. Parts of speech provide an organized way to align words and phrases, it is a fundamental meaning for a language to become more understandable and serve a specific purpose. Here, in this article, we will see what is Part of Speech, its types, and its uses. So let us dive in deeper to learn more about it!

Table of Content
What is Part of Speech?
Parts of speech chart.
- Different Types of Parts of Speech :
- Parts of Speech Examples Using Sentences
- Quiz to practice Parts of Speech
Parts of Speech – FAQs
The English language has thousands of words and every word has some function to perform. Some words are there to show action, some to join, and some to name something. There are 8 different parts of speech including nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, prepositions, conjunction, and interjection. And together, all the functions performed by words in the English language fall under Parts of speech.
Parts of Speech Definition
The parts of speech are the “traditional grammatical categories to which words are assigned in accordance with their syntactic functions, such as noun, verb, adjective, adverb, and so on.” In other words, they refer to the different roles that words can play in a sentence and how they relate to one another based on grammar and syntax.
All Parts of Speech with Examples
There are 8 different types of parts of speech i.e., Nouns, Pronouns, Adjectives, Verbs, Adverb, prepositions, Conjunction, and Interjection.
Noun –
A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, state, or quality. It can be singular or plural. Nouns are a part of speech.
- Function: Refers to Things or person
- Examples: Pen, Chair, Ram, Honesty
- Sentences: Cars are expensive, This chair is made of wood, and Ram is a topper, Honesty is the best policy.
Pronoun –
The word used in place of a noun or a noun phrase is known as a pronoun. A pronoun is used in place of a noun to avoid the repetition of the noun.
- Function: Replaces a noun
- Examples: I, you, he, she, it, they
- Sentences: They are expensive, It is of wood, He is a topper, It is the best policy
Adjective –
A word that modifies a noun or a pronoun is an adjective. Generally, an adjective’s function is to further define and quantify a noun or pronoun.
- Function: Describes a noun
- Examples: Super, Red, Our, Big, Great, class
- Sentences: Supercars are expensive, The red chair is for kids, Ram is a class topper, and Great things take time.
Verb –
A word or a group of words that describes an action, a state, or an event is called a verb. A verb is a word that says what happens to somebody or what somebody or something does.
- Function: Describes action or state
- Sentences: I play football, I will be a doctor, I like to work, I love writing poems.
Adverb –
A verb, adjective, another adverb, determiner, clause, preposition, or sentence is typically modified by an adverb . Adverbs often answer questions like “how,” “in what way,” “when,” “where,” and “to what extent” by expressing things like method, place, time, frequency, degree, level of certainty, etc
- Function: Describes a verb, adjective, or adverb
- Examples: Silently, too, very
- Sentences: I love reading silently, It is too tough to handle, He can speak very fast.
Preposition –
A preposition is called a connector or linking word which has a very close relationship with the noun, pronoun or adjective that follows it . Prepositions show position in space, movement, direction, etc.
- Function: Links a noun to another word
- Examples: at, in, of, after, under,
- Sentences: The ball is under the table, I am at a restaurant, she is in trouble, I am going after her, It is so nice of him
Conjunction –
A conjunction is a word that connects clauses, sentences, or other words. Conjunctions can be used alone or in groups of two.
- Function: Joins clauses and sentences
- Examples: and, but, though, after
- Sentences: First, I will go to college and then I may go to Fest, I don’t have a car but I know how to drive, She failed the exam though she worked hard, He will come after he finishes his match.
Interjection –
An interjection is a word or phrase expressing some sudden feelings of sadness or emotions.
- Function: Shows exclamation
- Examples: oh! wow!, alas! Hurray!
- Sentences: Oh! I got fail again, Wow! I got the job, Alas! She is no more, Hurray! We are going to a party.
These are the main parts of speech, but there are additional subcategories and variations within each. Understanding the different parts of speech can help construct grammatically correct sentences and express ideas clearly.
Sentence Examples for the 8 Parts of Speech
- Examples: Luggage, Cattle.
- Sentence: Never leave your luggage unattended.
- In some places, cattle are fed barely.
- Examples: who, either, themselves
- Sentence: I know a man who plays the guitar very well.
- Either of the two cars is for sale.
- They enjoyed themselves at the party.
- Examples: kind, moving, wounder.
- Sentence:
- She is a kind person.
- Boarding a moving bus can be dangerous.
- Never poke a wounded animal.
- Examples: Praise, Hate, Punish
- Sentence: She always praises her friends.
- I don’t hate anybody.
- The boy has been punished by his teacher
- Examples: Always, enough, immediately
- Sentence: we should always help each other.
- We should be wise enough to understand what is good for us.
- We should leave bad habits immediately.
Preposition
- Examples: Off, Below, From. to
- He plunged off the cliff
- I live below the 9th floor.
- I travel daily from Delhi to Noida.
Conjunction
- Examples: whereas, as well as, so,
- Sentence: The new software is fairly simple whereas the old one was a bit complicated.
- The finance company is not performing well as well as some of its competitors.
- He was ready so he may come.
Interjection
- Examples: oops! whoa! phew!
- Sentence: Oops! I forgot to mention her name.
- Whoa! you drive fast.
- Phew! That was a close call, we had a narrow escape.
Parts of Speech Exercise – Test your Knowledge of Part of speech
Choose the correct Parts of Speech of the BOLD word from the following questions.
1. Let us play, Shall We?
a. Conjunction b. Pronoun c. Verb
2. I t is a good practice to arrange books on shelves.
a. Verb b. Noun c. Adjective
3. Whose books are these?
a. Pronoun b. Preposition c. verb
4. Father, please get me that toy.
a. Pronoun b. Adverb c. Adjective
5. His mentality is rather obnoxious.
a. Adverb b. Adjective c. Noun
6. He is the guy whose money got stolen.
a. Pronoun b. Conjunction c. Adjective
7. I will have finished my semester by the end of this year.
a. Interjection b. Conjunction c. Preposition
8. Bingo! That’s the one I have been looking for
a. Interjection b. Conjunctio c. Preposition
Quiz Answers:
1. c, 2. b, 3. a, 4. c, 5. a, 6. b, 7. c, 8. a
Also Check:
- English Grammar
- Figures of Speech
- Learn English Grammar Online
- Difference Between Adjective and Verb
Q1. What are Parts of Speech?
A word is assigned to a category as per its function, and those categories are together known as Parts of Speech.
Q2. What are the 8 Parts of Speech?
Noun, Pronoun, Adjective, Verb, Adverb, Preposition, Conjunction, Interjection.
Q3. How many Parts of Speech are there?
There are a total of 8 parts of Speech.
Q4. What Part of Speech is “our”?
“Our” is a adjective type of Part of Speech. Eg. Our car.
Q5. What Part of Speech is “Quickly”?
Adverb. let us understand it with this example – Milk sours quickly in warm weather.
Similar Reads
- English Grammar : Learn Rules of Grammar and Basics Whether you're just starting on your journey to learn the English language or you've been studying for some time and find yourself struggling with English grammar, with a little bit of perseverance, anyone can learn to speak and write English with confidence and accuracy. English grammar is a set of 9 min read
- Parts of Speech: Definitions, Examples & 8 Types Every word is a part of speech playing a specific role in sentences or paragraphs. Parts of speech provide an organized way to align words and phrases, it is a fundamental meaning for a language to become more understandable and serve a specific purpose. Here, in this article, we will see what is Pa 8 min read
- What is a Noun? Types, Definitions and Examples (List) In simple terms, a noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns are one of the basic building blocks of language, and they help us identify and refer to the people, objects, and concepts in our everyday communication. Examples of nouns include "dog" (a thing), "teacher" (a person 15 min read
- Proper Noun - Definition, Examples, & Rules There are two primary categories of nouns: common and proper. Proper nouns are name words that are used to designate or categorize a particular person, place, or thing, whereas common nouns are generic. Make sure that the first letter of a proper noun is always capitalized. Read through the followin 6 min read
- Common Noun - Definition, Examples, List & Usage What is a common noun? and what is the difference between common nouns and proper nouns? You must have this question in your mind. In this article, we will explore more about common nouns and get to know about the differences between a common and proper noun. Table of Content What is a Common Noun?C 6 min read
- Plural Noun - Rules and Examples In English, there are different rules for forming plurals and some exceptions to the authorities. Therefore, it is essential to understand the rules and exceptions of plural nouns to use them correctly in written and spoken English. In this article, we will discuss its rules with examples in brief a 9 min read
- Possessive Noun - Meaning, Usage, Rules and Examples A possessive noun is an important part of the English language and writing. They play an important role to indicate ownership or possession. You can express relationships with people, things, and ideas. In this article, we will learn about the concepts of Possessive Noun, their meaning, usage, rules 7 min read
- What is Collective Noun? List of Examples, Uses and Exercises A collective noun refers to a group or collection of people, animals, or things. It represents a singular entity made up of multiple individuals. Examples of Collective nouns include Team (A team of players), Herd (A herd of cattle), School (A school of fish) etc. In this article, We have discussed 10 min read
- Abstract Nouns - Definition, Examples, List, Usage An abstract noun is a kind of noun that represents ideas, things, and experiences. It is an important part of Nouns. It is an important topic for all students, especially for those who are preparing for competitive examinations. One or more questions from this topic are asked in every competitive ex 4 min read
- What is a Compound Noun? Definition, Types & Examples Compound nouns are used to identify a class of people, places, things or a particular name. It is an important topic for all students, especially for those who are preparing for competitive examinations. One or more questions from this topic are asked in every competitive examination. This article 7 min read
- What are Countable Noun? Countable Noun includes all those things, we can count, whether it is in singular or plural form. A countable noun is used in the form of a singular or plural in a sentence. Because if we can count something then it can be either one or more than one. Do you want to know more about Countable Noun? G 11 min read
- What are Uncountable Noun - How to use them? According to English's grammar, we cannot divide them into separate elements, so for this reason, they are called uncountable nouns. The uncountable noun is another type of noun in traditional English Grammar. Uncountable nouns are such as oil, milk, sugar, salt, patience, juice, bravery, etc. Mater 7 min read
- Material Noun: Definition, Examples, Rules & Exercises Material NounThe noun is used mainly in five ways in English Grammar, in which all differences have their separate existence. Material Noun is one of those which addresses such a Noun that can only be measured or weighed but cannot be counted at all. A Material Noun is a special name given to things 7 min read
- Pronoun Definition - Rules and Types of Pronouns A strong command of Grammar is essential for Candidates for Competitive exams. So, concentrating on pronouns can also be quite beneficial as pronouns are one of the strongest and most important parts of speech. We will talk about the different types of Pronouns and their usage & rules in this ar 9 min read
- Reflexive Pronoun The term 'reflexive' refers to something aimed against oneself. The reflexive pronoun would be a form of pronoun that is accompanied by the predecessor, which must be positioned within a single phrase. A reflexive pronoun in English grammatical signifies that the individual doing the verb's behavior 5 min read
- Subject Pronouns - Definition, Example and Exercise Subject pronoun is an essential topic of parts of speech. In recent years, a number of tricky questions are asked in various competitive examinations on this topic. So it is very useful to learn this topic correctly. To know more about the subject Pronouns you must read through the article. What is 4 min read
- Relative Pronouns - Definition, Uses and Examples A Relative pronoun is a type of pronoun that introduces a subordinate clause and relates it to the main clause. A clause beginning with a relative pronoun is poised to answer questions such as Which one? How many? or What kind? Who, whom, what, which, etc. In this article, we will explore the concep 8 min read
- Demonstrative Pronouns - Definition and Examples The demonstrative pronoun is another main type or one kind of pronoun. which one uses noun place. demonstrative pronoun used to indicate particular things or persons or directions. Pronouns mainly work to stop the repetition of nouns, which makes sentences beautiful and meaningful. From this Pronoun 7 min read
- Possessive Pronouns - Definition, Usage and Examples Possessive Pronouns are used to indicate the possession or ownership or relation of a person/thing to another person/thing i.e. Possessive Pronouns are used to describe people, animals, or things that a person or be related to something. A possessive pronoun is another kind or type of pronoun. When 6 min read
- Indefinite Pronoun Any indeterminate pronoun is a term that lacks a particular familiar recipient. Indefinite pronouns vary from definite pronouns. Indefinite pronouns have the ability to indicate either count as well as non-count nouns. They frequently have associated forms across all these categories. An indefinite 6 min read
- Personal Pronoun - Definition, Rules and Examples Personal pronouns are short words that are used in place of a person's own name. Each English personal pronoun shows the person, gender, number, and case of the noun it replaces. I, you, he, she, it, we, they, me, him, her, us, and them are all personal pronouns. What are Personal Pronouns? Those Pr 8 min read
- Interrogative Pronoun The Pronoun is just a term that substitutes a noun. Many English phrases contain pronouns, which include inquiries. An interrogative pronoun is a form of pronoun that is continually asking for replies. When posing a question, an interrogative pronoun serves to replace a person and an object. What Is 5 min read
- Reciprocal Pronouns - Definition, Examples & Uses The pronoun, and particularly the reciprocal pronoun, will be the center of our attention. Let's start with an explanation of a pronoun. In a language, a pronoun is a term that replaces a noun, or another pronoun. A reciprocal pronoun is one that links two previously defined nouns that are both gett 6 min read
- What is a Verb? Types, Uses, Examples A verb is an important part of the English language and is classified under the Parts of Speech chapter. It is very important for all students, especially for those who are preparing for competitive exams. More than two questions are asked about this topic in every competitive examination. A verb is 13 min read
- Verb Forms Verbs are one of the most essential parts of speech in any language, as they express actions, states, or occurrences. Understanding the different forms of verbs is key to mastering grammar and effective communication. Verb forms can vary depending on tense, voice, and mood, and knowing how to use th 8 min read
- Main Verbs - Meaning, Types and Examples A verb is a part of speech used to show an action. There are several other sorts of verbs. The main verbs, on the contrary side, are the ones that explicitly describe an activity which the particular topic is conducting. These are the primary verbs in a phrase that carry the main meaning. Main Verbs 6 min read
- Helping Verb: Definition, Types and Examples In English grammar, a Helping verb is a verb that comes before a main verb or lexical verb in a sentence. An auxiliary/helping verb and a main verb together form a verb phrase. Helping verbs & auxiliary verbs are mostly equal. we often get confused about how to use main verbs and helping verbs i 7 min read
- Auxiliary Verbs: Definition, Examples & List Auxiliary verbs are needed to make our sentences more exciting and impressive. Auxiliary verbs are the first step in forming a complete sentence. When used with the main verb, auxiliary verbs finish sentences. Using auxiliary verbs is about expressing your feelings, making a statement, asking a ques 10 min read
- Irregular Verbs Irregular verbs are an important type of verb in the English language. It does not follow normal rules of grammar. It is an important topic for all students, especially for those who are preparing for competitive examinations. In this article, we will delve into the world of irregular verbs, and exp 9 min read
- What Are Modal Verbs? – Definition, Usage & Examples Any competitive government exam, including those for CGL, banking, and the armed services, assesses a candidate's command of the English language. There is a focus on testing the use of grammar in the English language section. As a result, understanding grammar rules becomes essential. One should be 8 min read
- What is A Gerund? Definition and Examples Understanding the difference between a gerund and other parts of speech is an important step in perfecting your grammar and writing skills. A gerund is a verb form used in the third person, meaning it's used as a noun. The form of the gerund is not that important, because this blog post is about how 8 min read
- Adjective - Definition, List, Types, Uses and Examples When we discuss Adjectives, it means those words which well describe a Noun or a Place, Person, Thing, or Idea. An adjective is the only word that can create a major difference between the two.Let's discuss this topic in detail and also bookmark it to get back to the article whenever we want to revi 10 min read
- Proper Adjectives Definition and Examples An appropriate adjective is a subcategory of the wider category of adjectives in particular. Adjectives are one of the eight fundamental parts of speech in English, and it is critical to understand and be able to distinguish which parts of speech make up a full sentence. Some pupils may already be f 6 min read
- Possessive Adjectives - Definition, Example and List How do possessive adjectives contribute to expressing ownership and help to indicate the relationship between people, ideas, and objects? Do you want to know more about Possessive adjectives? This article will help you to explore more about Possessive Adjectives along with their usage, examples, and 5 min read
- Interrogative Adjective - Meaning, Definition and Examples Understanding and learning about interrogative adjectives can greatly enhance your communication skills, helps you to seek information, and engages you in meaningful conversations. Here you will explore the importance of Interrogative along with rules and examples that will provide you valuable insi 5 min read
- What Is an Adverb? Definition, List & Examples In this article, we will learn about "Adverbs". A verb, adjective, another adverb, determiner, clause, preposition, or sentence is typically modified by an adverb. Adverbs often answer questions like "how," "in what way," "when," "where," and "to what extent" by expressing things like method, place, 10 min read
- Conjunctive Adverbs - Meaning, Examples and Exercises Are you having trouble with conjunctive adverbs? Have you ever wanted to express yourself more clearly and effectively, but just didn’t know where to start? In this article, we'll provide a comprehensive overview of the important role that conjunctive adverbs play in writing a great piece of literat 6 min read
- Adverbs of Time - Examples, Meaning, and Definition If you are looking for a guide that explains what is adverbs of time with suitable examples, then here in this blog post we will learn about adverbs of time and how to use them with examples. So without wasting time, let's dig into the article. Adverbs of Time inform us when an activity occurred. It 7 min read
- Adverbs of Frequency - Definition, Examples, and Usage Adverbs of Frequency are defined as words that modify verbs to tell us how often something happens Go through this blog post to get a detailed overview of adverbs of frequency, and how to use them with all suitable examples. What is adverb frequency? this question may arise in your mind when you hea 10 min read
- Adverbs of Place - Definition, List and Examples In the world of English grammar, adverbs of place specify where something happens. Basically, it can be used to describe a place, a direction, or a place in relation to something else. If you're looking for a detailed guide to adverbs of place, in this article we'll look at how adverbs of place work 7 min read
- What are Adverbs of Degree? Definition, List and Examples Adverbs are commonly used in English to explain the adjective, verb, or another adverb inside a paragraph. Among many of the different kinds of adverbs, a degree adverb assists speakers in expressing the concentration of a statement in a paragraph. The Adverb of degree answers the question, "How muc 8 min read
- Adverbs of Manner - Meaning, Definition and Examples Adverbs of manner are a type of parts of speech. It denotes the manner of action done by the Subject. It is an important topic for all students, especially for those who are preparing for competitive examinations. One or more questions from this topic are asked in every competitive examination. Tab 7 min read
- What is a Conjunction - Meaning, Definition, Types & Exercises Conjunctions are essential tools in the English language, used to connect words, phrases, or sentences to create more complex and meaningful statements. Without conjunctions, our sentences would be short and choppy, lacking flow and coherence. In the vast realm of language, there exists a small but 9 min read
- Subordinating Conjunction - Meaning, Definition, Types and Examples It is a very useful topic for joining two sentences in English and also important for all students, especially for those who are preparing for competitive examinations. A few questions on this topic are asked in every competitive examination. Table of Content What is a Subordinating Conjunction? De 6 min read
- Preposition Prepositions are considered one of the essential topics of the English language. They help in coordinating the usage of words and phrases. These are called prepositions because they relate to something before the word they follow. The below article will deal with the rules of prepositions in the Eng 11 min read
- Interjections - Definition, Types, Rules and Examples An interjection is a word or phrase expressing some kind of sudden feelings of sadness or emotions. Interjections are a type of part of speech, but in a sentence, they are not grammatically connected to other parts of a sentence. Interjections are those common words which use in everyday speech and 11 min read
- Definite and Indefinite Articles ( A, An, The) Table of ContentWhat is an Article? Definite and Indefinite ArticlesWhat are Definite Articles?What are Indefinite Articles?Definite and Indefinite Articles ExamplesDifference Between Definite and Indefinite Articles Definite and Indefinite Articles QuestionsFAQ's on Definite and Indefinite Articles 9 min read
- Subject-Verb Agreement Rules: Examples & Exercises Have you ever heard of the term subject-verb agreement? This is your chance to discover what subject-verb agreement is, what is meant by "concord," and the guidelines that will assist you in comprehending how it functions. In this article, we'll understand the rules of subject-verb agreement, exampl 11 min read
- Active and Passive Voice Rules for Competitive Exams Active and Passive voice is a particularly essential grammatical structure used in the English language. Understanding the rules governing their usage is crucial for effective communication. In this article, we will delve into the fundamentals of the active and passive voice. we will also explore th 8 min read
- What is Tense? Types, Definitions & Examples Earlier we have already discussed how important tenses are in English Grammar as the very basis of English Grammar is built on tenses. Once you complete the tenses then you will understand every part and use of tenses. You already know that there are three tenses- past, present, and future; and four 8 min read
- Tense Chart in English - Rules, Examples, Types & Mind map Tense Chart: The Tense Chart is a visual representation of the various verb tenses in English. It organizes the verb tenses in English. It outlines the various forms of the verb according to their uses. By using a tense chart, one can easily understand the relationship between the various forms of v 10 min read
- SSC/Banking
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Parts of Speech: Definitions, Categories and Examples
By: Author English Study Online
Posted on Last updated: August 28, 2024
Sharing is caring!
In this reference, we will break down each part of speech and provide examples to help you understand their usage. We will also discuss how to identify the different parts of speech in a sentence and provide tips on how to use them correctly. Let’s get started!

Parts of Speech – Created by Englishstudyonline
Table of Contents
What is a Parts of Speech?
A part of speech is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence. These roles help you understand how words function in grammar .
There are typically eight main parts of speech in English:
- Nouns : Words that name people, places, things, or ideas.
- Pronouns : Words that replace nouns, such as he, she, it .
- Verbs : Words that describe actions or states, like run, is .
- Adjectives : Words that describe or modify nouns, like blue or quick .
Some grammars list additional parts of speech:
- Adverbs : Words that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, such as quickly .
- Prepositions : Words that show relationships between a noun (or pronoun) and another word, like in or on .
- Conjunctions : Words that connect clauses, sentences, or words, such as and or but .
- Interjections : Words that express emotion, like wow or oops .
Some sources also include:
- Determiners/Articles : Words that modify nouns and specify which one, like the, a .
Categories of Parts of Speech
Nouns are words that represent people, places, things, or ideas. They are one of the most important parts of speech in English and are used in nearly every sentence. In this section, we will explore the different types of nouns and their functions.
- Common Nouns : General names for people, places, or things. Not capitalized unless at the start of a sentence. Examples : “book,” “city,” “teacher.”
- Proper Nouns : Specific names for people, places, or things. Always capitalized. Examples : “Harry Potter,” “New York City,” “Ms. Johnson.”
- Abstract Nouns : Names for ideas, concepts, or emotions that are intangible. Examples : “love,” “happiness,” “freedom.”
- Collective Nouns : Names for groups of people or things; can be singular or plural. Examples : “team,” “family,” “herd.”
2. Pronouns
Pronouns are words that replace nouns in a sentence. They help avoid repetition and make sentences clearer. Here are different types of pronouns in English:
- Personal Pronouns : Refer to specific people or things and can be subjects or objects. Examples : I/me, you/your/yours, he/him/his, she/her/hers, it/its.
- Demonstrative Pronouns : Point to specific people or things and indicate distance. Examples : this (near), that (far), these (plural, near), those (plural, far).
- Interrogative Pronouns : Used to ask questions. Examples : who (person), whom (person, object), whose (possession).
- Indefinite Pronouns : Refer to non-specific people or things. Examples : anybody, anyone, anything, each, either, everybody, everyone, everything.
- Action Verbs : Describe actions performed by the subject. Examples : Run, Jump, Sing, Dance, Write.
- Linking Verbs : Connect the subject to a noun, pronoun, or adjective that describes it; they do not show action. Examples : Is, Are, Was, Were, Seem.
- Helping Verbs : Work with the main verb to express tense, voice, or mood; they have no meaning on their own. Examples : Am, Is, Are, Was, Were.
4. Adjectives
Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns or pronouns, giving more information about their qualities, quantity, or identity. Here are three types of adjectives:
- Descriptive Adjectives : Describe the characteristics or qualities of a noun or pronoun. Examples : Beautiful, Tall, Thin, Ugly, Smart, Kind. Sentence Example : “The red car is fast.” (“red” describes the color; “fast” describes the speed).
- Quantitative Adjectives : Indicate the quantity or amount of a noun or pronoun, answering “how much” or “how many.” Examples : Few, Many, Several, Some, All, No. Sentence Example : “I have two apples.” (“two” describes the number of apples).
- Demonstrative Adjectives : Point to specific nouns or pronouns, answering “which one” or “whose.” Examples : This, That, These, Those. Sentence Example : “This book is mine.” (“this” specifies the book).
Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, providing more detail about an action, adverbs of manner, adverbs of place, adverbs of time, adverbs of frequency , adverbs of degree, or intensity.
Examples of adverbs:
- I left my keys here . (Adverb of place)
- She arrived late because she missed the bus. (Adverb of time)
- James visits his grandmother weekly . (Adverb of frequency)
- Please drive carefully on the wet roads. (Adverb of manner)
- She was extremely tired after the long journey. (Adverb of degree)
6. Prepositions
Prepositions are words that show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence, indicating position, direction, or time.
Prepositions of Time : Indicate when an action takes place. Examples :
- “At” for specific times: “at 2 pm,” “at midnight.”
- “In” for longer periods: “in the morning,” “in October.”
- “On” for dates: “on Monday,” “on July 4th.”
Prepositions of Place : Indicate where something is located. Examples :
- “In” for enclosed spaces: “in the house,” “in the car.”
- “On” for surfaces: “on the table,” “on the floor.”
- “At” for specific locations: “at the park,” “at the beach.”
Prepositions of Direction : Indicate movement from one place to another. Examples :
- “To” for movement towards: “I am going to the store.”
- “From” for movement away: “I am coming from the park.”
- “Towards” for movement in a direction: “I am walking towards the museum.”
7. Conjunctions
Conjunctions are words that connect words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence, helping to create complex sentences and showing relationships between ideas. There are three main types of conjunctions: coordinating, subordinating, and correlative.
Coordinating Conjunctions : Connect words, phrases, or independent clauses of equal importance. Remember them using FANBOYS : for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so. Examples :
- “I like pizza and pasta .”
- “He wanted to go to the beach, but it was raining.”
Subordinating Conjunctions : Connect dependent clauses to independent clauses, showing relationships like cause and effect, time, condition, or contrast. Examples : because, although, while, if, unless, since.
- “Because it was raining, we stayed inside.”
- “While I was studying, my roommate was watching TV.”
Correlative Conjunctions : Work in pairs to connect elements in a sentence, showing a relationship between them. Examples : both…and, either…or, neither…nor, not only…but also.
- “Both my sister and I like to read.”
- “Not only was he late, but he also forgot his homework.”
8. Interjections
In English grammar, interjections are words or phrases that express strong emotions or feelings. They are also known as exclamations and are one of the eight parts of speech in English. Interjections are grammatically independent from the words around them, and they can often be removed from a sentence or context without affecting its basic meaning.
Interjections can be used to express a wide range of emotions, including surprise, joy, anger, frustration, and pain. Some common examples of interjections include “ wow ,” “ ouch ,” “ yay ,” “ oh no ,” and “ oops .” They can be used to add emphasis to a sentence or to convey a particular tone or mood.
9. Articles/Determiners
In English grammar, articles and determiners are words that are used with nouns to provide more information about them. They help us to understand the context and meaning of a sentence.
There are three articles in the English language: “ the ,” “ a, ” and “ an. ” “The” is known as the definite article because it refers to a specific noun that has already been mentioned or is known to the reader. For example, “The cat is sleeping on the sofa.” In this sentence, “the” refers to a specific cat that has already been mentioned or is known to the reader.
“A” and “an” are known as indefinite articles because they refer to any member of a group or class of nouns. “A” is used before words that begin with a consonant sound, while “an” is used before words that begin with a vowel sound. For example, “I need a pen” and “She ate an apple.”
Determiners
Determiners are words that come before a noun to provide more information about it. They can include articles, as well as words like “ this ,” “ that ,” “ these ,” and “ those .”
In addition to these, there are other types of determiners such as possessive determiners (e.g. “my,” “your,” “his,” “her,” “its,” “our,” and “their”), demonstrative determiners (e.g. “this,” “that,” “these,” and “those”), and quantifying determiners (e.g. “some,” “any,” “many,” “few,” “several,” etc.).
Determiners can also be used with adjectives to provide more information about a noun. For example, “She ate the delicious apple” and “I saw that beautiful sunset.”
Examples of Parts of Speech
- Noun – The dog barked loudly.
- Pronoun – They went to the park together.
- Verb – She writes beautiful poetry.
- Adverb – He runs very quickly.
- Adjective – The red car is fast.
- Preposition – The cat is sitting on the sofa.
- Conjunction – She wanted to go for a walk, and he wanted to stay home.
- Interjection – Wow! That was an incredible performance.
Practical Exercises
Exercise 1: Identify the Part of Speech
Read each sentence and identify the underlined word’s part of speech (Noun, Pronoun, Verb, Adverb, Adjective, Preposition, Conjunction, Interjection).
- The beautiful garden is full of flowers.
- She quickly finished her homework.
- Wow! That was a great surprise.
- The cat hid under the bed.
- I want to go out, but it’s raining.
- He is a very talented musician.
- The children play in the park every evening.
- The cake is delicious .
- After lunch, we went for a walk.
- They will arrive at the airport soon.
- Interjection
- Preposition
- Conjunction
Exercise 2: Fill in the Blanks with the Correct Part of Speech
Choose the correct word from the list and fill in the blanks with the appropriate part of speech.
Word List: (and, beautiful, suddenly, them, book, Wow, under, write, she, quickly)
- The weather is so __________ today.
- I have to __________ an essay for my class.
- He ran __________ to catch the bus.
- The ball rolled __________ the table.
- They read a __________ together every night.
- She wanted to go to the park, __________ it started raining.
- Can you give this note to __________?
- __________! That was an amazing goal!
- __________ is going to the market.
- The bird flew away __________.
- beautiful (Adjective)
- write (Verb)
- quickly (Adverb)
- under (Preposition)
- book (Noun)
- and (Conjunction)
- them (Pronoun)
- Wow (Interjection)
- She (Pronoun)
- suddenly (Adverb)
- Recent Posts
- Juridical Process vs. Judicial Process: Understanding the Crucial Differences - December 14, 2023
- Compound Nouns: How to Use Them Effectively in English - November 9, 2023
- English Tenses: A Beginner’s Guide in English - November 6, 2023
- Words with Friends Cheat
- Wordle Solver
- Word Unscrambler
- Scrabble Dictionary
- Anagram Solver
- Wordscapes Answers
Make Our Dictionary Yours
Sign up for our weekly newsletters and get:
- Grammar and writing tips
- Fun language articles
- #WordOfTheDay and quizzes
By signing in, you agree to our Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy .
We'll see you in your inbox soon.
What Are the 8 Parts of Speech? Examples and Usage

- DESCRIPTION yellow circles with 8 parts of speech list
- SOURCE Created by Karina Goto for YourDictionary
- PERMISSION Owned by YourDictionary, Copyright YourDictionary
There are eight parts of speech in English: nouns, verbs, adjectives, pronouns, adverbs, conjunctions, prepositions, and interjections. While some parts of speech are more common or versatile than others, they’re all stacked like bricks in a sentence — and you can’t move one without bringing the whole sentence (or wall) down around it. These parts of speech examples demonstrate how each part of speech works, and how they modify or link to each other.
What Is a Part of Speech?
A part of speech is a word with a specific purpose in a sentence. You can categorize every English word into these parts of speech, based on what they do.

- DESCRIPTION illustration of girl baking a cake with labelled sentence
- SOURCE Iryna Vasylkiv / iStock / Getty Images Plus / via Getty created by YourDictionary
- PERMISSION Used under Getty Images license
For example, nouns are the people, places, and things in a sentence, and verbs are what they do. But while every sentence requires a noun and a verb, those aren’t the only parts of speech you’ll find in writing.

Parts of Speech With Examples Printable 22
Nouns name a person, place, thing, or idea. They function as the subject or the object of a sentence — the person or thing that either performs the action or receives the action.
Examples of nouns include:
- Send in the clowns .
- Brazil is a beautiful country .
- I love listening to music .
- How many cats do you have?
- Mia and Zoe value their friendship .
Verbs express action or a state of being. They're what you (or any nouns) do. When you change the verb's tense , you show that an action was done in the past, present, or future.
Examples of verbs include:
- We walked to the park.
- Janine has been to Minneapolis.
- That dog smells funny.
- You will need your snow boots today.
- My class is going to the museum.
3. Adjectives
Adjectives modify or describe a noun. They typically come before the noun they describe.
Examples of adjectives include:
- The sleepy bear hibernated all winter.
- It's a long drive, but it's worth the trip.
- Should I buy the blue jeans or the purple sweater?
- The twelve-year-old boy asked a question.
- Place the large silver spoon on the table.
4. Pronouns
Pronouns replace nouns to simplify speech and writing. They function as subjects and objects in sentences, just like nouns.
Examples of pronouns include:
- She is the smartest kid in class.
- George took the book from him .
- Who is coming to the party tonight?
- Don’t touch that cup; it’s mine .
- They really like their pottery class.
Adverbs modify or describe a verb, adjective, or another adverb. They provide information about an action’s time, place, manner, frequency, or degree.
Examples of adverbs include:
- Joe grumpily got out of bed.
- Sara ran very quickly to school.
- Your brother is very rude.
- I’ll have that done tomorrow .
- That's quite expensive, don't you think?
6. Conjunctions
Conjunctions connect parts of a sentence. They can join words, phrases, or clauses to add more information to a sentence.
Examples of conjunctions include:
- You'll need to study all night if you want to pass tomorrow's test.
- Go to the store and buy some milk.
- Kristopher doesn't have enough experience. Therefore , we will not hire him.
- I’d love to make dinner, but my stove isn’t working.
- We made you this quilt because we love you.
7. Prepositions
Prepositions show relationships between nouns in a sentence. They show the location of a noun relative to another noun or pronoun.
Examples of prepositions include:
- Between you and me, I wouldn't trust Andy.
- The coffee shop is across the street.
- Put the carrots in the refrigerator, please.
- Should we add more sugar to the batter?
- Mark works with my sister at the bank.
8. Interjections
Interjections interrupt sentences to show emotions. You can separate them from a sentence with a comma, period, or exclamation point, depending on the emotion.
Examples of interjections include:
- Bah , who cares what they think anyway?
- If Cody asked me out on a date, gosh , that'd make my day.
- I spilled the coffee everywhere. Oops !
- Hey ! That’s my train ticket!
- Oh no . I think I failed my math test.
Are Articles and Determiners Parts of Speech?
Two additional parts of speech — articles ( a, an, the ) and determiners ( that, my, some ) — also appear in sentences. So why are there only eight parts of speech instead of ten?
While some style guides and lists may add articles and determiners to the parts of speech, these parts of speech are technically adjectives. They modify nouns to add specificity to a sentence.
These example sentences show articles and determiners in bold, while the nouns they modify are underlined.
- The detective asked me some questions .
- I gave my brother an umbrella .
- He found several kittens in the shed .
- Do you want any milk ?
- Please hand me those tools .
Building New Sentences, One Brick at a Time
Learning the parts of speech is just the first step to building a proper sentence. But parts of speech are slightly different from parts of a sentence — and you need to know both in order to properly format your writing. Otherwise, you may encounter grammatical errors such as sentence fragments or run-on sentences .
- Humanities ›
- English Grammar ›
The 9 Parts of Speech: Definitions and Examples
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
A part of speech is a term used in traditional grammar for one of the nine main categories into which words are classified according to their functions in sentences, such as nouns or verbs. Also known as word classes, these are the building blocks of grammar.
Every sentence you write or speak in English includes words that fall into some of the nine parts of speech. These include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections. (Some sources include only eight parts of speech and leave interjections in their own category.)

Parts of Speech
- Word types can be divided into nine parts of speech:
- prepositions
- conjunctions
- articles/determiners
- interjections
- Some words can be considered more than one part of speech, depending on context and usage.
- Interjections can form complete sentences on their own.
Learning the names of the parts of speech probably won't make you witty, healthy, wealthy, or wise. In fact, learning just the names of the parts of speech won't even make you a better writer. However, you will gain a basic understanding of sentence structure and the English language by familiarizing yourself with these labels.
Open and Closed Word Classes
The parts of speech are commonly divided into open classes (nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs) and closed classes (pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections). Open classes can be altered and added to as language develops, and closed classes are pretty much set in stone. For example, new nouns are created every day, but conjunctions never change.
In contemporary linguistics , parts of speech are generally referred to as word classes or syntactic categories. The main difference is that word classes are classified according to more strict linguistic criteria. Within word classes, there is the lexical, or open class, and the function, or closed class.
The 9 Parts of Speech
Read about each part of speech below, and practice identifying each.
Nouns are a person, place, thing, or idea. They can take on a myriad of roles in a sentence, from the subject of it all to the object of an action. They are capitalized when they're the official name of something or someone, and they're called proper nouns in these cases. Examples: pirate, Caribbean, ship, freedom, Captain Jack Sparrow.
Pronouns stand in for nouns in a sentence . They are more generic versions of nouns that refer only to people. Examples: I, you, he, she, it, ours, them, who, which, anybody, ourselves.
Verbs are action words that tell what happens in a sentence. They can also show a sentence subject's state of being ( is , was ). Verbs change form based on tense (present, past) and count distinction (singular or plural). Examples: sing, dance, believes, seemed, finish, eat, drink, be, became.
Adjectives describe nouns and pronouns. They specify which one, how much, what kind, and more. Adjectives allow readers and listeners to use their senses to imagine something more clearly. Examples: hot, lazy, funny, unique, bright, beautiful, poor, smooth.
Adverbs describe verbs, adjectives, and even other adverbs. They specify when, where, how, and why something happened and to what extent or how often. Many adjectives can be turned into adjectives by adding the suffix - ly . Examples: softly, quickly, lazily, often, only, hopefully, sometimes.
Preposition
Prepositions show spatial, temporal, and role relations between a noun or pronoun and the other words in a sentence. They come at the start of a prepositional phrase , which contains a preposition and its object. Examples: up, over, against, by, for, into, close to, out of, apart from.
Conjunction
Conjunctions join words, phrases, and clauses in a sentence. There are coordinating, subordinating, and correlative conjunctions. Examples: and, but, or, so, yet.
Articles and Determiners
Articles and determiners function like adjectives by modifying nouns, but they are different than adjectives in that they are necessary for a sentence to have proper syntax. Articles and determiners specify and identify nouns, and there are indefinite and definite articles. Examples of articles: a, an, the ; examples of determiners: these, that, those, enough, much, few, which, what.
Some traditional grammars have treated articles as a distinct part of speech. Modern grammars, however, more often include articles in the category of determiners , which identify or quantify a noun. Even though they modify nouns like adjectives, articles are different in that they are essential to the proper syntax of a sentence, just as determiners are necessary to convey the meaning of a sentence, while adjectives are optional.
Interjection
Interjections are expressions that can stand on their own or be contained within sentences. These words and phrases often carry strong emotions and convey reactions. Examples: ah, whoops, ouch, yabba dabba do!
How to Determine the Part of Speech
Only interjections ( Hooray! ) have a habit of standing alone; every other part of speech must be contained within a sentence and some are even required in sentences (nouns and verbs). Other parts of speech come in many varieties and may appear just about anywhere in a sentence.
To know for sure what part of speech a word falls into, look not only at the word itself but also at its meaning, position, and use in a sentence.
For example, in the first sentence below, work functions as a noun; in the second sentence, a verb; and in the third sentence, an adjective:
- Bosco showed up for work two hours late.
- The noun work is the thing Bosco shows up for.
- He will have to work until midnight.
- The verb work is the action he must perform.
- His work permit expires next month.
- The attributive noun (or converted adjective) work modifies the noun permit .
Learning the names and uses of the basic parts of speech is just one way to understand how sentences are constructed.
Dissecting Basic Sentences
To form a basic complete sentence, you only need two elements: a noun (or pronoun standing in for a noun) and a verb. The noun acts as a subject, and the verb, by telling what action the subject is taking, acts as the predicate.
In the short sentence above, birds is the noun and fly is the verb. The sentence makes sense and gets the point across.
You can have a sentence with just one word without breaking any sentence formation rules. The short sentence below is complete because it's a verb command with an understood "you" noun.
Here, the pronoun, standing in for a noun, is implied and acts as the subject. The sentence is really saying, "(You) go!"
Constructing More Complex Sentences
Use more parts of speech to add additional information about what's happening in a sentence to make it more complex. Take the first sentence from above, for example, and incorporate more information about how and why birds fly.
- Birds fly when migrating before winter.
Birds and fly remain the noun and the verb, but now there is more description.
When is an adverb that modifies the verb fly. The word before is a little tricky because it can be either a conjunction, preposition, or adverb depending on the context. In this case, it's a preposition because it's followed by a noun. This preposition begins an adverbial phrase of time ( before winter ) that answers the question of when the birds migrate . Before is not a conjunction because it does not connect two clauses.
- What Are Word Blends?
- Figure of Speech: Definition and Examples
- Definition and Examples of Adjectives
- Subjects, Verbs, and Objects
- What Is a Rhetorical Device? Definition, List, Examples
- What Is The Speech Act Theory: Definition and Examples
- A List of Exclamations and Interjections in English
- Definition and Examples of Discourse
- The Best Sites to Learn New Words Every Day
- What Is Nonverbal Communication?
- Examples and Usage of Conjunctions in English Grammar
- Definition and Examples of Ambiguity
- Linguistic Variation
- Definition and Examples of Interjections in English
- Understanding the Types of Verbs in English Grammar
- Complex Words in English

English Teacher KBob
Learn English Here
What Are The 8 Parts Of Speech In The English Language?
Ever stopped to think about what makes the English language tick? It’s all about the parts of speech! These are like the building blocks of every sentence, giving meaning and structure to our words.
Use Google Translate
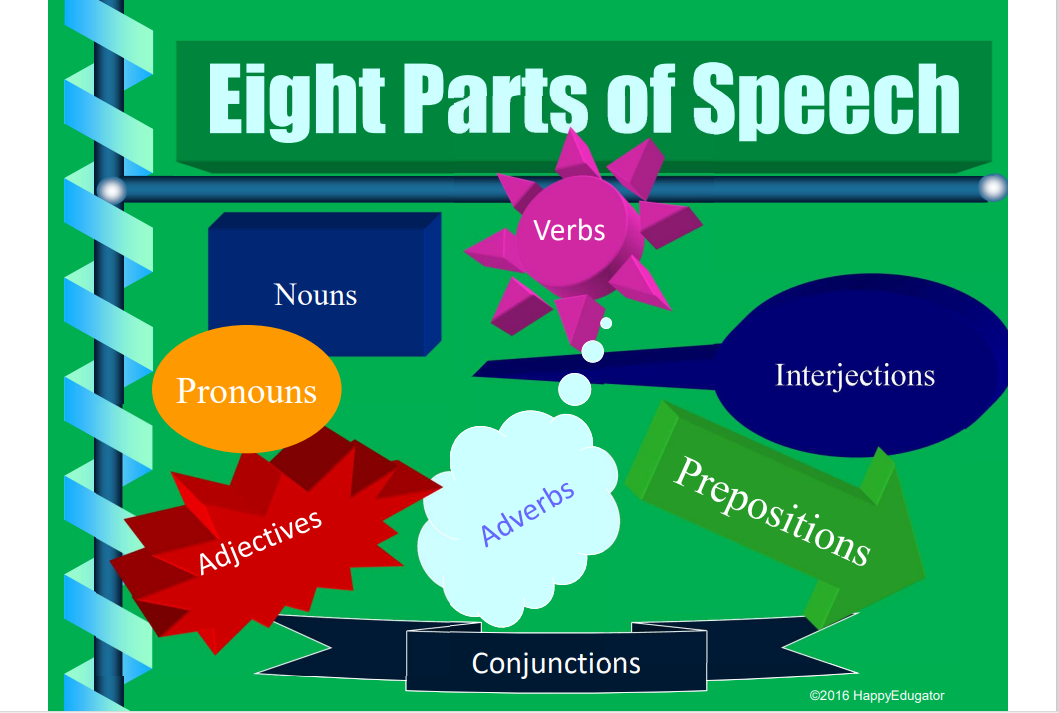
Understanding these eight parts of speech isn’t just for grammar nerds. It’s the secret sauce that helps you write clearer, more effective text, and aids in understanding what others are saying. When you get a grip on these basics, English starts to make more sense—whether you’re crafting an email, writing an essay, or just trying to keep up with a quick chat.
We’ll touch on nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. This isn’t some boring grammar lecture. Think of it more like getting to know a toolbox where each tool has a specific job to make your sentences come alive.
Stick with me as we explore each one, with examples and tips that’ll help you use them like a pro. By the end, you’ll see how much punch a well-crafted sentence can pack. This is just the start on your journey to mastering English language skills.
Exploring the Eight Essential Parts of Speech
Let’s break it down: when we talk about parts of speech, we’re talking about the role each word plays in a sentence. Think of each part as a unique ingredient that adds flavor and depth to our sentences.
So, what are the parts of speech? Here they are—nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Each one does something special to sculpt a sentence, making it convey exactly what you mean.
Ever seen a sentence without a noun or a verb? It’s like a pizza without cheese—not really doing its job. Nouns tell us what or who we’re talking about. Verbs let us know what actions are taking place or set the overall state.
Pronouns come in clutch when you don’t want to keep saying the same word over and over. They keep things from getting super repetitive. Adjectives and adverbs spring into action next, adding some pizazz and detail to our descriptions.
Prepositions weave extra elements into your sentences by showcasing relationships, while conjunctions are the glue keeping everything connected smoothly. And interjections—well, they’re those little exclamations that add a punch of emotion when needed.
Grasping the role of each is all about setting yourself up to express whatever you want, whenever you want. This means breaking beyond just tossing words together and truly understanding how they enhance what you’re conveying.
In-Depth Breakdown of Each Part of Speech
Nouns are the cornerstone of our sentences. They help us label the world, covering everything from people and places to ideas and objects. Think common nouns like ‘city,’ proper nouns like ‘London,’ and abstract concepts like ‘freedom.’ Spotting them is about recognizing names and things.
Pronouns step in to streamline our sentences. Instead of repeating ‘John’s car,’ you’d say ‘his car.’ You’ll encounter personal pronouns (like ‘she’), possessive ones (like ‘hers’), and even reflexive ones (like ‘myself’). Keep an eye out for mix-ups, like mismatched pronouns and nouns.
Verbs are action-packed. They show what’s happening—running, thinking, being. Beyond clear actions, they also express states with linking verbs like ‘is’ or ‘seems.’ And don’t forget auxiliary verbs—’have’ or ‘will’—that help convey precise meanings through different tenses.
Adjectives are all about adding color, size, and quality to nouns. They transform a simple ‘house’ into a ‘big, blue house.’ Keep them close to the nouns they modify to ensure clarity and impact in your writing.
Adverbs take it a notch up by modifying verbs, adjectives, or even other adverbs. They tell us how, when, where, and to what extent. Words like ‘quickly’ or ‘very’ add layers but be cautious about overuse—it can clutter your writing.
Prepositions are small but mighty, showcasing relationships between entities. They introduce phrases like ‘on the table’ or ‘during the morning.’ Getting these right helps your sentences paint a clear picture of context and sequence.
Conjunctions are your sentence builders, connecting words and ideas. Whether it’s coordinating ones like ‘and,’ subordinating like ‘because,’ or correlative like ‘either/or,’ they boost readability when used wisely.
Interjections bring zest with a simple word or phrase. A ‘wow!’ or ‘oh!’ can add emotion, but they’re best in moderation to maintain tone and style across your writing.
Common Missteps and Mastery Tips
Recognizing the nuances between similar words is essential for sharp writing. Words like ‘fast’ can function as both an adjective and an adverb. Notice their placement and purpose—’fast car’ versus ‘run fast’—to understand their roles.

Balance is key when wielding these parts of speech. Overloading sentences with adjectives or adverbs can muddle clarity, while underusing them leaves writing dry and lifeless. Aim for a mix that respects the rhythm and flow of your language.
Practice is where you’ll start mastering these concepts. Try swapping out nouns for pronouns in a sentence, or experiment with different tense verbs to see how they shift meaning. Playing with structure in everyday sentences builds a deeper understanding.
To test your skills, consider tackling simple exercises. Take a short paragraph and identify each part of speech—nouns, verbs, and so on. This sort of practical application ingrains the concepts in your mind.
By keeping these strategies in your toolkit, you’re not just learning grammar rules—you’re refining your ability to communicate powerfully and effectively. Writing becomes not just an act, but a craft you hone over time.
Leave questions and comments in the space below.
2 thoughts on “What Are The 8 Parts Of Speech In The English Language?”
This is a fantastic overview of the parts of speech! Understanding these foundational elements truly is like building a toolbox for effective communication. I appreciate the accessible explanations and practical examples—it makes each part of speech feel approachable and applicable, even for everyday use.
I found the tips on balancing adjectives and adverbs especially valuable. It’s easy to get carried away with descriptions, but striking that balance really does enhance clarity and impact. I also loved the idea of practicing with simple exercises to reinforce these concepts.
For anyone looking to improve their writing, mastering these basics is a game changer. Thanks for breaking it down in such an engaging way!
Thanks for your comments JealousLi.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Parts of Speech – A Guide to Types and Real-World Examples That Inspire
Updated: 15 Oct 2024
Every word you use in English has a particular job, which we call a part of speech ! Imagine it like a team where each player has a unique role to play. Some words help us name things, some show action, and others describe how things are. Understanding parts of speech is like unlocking a secret code that makes sentences come alive and sparkle!
In this article, we’re going on a fun journey to explore what parts of speech are, the different types, and some superb examples that will help you become a superstar at expressing yourself. You’ll be amazed at how powerful words can be!
Table of Content
Definition:, types of noun, types of pronoun, types of verb, how do adjectives work, examples of adjectives, types of adjectives, examples of adverbs, types of adverbs, types of preposition:, types of conjunctions, types of interjections:, types of determiners:, types of articles:.
So, let’s jump in and unlock the magic of words together! First, we’ll learn the definition of parts of speech and discover why they’re so important. Get ready for an adventure in language!
What are Parts of Speech?

Parts of speech are one of the first exciting grammar topics we dive into when we start our journey in school or begin learning the English language. Think of parts of speech as the building blocks of sentences, where each word plays a unique role that brings our ideas to life!
- Merriam-Webster Dictionary defines parts of speech as “any of the classes of words that have similar grammatical properties; especially: a class (such as noun, verb, or adjective) that has a specific function in a sentence.”
- Collins English Dictionary defines parts of speech as “any of the categories into which words are classified according to their functions in a sentence, such as nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs.”
- Macmillan Dictionary defines parts of speech as “the different types of words in a language that have similar grammatical functions, including nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs.”
So, based on these definitions, we can understand that parts of speech are categories of words that help us see how sentences are formed. They include names (nouns), action words (verbs), describing words (adjectives), and more. By learning about parts of speech, we gain the tools to express ourselves clearly and creatively!
Now, let’s move on to the different types of parts of speech and see some examples. This will help us understand how these words work together in sentences. Let’s explore!
Parts of Speech Types and Their Impactful Examples
In English, eight parts of speech help us build sentences and express our ideas clearly. Here they are:
- Noun: Names a person, place, thing, or idea.
- Pronoun: Replaces a noun.
- Verb: Shows action or a state of being.
- Adjective: Describes a noun.
- Adverb: Describes a verb, adjective, or another adverb.
- Preposition: Shows the relationship between a noun (or pronoun) and other words.
- Conjunction: Connects words, phrases, or clauses.
- Interjection: Expresses strong emotion or surprise.
Now, let’s discuss each type in detail, one by one!
A Noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns are essential in our sentences because they help us know what we discuss! Think of nouns as the heroes of our sentences—they can be the subject , which means they do the action.
For example:
- “The dog barks.” The word “dog” is the hero who is barking!
- The cat chased the mouse.
(“The cat” is the subject noun doing the chasing.)
- Sarah loves to paint.
(“Sarah” is the subject noun who loves to paint.)
Nouns can also function as the object of a verb, which refers to the person or thing affected by the action.
For Example:
- Sara gave her brother a gift. (“Her brother” is the object noun receiving the gift.)
- They built a sandcastle at the beach. (“A sandcastle” is the object noun that was built.)
- The dog fetched the ball. (“The ball” is the object noun the dog fetched.)
Common Noun:
- A common noun refers to nonspecific people, places, things, or concepts. It’s like a general name that could apply to many things.
- Example: dog, city, book, happiness
- Sentence: “The dog barked loudly in the park.”
Proper Noun:
- A proper noun refers to specific people, places, things, or concepts. Proper nouns are always capitalized because they name unique entities.
- Example: Eiffel Tower, Sarah, London, January
- Sentence: “We visited the Eiffel Tower last summer.”
Collective Noun:
- A collective noun refers to a group of people or things considered a single unit. It’s like a particular word for a collection!
- Example: team, flock, class, family
- Sentence: “The team celebrated their victory together.”
Abstract Noun:
- An abstract noun is a word that describes ideas, qualities, or feelings that we can’t see or touch. These nouns represent things we can think about but not physically hold.
- Examples: love, freedom, bravery, sadness
- Sentence: “Her bravery inspired everyone around her.”
Another way to classify nouns is by whether they are countable or uncountable.
Countable Nouns:
- Countable nouns are things we can count easily. They have singular and plural forms, meaning you can say “one” or “two” or more!
- Examples: apple, book, car, child
- Sentence: “I have three apples in my bag.” (Here, you can count the apples!)
Uncountable Nouns:
- Uncountable nouns are things we cannot count individually because they are seen as a whole or a mass. These nouns usually don’t have a plural form.
- Examples: water, sugar, information, music
- Sentence: “I need some water after my run.” (Here, you don’t count water in individual units; it’s a mass.)
A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun, which makes our sentences easier to read. Think of it like a helper!
For example, instead of saying, “Tom likes ice cream, and Tom eats ice cream,” we can say, “Tom likes ice cream, and he eats it.”
In this case, he is the pronoun that replaces Tom. Pronouns help us avoid repeating the exact words all the time. They can refer to places, people, things, or ideas.
For Example
- “James loves basketball, and he plays every weekend.” Here, “he” replaces James, so we don’t have to repeat his name.
- “Maria is a great artist, and she paints beautiful pictures.” In this sentence, “she” takes the place of Maria.
- “The cat is very playful. It loves to chase its tail.” “It” refers to the cat, helping us avoid repeating the word.
Here are some types of pronouns :
Personal Pronouns:
- These pronouns refer to specific people or things.
- Examples: I, you, he, she, it, we, they
- Sentence: “I love reading books, and she enjoys them too.”
Possessive Pronouns:
- These show ownership or belonging.
- Examples: mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, theirs
- Sentence: “That book is mine , and this one is yours .”
Reflexive Pronouns:
- These refer back to the sentence’s subject and end in “-self” or “-selves.”
- Examples: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, yourselves, themselves, ourselves
- Sentence: “I made the cake myself. “
Demonstrative Pronouns:
- These point to specific things or people.
- Examples: this, that, these, those
- Sentence: “This is my favorite toy, but that one is cool too.”
Interrogative Pronouns:
- These are used to ask questions.
- Examples: who, whom, whose, which, what
- Sentence: “ Who is your best friend?”
Relative Pronouns:
- These introduce a clause and relate to a noun mentioned before.
- Examples: who, whom, whose, which, that
- Sentence: “The book that I read was amazing.”
Indefinite Pronouns:
- These refer to nonspecific people or things.
- Examples: anyone, everyone, someone, nobody, all, some, few
- Sentence: “ Everyone is excited for the party!”
You may also Like these posts
- What is a Personal Pronoun? Everything You Need to Know
- Interjections Explained – Definition, Types, and Uses
- What is an Intensive Pronouns? Learn with Examples & Uses
- What Is an Adjective? Definition, Forms, Types, and Examples
- What is an Adverb? Everything You Need to Know
A verb is an exciting word that tells us what someone or something is doing! It can show an action (like “jump” or “run”), something that happens (like “become” or “change”), or a state of being (like “exist” or “feel”). Verbs are super crucial because every complete sentence needs at least one to make sense!
For example, in the sentence “The dog barks, ” the verb “barks” tells us what the dog is doing.
What’s cool about verbs is that they can change their form based on different things! They can change depending on the subject (like who or what is doing the action), the tense (when the action happens, like past or present), the mood (like asking a question), and the voice (like when the action is done to the subject).
- “She runs fast in the race.” (Action Verb)
- “He will become a great artist.” (Linking Verb)
- “He is playing soccer right now.” (Helping Verb)
- “I know the answer to the question.” (State of Being)
Here are some types of verbs :
Action Verbs:
- These verbs show what someone or something is doing. They can be physical actions or mental actions.
- Examples: run, jump, swim, think, laugh
- Sentence: “She jumps on the trampoline.”
Linking Verbs:
- These verbs connect the subject of a sentence to more information about that subject. They don’t show action but instead describe a state of being.
- Examples: am, is, are, was, were, seem, become
- Sentence: “He is my best friend.”
Helping Verbs (Auxiliary Verbs):
- These verbs help the main verb in a sentence by extending its meaning, often to indicate tense, mood, or voice.
- Examples: have, has, had, will, shall, can, may
- Sentence: “She has finished her homework.”
Transitive Verbs:
- These verbs require an object to receive the action. They transfer action from the subject to the object.
- Examples: give, send, make, eat
- Sentence: “He gave her a gift.”
Intransitive Verbs:
- These verbs do not require an object to complete their meaning. They express action or a state of being without an object.
- Examples: sleep, laugh, arrive, go
- Sentence: “The baby sleeps soundly.”
Regular Verbs:
- These verbs follow a standard pattern when changing tenses, typically adding “-ed” for the past tense.
- Examples: walk (walked), talk (talked), play (played)
- Sentence: “She walked to school yesterday.”
Irregular Verbs:
- These verbs have unique forms and do not follow standard patterns when changing tenses.
- Examples: go (went), eat (ate), have (had)
- Sentence: “He went to the park.”
Phrasal Verbs:
- These are combinations of a verb and one or more particles (prepositions or adverbs) that change the meaning of the original verb.
- Examples: give up, look after, run out
- Sentence: “She gave up trying to solve the puzzle.”
4. Adjective
An adjective is like a magical word that gives life to nouns and pronouns! It describes them by telling us more about them, such as their color, size, shape, or feelings. Think of adjectives as special paintbrushes that help us create a colorful picture in our minds!
Adjectives can appear in two ways:
- Attributive Adjectives: These adjectives come before a noun to describe it.
- Example: “I have a blue bicycle.” (Here, blue tells us what color the bicycle is!)
- Predicative Adjectives: These adjectives come after a linking verb (like “is”) to describe the subject.
- Example: “The sky is clear. ” (In this case, clear tells us what kind of sky it is!)
- The happy puppy wagged its tail.”
- “He is the tallest player on the team.”
- “She runs fast during the race.”
- “The shiny car caught everyone’s attention.”
Descriptive Adjectives:
- These adjectives describe qualities or features of a noun, helping us understand more about it.
- Examples: beautiful, tall, colorful
- Sentence: “She wore a beautiful dress.”
Quantitative Adjectives:
- These adjectives show how much or how much of something there is.
- Examples: some, many, few, three
- Sentence: “I have three apples.”
Demonstrative Adjectives:
- These adjectives point out specific nouns. They include “this,” “that,” “these,” and “those.”
- Sentence: “ This book is my favorite.”
Possessive Adjectives:
- These adjectives show ownership or possession. They include words like “my,” “your,” “his,” “her,” “its,” “our,” and “their.”
- Examples: my, your, his, their
- Sentence: “That is her bicycle.”
Interrogative Adjectives:
- These adjectives are used to ask questions about nouns. They include words like “which,” “what,” and “whose.”
- Examples: which, what, whose
- Sentence: “ Which movie do you want to watch?”
Indefinite Adjectives:
- These adjectives provide a general description of nouns without being specific. They include words like “some,” “any,” “few,” and “many.”
- Examples: some, any, several
- Sentence: “There are few cookies left.”
Comparative Adjectives:
- These adjectives compare two nouns, often ending in “-er” or using “more.”
- Examples: taller, faster, smarter
- Sentence: “My dog is taller than yours.”
Superlative Adjectives:
- These adjectives compare three or more nouns, often ending in “-est” or using “most.”
- Examples: tallest, fastest, smartest
- Sentence: Sara is the smartest student in the class.”
An adverb is a particular word that gives us more information about a verb, an adjective, or even another adverb! It tells us how, when, where, or to what extent something occurs.
For example, if you say someone runs fast, the word “ fast ” is an adverb because it describes how the person runs. Sometimes, adverbs are made by adding “ -ly ” to an adjective, like turning “ quick ” into “quickly. ” But remember, not all adverbs have this ending, and not all words that end in “ -ly ” are adverbs.
- She sings beautifully .
- He will come tomorrow .
- The cat is hiding inside .
Here are some types of adverbs with examples:
Adverbs of Manner:
- Describe how an action is done.
- Example: She dances gracefully.
Adverbs of Time:
- Tell us when something happens.
- Example: We will leave soon.
Adverbs of Place:
- Show where an action happens.
- Example: The dog ran outside.
Adverbs of Degree:
- Indicate the intensity or degree of an action, adjective, or adverb.
- Example: He is highly talented.
Adverbs of Frequency:
- Tell us how often something happens.
- Example: I always brush my teeth.
6. Preposition
A preposition is a word or phrase that helps us understand how different parts of a sentence relate to each other. Think of prepositions as little connectors that show us where something is, when something happens, or which direction it goes!
For example, in the sentence “The cat is on the table,” the word “on” is a preposition because it tells us where the cat is.
- The dog is under the bed.
- He fell asleep during the movie.
- The bird flew into the house.
Prepositions of Place:
- These prepositions tell us where something is located.
- The book is on the table.
- The cat is under the chair.
- She is sitting beside her friend.
Prepositions of Time:
- These prepositions indicate when something happens.
- We will meet at noon.
- The movie starts before dinner.
- She was born during the summer.
Prepositions of Direction:
- These prepositions show where something is going or the direction of an action.
- He walked to the park.
- The bird flew over the house.
- They ran into the store.
Prepositions of Manner:
- These prepositions describe how something is done.
- She spoke with confidence.
- He painted the picture in a hurry.
Compound Prepositions:
- These phrases comprise two or more words that act as a single preposition.
- The cat jumped on top of the fence.
- She is going in front of the class to present.
7. Conjunctions
A conjunction is a unique word that connects different parts of a sentence. Consider conjunctions the glue that holds words, phrases, or whole sentences together! They help our ideas flow smoothly and make our sentences more interesting.
For example, in the sentence “I want to play soccer, but it’s raining,” the word “but” is a conjunction because it connects two ideas.
- I wanted to eat pizza, but my sister chose sushi.
- Either we can watch a movie, or we can play a game.
Coordinating Conjunctions:
- Connect words, phrases, or independent clauses with a similar or equal structure.
- Examples: for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so (often remembered by the acronym FANBOYS).
Subordinating Conjunctions:
- Connect an independent clause with a dependent clause to highlight their relationship.
- Examples: because, although, since, unless, if, while, when.
Correlative Conjunctions:
- Work in pairs to connect balanced words or phrases.
- Examples: either…or, neither…nor, both…and, whether…or, not only…but also.
Conjunctive Adverbs:
- These act as conjunctions to connect independent clauses and often provide a transition or show the relationship between ideas.
- Examples: however, therefore, moreover, consequently, thus.
8. Interjections
An interjection is a word or phrase that expresses a strong emotion, feeling, or reaction. It is often used to convey excitement, surprise, happiness, anger, or other emotions. Interjections are unique in that they do not grammatically connect to the other parts of the sentence and can often stand alone without affecting the overall meaning.
- Surprise: “Wow! That’s incredible!”
- Happiness: “Yay! We won the game!”
- Disappointment: “Oh no! I lost my keys!”
- Greetings: “Hello! How are you today?”
- Command: “Stop! That’s dangerous!”
Emotion-based Interjections:
- These interjections express strong emotions and are often followed by an exclamation mark.
- Examples:
- “Wow!” (surprise)
- “Yay!” (joy)
- “Oh!” (realization or understanding)
Greeting Interjections:
- Used to greet someone, these exclamations can stand alone or be part of a more significant sentence.
- “Hello!” (greeting)
- “Hey!” (informal greeting)
- “Hi!” (friendly greeting)
Command Interjections:
- These interjections express commands or requests, usually followed by an exclamation mark.
- “Stop!” (command)
- “Wait!” (request for pausing)
- “Listen!” (call for attention)
Pain or Discomfort Interjections:
- These interjections convey reactions to physical sensations, often related to pain or discomfort.
- “Ouch!” (pain)
- “Yikes!” (fear or concern)
- “Phew!” (relief)
Surprise or Shock Interjections:
- Used to express shock, disbelief, or unexpected occurrences.
- “Oh my!” (astonishment)
- “Goodness!” (surprise)
- “Gosh!” (mild surprise)
Filler Interjections:
- These interjections fill pauses in conversation and do not express strong emotion but can indicate thought or hesitation.
- “Um” (hesitation)
- “Well” (transition)
- “You know” (informal filler)
Other Parts of Speech
While we often learn about the eight main parts of speech, language is rich and varied, and some words fit into categories beyond the traditional eight. Two important categories are determiners and articles.
Determiners
A determiner is a word that helps describe a noun by showing quantity, possession, or position. Think of determiners as guides that give us more information about nouns.
Demonstrative Determiners:
- “ This book is my favorite.”
- “ That tree is taller than the others.”
Possessive Determiners:
- “ My dog loves to play fetch.”
- “ Her dress is beautiful.”
Quantifiers:
- “I have some friends coming over.”
- “ Many students participated in the competition.”
An article is a word that modifies a noun by indicating whether the noun is specific or general. Articles help us understand if we’re talking about something unique or just an example of something.
Definite Article (the):
- “ The cat sat on the mat.”
- “I visited the Eiffel Tower last summer.”
Indefinite Articles (a and an):
- “I saw a bird in the garden.”
- “Sadia wants to be an artist when she grows up.”
Understanding the parts of speech is essential for everyone who wants to communicate better. They are like building blocks that help us express our thoughts and feelings. Nouns are the names of people, places, or things, while verbs show action. Adjectives describe nouns, making our sentences colorful, and adverbs tell us more about verbs.
Learning to use these parts of speech allows us to tell stories, share our ideas, and connect with others more easily. Each word we choose helps us express ourselves and make our conversations enjoyable.
So, keep practicing and using the parts of speech in your writing and speaking. They are tools that will help you share your thoughts clearly and creatively. Remember, your words have power; learning about them can make you a better communicator!
What are the 8 parts of speech?
The eight parts of speech—noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection—each play a unique and essential role in our sentences.
What is the definition of parts of speech?
A part of speech is a class of words that includes adjectives, adverbs, conjunctions, interjections, nouns, prepositions, pronouns, and verbs. These words are grouped based on the types of ideas they express and how they function in a sentence.
How do we identify parts of speech?
Nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs frequently have distinct word endings known as suffixes. Examining these suffixes allows you to easily differentiate the words from other parts of speech and understand their roles within a sentence. This simple approach clarifies the word’s meaning and enhances your overall comprehension of the sentence structure.
Why are parts of speech important?
Parts of speech are essential because they help us understand how words work together in sentences. This knowledge improves our writing and speaking skills, making communication more transparent and effective.
How do parts of speech work in a sentence?
Each part of speech has a specific role. For instance, nouns name things, verbs show action, adjectives describe nouns, and adverbs modify verbs. Understanding their roles helps us create meaningful sentences.
Please Write Your Comments
Englishal.com.
Congratulations!
You have subscribed for englishal.com Newsletter
You have subscribed for our SEO Tips & Tricks

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Some modern grammars add others, such as determiners and articles.
Dec 5, 2024 · Open word classes are the parts of speech that regularly acquire new words. Language evolves, and that evolution usually takes place in nouns, adjectives, adverbs, and verbs. In 2022, new words added to the Merriam-Webster dictionary included dumbphone (noun), greenwash (verb), and cringe (adjective).
The Part of Speech Is Determined by the Word's Function In a sentence, every word or phrase can be classified as one of the nine parts of speech depending on its function in the sentence. Remember that, in English, a word that performs a particular function in one sentence might perform a different function in another.
FAQ 10: Why is it important to understand parts of speech? Answer: Understanding parts of speech is crucial for constructing grammatically correct sentences, improving writing clarity, and enhancing communication skills. It helps learners identify and use words correctly and understand how words interact in a sentence.
Nov 16, 2023 · Every word is a part of speech playing a specific role in sentences or paragraphs. Parts of speech provide an organized way to align words and phrases, it is a fundamental meaning for a language to become more understandable and serve a specific purpose.
Aug 28, 2024 · A part of speech is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence. These roles help you understand how words function in grammar. There are typically eight main parts of speech in English: Nouns: Words that name people, places, things, or ideas. Pronouns: Words that replace nouns, such as he, she, it. Verbs: Words that describe ...
Dec 20, 2022 · Knowing the different parts of speech is essential for good grammar. Become an expert at knowing when and what parts of speech to use with these examples.
May 2, 2024 · A part of speech is a term used in traditional grammar for one of the nine main categories into which words are classified according to their functions in sentences, such as nouns or verbs. Also known as word classes, these are the building blocks of grammar.
Nov 2, 2024 · Understanding these eight parts of speech isn’t just for grammar nerds. It’s the secret sauce that helps you write clearer, more effective text, and aids in understanding what others are saying. When you get a grip on these basics, English starts to make more sense—whether you’re crafting an email, writing an essay, or just trying to ...
Oct 15, 2024 · Every word you use in English has a particular job, which we call a part of speech! Imagine it like a team where each player has a unique role to play. Some words help us name things, some show action, and others describe how things are. Understanding parts of speech is like unlocking a secret code that makes sentences come alive and sparkle!