

Excel Data for Pivot Table Practice
To solve these problems, you need to be familiar with inserting pivot tables , using slicers , utilizing calculated fields , inserting pivot pie charts , building a data model , and grouping by year . If you have Excel 2010 or later, you can solve these exercises without any compatibility issues.
Download the Practice Workbook
Excel Practice Data for Pivot Table.xlsx
Problem Overview
There are seven columns and 714 rows in our dataset, which represents sales data for a company from 2019 to 2022. The “Amount” column refers to the sales amount for the particular date.
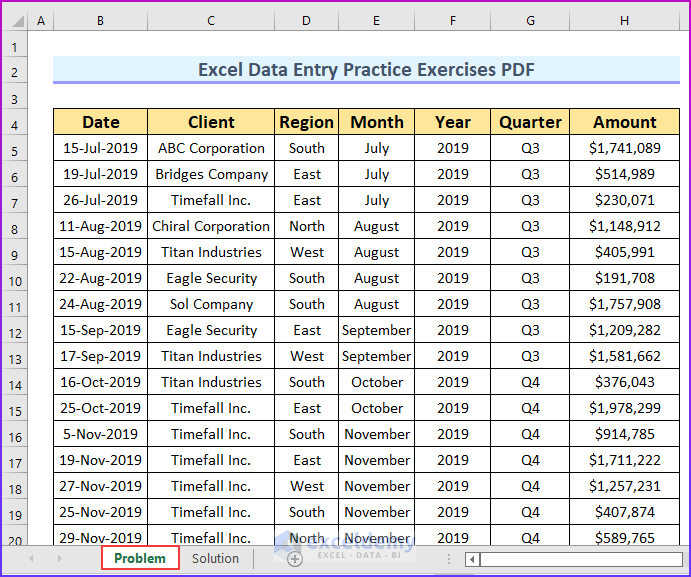
Here’s a list of exercises:
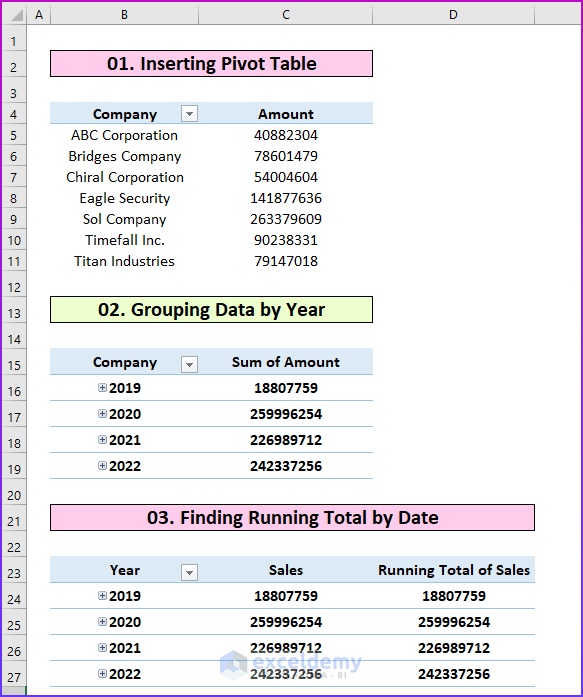
- Exercise 01 – Inserting a Pivot Table: Make a pivot table, then remove the grand total and edit the pivot table . Then, hide the Gridlines from the table.
- The following animated image shows how to hide the grand total value.
- Exercise 02 – Grouping Data by Year: Group the sales amount by the year. Additionally, you can try to group the data by weeks and months .
- Exercise 03 – Finding a Running Total by Date: Find the running total by date using the data.
- Exercise 04 – Inserting a Pie Chart: Create a pie chart from the data in this problem.
- Exercise 05 – Adding Slicers to the Pivot Table: Insert a slicer to the pivot table.
- Exercise 06 – Using a Calculated Field: You will need to find the sales tax which is 5% of the total sales using the calculated field. Remember, to import the pivot table as a data model.
The following image shows the first three solutions.
What is ExcelDemy?

Rafiul Haq worked as an Excel and VBA Content Developer in Exceldemy for over two years and published almost 200 articles for the website. He is passionate about exploring new aspects of Excel and VBA. He received his Bachelor of Science in Mechanical and Production Engineering (MPE) from the Islamic University of Technology. Rafiul furthered his education by obtaining an MBA in Finance from the Institute of Business Administration (IBA) at the University of Dhaka. Apart from creating... Read Full Bio
Thank you!! Rafiul Haq.

Dear Minhajul ,
You are most welcome.
Regards ExcelDemy
Answer to exercise 3 is wrong. Sales and Running total of Sales have the same values. Otherwise nice exercise
Dear Qasim ,
Thanks for your suggestions we have updated our Exercise 3 you can check it now.
Great work exceldemy team! Really healped me a lot.
Dear Foysal ,
Do you have any YouTube channel?
Dear Ashab,
We do have a YouTube channel named ExcelDemy
Solve this in a video and upload on your youtube channel. Its a very helpful.
Hello Rao ,
We will try to upload it in our up coming videos.
What is the purpose of computing or finding the running total?
Hello Emz ,
The purpose of computing or finding the running total in a pivot table is to observe cumulative values over time or sequential categories. It will help you to identify trends, monitor progress, and understand how data accumulates. For example, in sales data, a running total allows you to see how much revenue has been generated up to a certain point. It provides insights into overall performance, allowing for easier analysis of growth or decline. This is especially useful in tracking inventory, financial data, or project timelines.
Leave a reply Cancel reply
ExcelDemy is a place where you can learn Excel, and get solutions to your Excel & Excel VBA-related problems, Data Analysis with Excel, etc. We provide tips, how to guide, provide online training, and also provide Excel solutions to your business problems.
See Our Reviews at

- User Reviews
- List of Services
- Service Pricing
- Create Basic Excel Pivot Tables
- Excel Formulas and Functions
- Excel Charts and SmartArt Graphics
- Advanced Excel Training
- Data Analysis Excel for Beginners

Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions PDF


- Our training courses Book any course as classroom , onsite or online training, or as one-to-one consultancy Excel Training Basic Excel Advanced Excel VBA Macros Office Scripts Excel Introduction Excel Intermediate Excel Advanced Excel Business Modelling Excel VBA macros Advanced VBA Fast track Excel VBA Basic Office Scripts Advanced Office Scripts Power Platform Training Pure Power BI DAX and fast-track Power Automate Power Apps Introduction to Power BI Adv. Power BI Reports Adv. Power BI Data DAX for Power BI Fast track Power BI Fast track Power BI/DAX Power Automate Desktop Basic Power Automate Advanced Power Automate Fast track Power Automate Power Apps Programming and AI SQL training Visual C# training Python training AI training Introduction to SQL Advanced SQL Fast track SQL Introduction to MySQL Introduction to Visual C# Intermediate C# Fast track C# Introduction to Python Advanced Python Fast track Python Using AI tools Using the OpenAI API SQL Server training Reporting Services Report Builder Integration Services Azure / SSAS Reporting Services Advanced SSRS Fast track SSRS Report Builder Introduction to SSIS Advanced SSIS Fast track SSIS SQL in Azure Data Studio SSAS - Tabular Model
Read our blogs , tips and tutorials
Try our exercises or test your skills
Watch our tutorial videos or shorts
Take a self-paced course
Read our recent newsletters
License our courseware
Book expert consultancy
Buy our publications
Get help in using our site
Across the UK
At your site
At your computer
551 attributed reviews in the last 3 years
Refreshingly small course sizes
Outstandingly good courseware
Whizzy online classrooms
Wise Owl trainers only ( no freelancers )
Almost no cancellations
We have genuine integrity
We invoice after training
Review 30+ years of Wise Owl
View our top 100 clients
Search our website
We also send out useful tips in a monthly email newsletter ...
Sign up to newsletter
Our training courses
Other training resources
Our training venues
Why we are different
- Wise Owl Training
- Excel training
- Pivot tables / charts

7,327 reviews
EXERCISE TOPIC
- Artificial Intelligence exercises (21)
- C# exercises (55)
- Excel exercises (186)
- Microsoft 365 exercises (55)
- Office Scripts exercises (21)
- Power Apps exercises (13)
- Power Automate and PAD exercises (39)
- Power BI exercises (219)
- Power Platform exercises (271)
- Python exercises (34)
- Report Builder exercises (141)
- SQL exercises (203)
- SQL Server exercises (360)
- SSAS exercises (30)
- SSIS exercises (28)
- SSRS exercises (99)
- VBA exercises (80)
EXCEL EXERCISES
- Excel (113)
- Excel VBA Macros (52)
- OfficeScripts (21)
- Excel basics (1)
- Creating formulae (10)
- Formatting worksheets (6)
- Basic printing (4)
- Absolute references (5)
- Range names (6)
- Conditional formulae (8)
- Conditional formatting (2)
- Basic tables (6)
- Formatting numbers and dates (4)
- Working with dates (1)
- Data validation (2)
- Protection (1)
- Advanced IFs (5)
- Lookup functions (10)
- Spill functions (1)
- Advanced lookup functions (4)
- Text functions (1)
- Advanced charts (4)
- Multiple worksheets (1)
- Advanced tables (2)
- Pivot tables / charts (7)
- Advanced pivot tables (3)
- Scenarios (2)
- Data tables (2)
- Advanced formulae (5)
- Building models (1)
- Masking (1)
- Cashflow calculations (1)
- Investment appraisal (1)
- Querying data (3)
PIVOT TABLES / CHARTS exercises
This page lists the 7 exercises about Pivot tables / charts in Excel on our website:
You can search our full list of Excel exercises here . Or why not learn to do them the right way on one of our Excel training courses ? You can attend our online training classes wherever you are in the world!

Head office
Kingsmoor House
Railway Street
Landmark Offices
99 Bishopsgate
Holiday Inn
25 Aytoun Street
© Wise Owl Business Solutions Ltd 2024. All Rights Reserved.
Pivot Table Examples
Pivot tables are the fastest and easiest way to quickly analyze data in Excel. These examples can save you time by solving common scenarios.
Quick Links

Pivot table basic count

Pivot table basic sum

Pivot table calculated field example

Pivot table calculated item example

Pivot table conditional formatting

Pivot table count birthdays by month

Pivot table count blanks

Pivot table count by month

Pivot table count by year
Pivot table count with percentage

Pivot table display items with no data
Pivot table filter by weekday

Pivot table group by age

Pivot table group by custom

Pivot table group by day of week

Pivot table group by quarter

Pivot table issue count by priority

Pivot table last 12 months

Pivot table last 4 weeks

Pivot table last 7 days

Pivot table latest values

Pivot table list unique values

Pivot table month over month

Pivot table months with no data

Pivot table most frequently occurring

Pivot table project estimate

Pivot table rank example

Pivot table remove deleted items

Pivot table running total

Pivot table show duplicates


Pivot table show top 3 values

Pivot table sum by month

Pivot table two-way average

Pivot table two-way count

Pivot table two-way sum

Pivot table unique count

Pivot table year over year

Pivot table year over year by month

Download 100+ Important Excel Functions
Get PDF Guide
Get Training
Quick, clean, and to the point training.
Learn Excel with high quality video training. Our videos are quick, clean, and to the point, so you can learn Excel in less time, and easily review key topics when needed. Each video comes with its own practice worksheet.

Excel Resources
- Career Guides
- Interview Prep Guides
- Free Practice Tests
- Excel Cheatsheets
💡 Expert-Led Sessions 📊 Build Financial Models ⏳ 60+ Hours Learning

Pivot Table Examples
Publication Date :
17 Mar, 2019
Blog Author :
WallStreetMojo Team
Edited by :
Ashish Kumar Srivastav
Reviewed by :
Dheeraj Vaidya, CFA, FRM
Table Of Contents
What Are Pivot Table Examples?
PivotTable is a table of stats that summarizes the data as sums, averages, and many other statistical measures. Let us assume that we got data of any real estate project with different fields like type of flats, block names, area of the individual apartments, and their other cost per various services, etc.
Table of contents
- Examples of Pivot Table in Excel
Important Things To Note
Frequently asked questions, recommended articles.
- Pivot Table sums up data through statistical measures like sums and averages.
- It eases the analysis of large amounts of data, such as in real estate projects with various flat types, block names, individual apartment areas, and service costs.
- To select a row or column, tap its letter or number.
- In Excel, modifying the format creates a duplicate format. Custom number formats affect the cells' appearance, not their values. On custom format removal, cells are present in the default format.
Examples Of Pivot Table In Excel
Below is the raw data for the PivotTable practice exercises.

Create a PivotTable using the above table.
PivotTable Example #1 - Performing Statistics Measures In PivotTable
In the Excel Pivot Table Example, we should perform the sum of the final product value to extract the value of different blocks got as below:
Drag the "Block Name" to "Rows" and "Sum of Final Product Value" to "Values" Fields.
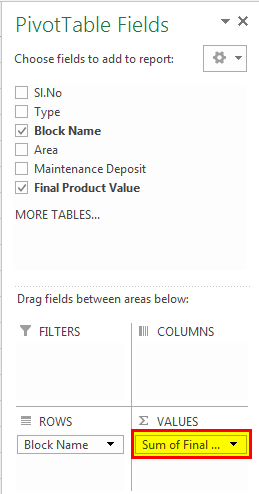
It shows that we have the "Cheeku" block with 293 million, "Donald" block with 212 million, "Mickey" block with 324 million, "Rainbow" block with 466 million, and "Strawberry" with 355 million. This table shows us that the "Rainbow" block got a higher value than the other blocks.
Let us count the number of flats for different blocks by changing the value field settings in Excel PivotTable to count as below:
Then, click on "Value Field Settings."
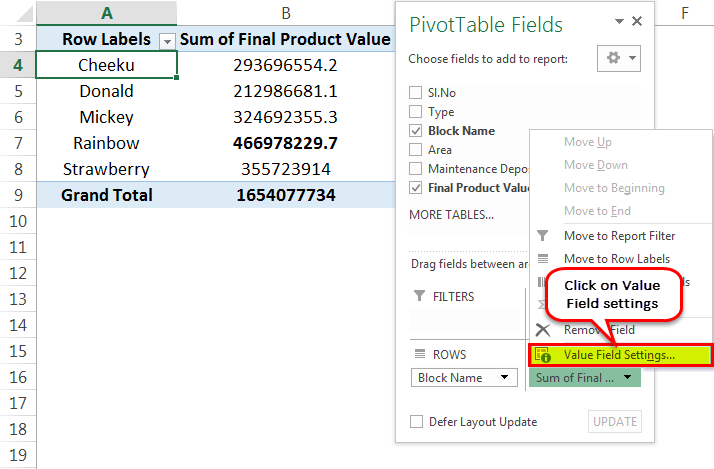
A dialog box appears. Select “Count” from "Summarize value field by."
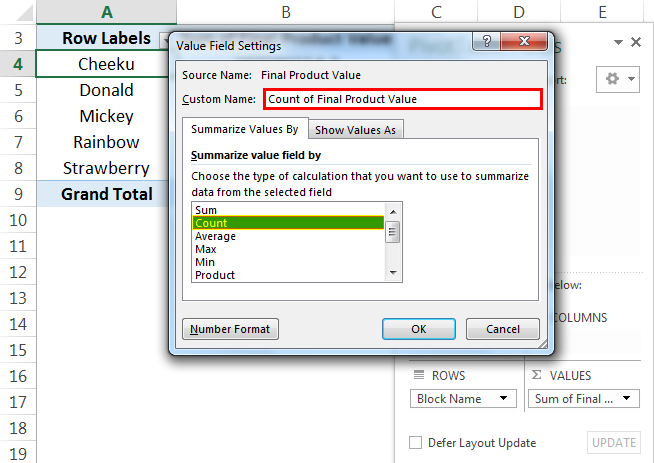
Then the PivotTable looks like as given below:
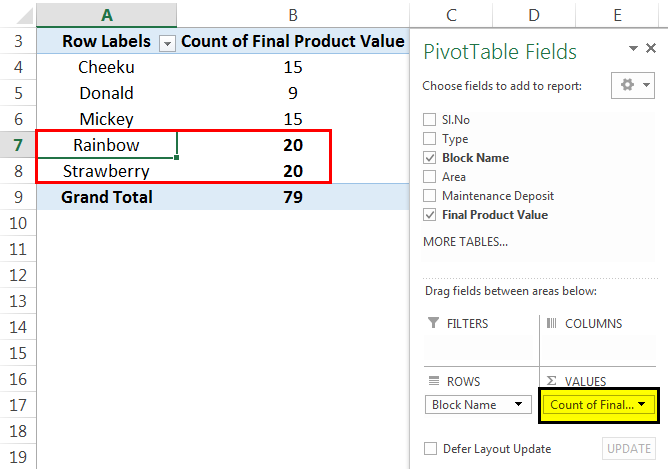
From the above tables, we can see how to change the field settings to count. Here, we can note that we got the highest number of flats in the "Rainbow" block and "Strawberry" block compared to other blocks. In total, we got 79 flats in this project.
AVERAGE:
In the PivotTable practice exercise example, we will find out the average price of the flat in each block by changing the value field settings from "Count" to "Average."
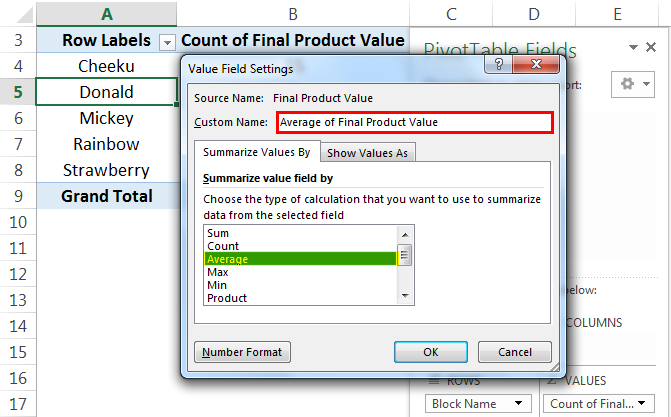
Then, PivotTable changes from "Count" to "Average," as given below:
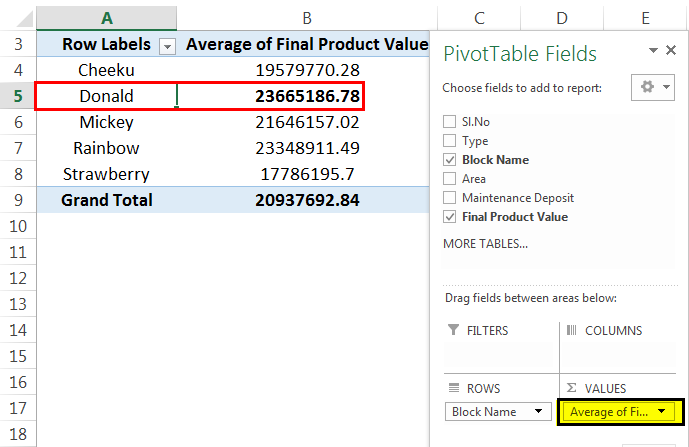
From the above PivotTable example, we can see that we got the average flat price in each block. The "Donald" block got the highest average flat price among other blocks.
Similarly, we can perform other statistical measures like Max, Min, Product, Standard deviation , etc., by changing the value field settings in this PivotTable example.
Pivot Table Example #2 - How Can We Modify The PivotTables In Excel
We can change the layout of the Excel PivotTable per our requirement by dragging the fields into areas where we want to place them.
In this example of a PivotTable in Excel, let us see how it works.
First, we must drag the “Maintenance Deposit” into the "Values" area to check each block's total maintenance price. You will get your table modified as below:
This PivotTable shows both maintenance deposit and an average price for different blocks. As discussed earlier, we can change the statistical measure by changing the value field setting.
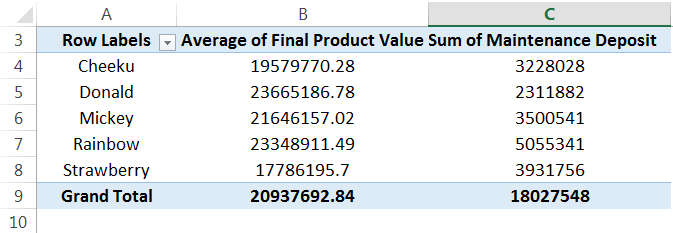
We can also modify the above table further by adding the type of units that are available as block-wise as below:
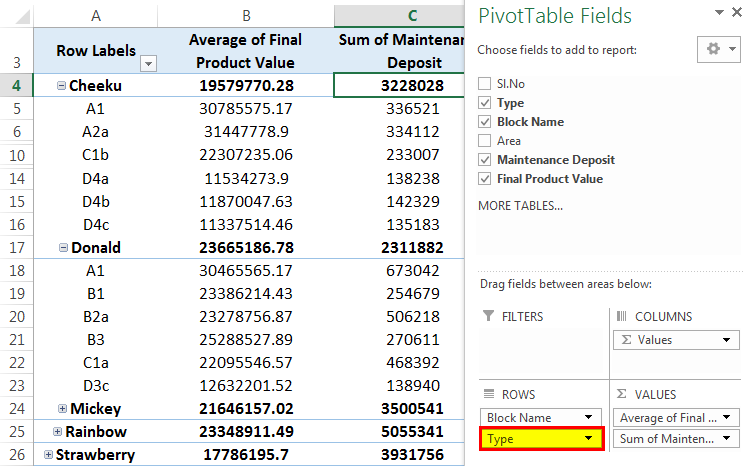
The above table shows that the type of flats in the "Cheeku" block are A1, A2a, B1, B2a, C1a, C1b, D1c, D2b, D3b, D4a, D4b, D4c. Similarly, we get for other blocks too.
Pivot Table Example #3 - Grouping The Fields In The Excel PivotTable
We can also create a group in Excel PivotTables to differentiate a few fields. In our PivotTable practice exercise example, let us create the "Strawberry" block, "Cheeku" block as "Group-1" and "Donald" block, "Mickey" block, and "Rainbow" block as "Group-2."Let us see how we can create these groups:
As per our above PivotTable example, select "Cheeku" and "Strawberry" with the help of the "Ctrl" key. Then, right-click on the mouse to get the list. Next, go to the "Group" option and then click on it.
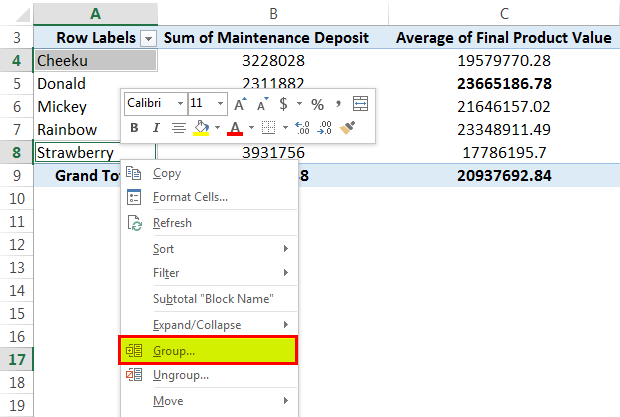
Now, we can see the group has been created as below:
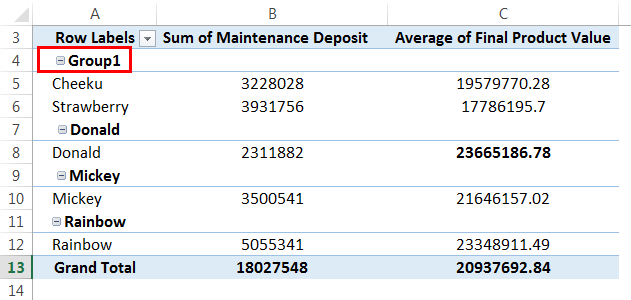
Similarly, we can select the rest of the block and do the same. Then, click on the "Group" again. Now, "Group-2" will also be created as follows:
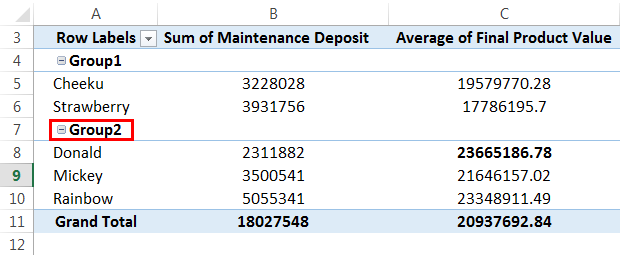
We can also name the group by editing the group and giving the names per our requirements.
PivotTable Example #4 - Creating Multi-Levels In Excel Pivot Table
Creating multi-levels in PivotTable is easy by just dragging the fields to any specific area in a PivotTable.
But here, in the example of the PivotTable, we understand how we can also make great insight into this multilevel PivotTable.
First, we need to drag the "Block Name" into "ROWS" as we find some insight into the block of the project. Then, drag the "Final Product Value" to the "VALUES" area as we get the sum of all flats units value of a particular block in the table.
Drag the "Final Product Value" to the "VALUES" area to create a multi-level table.
We can see the table with two columns with "Final Product Value" for different blocks below:
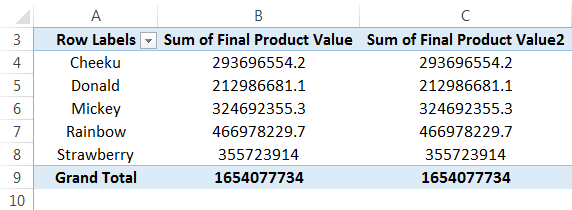
Now, let us find out some insight from this data. To do so, we should change the value field set to any measures that need to be considered. Here, we will take a percentage to see the contribution of different blocks in terms of the product value as below:
Go to "Value Field Settings," then select “Show values as.” In that, select “% of Column Total.”
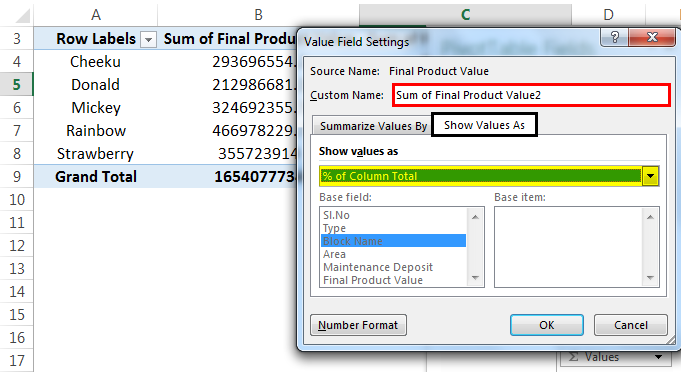
We can see the table with a percentage in "Sum of Final Product Value2" below:
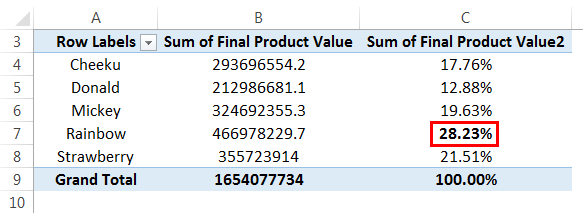
From the above data, we can understand that the "Cheeku" block had contributed 17.76%, "Donald" – 12.88%, "Micky" – 19.63%, and "Rainbow" – 28.23%, and "Strawberry" – 21.51% of the total value of the project. A "Rainbow" block is the highest contributor among all other blocks.
Similarly, we can perform different multi-level operations using a PivotTable, which provides great insight into the data.
PivotTable Example #5 - Creating Frequency In Excel PivotTable
Earlier in the example of the PivotTable, we had seen grouping the name of the blocks. Now, let us group the value to create a frequency that shows us the number of units that fall under a certain area category.
First, drag the area field into "ROWS" and again drag the same area field into the "VALUES" area. By default, the "VALUES" area gives the sum of the area, so we should change it to count because here, our goal is to find several units in a particular area category.
Now, right-click on any cell of the row labels and the select group.
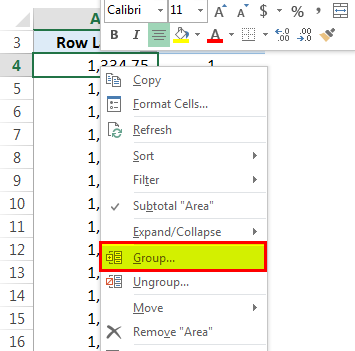
Then, the "Grouping" window will pop out where we have to give the starting number for the frequency to get started and the ending number. In addition, we have to provide a number that will create a frequency.
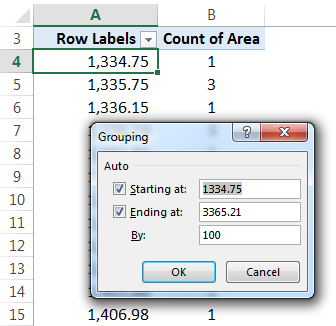
Let us provide the conditions as a starting point as 1000 and ending at 3400. Then, it should be split by 400.
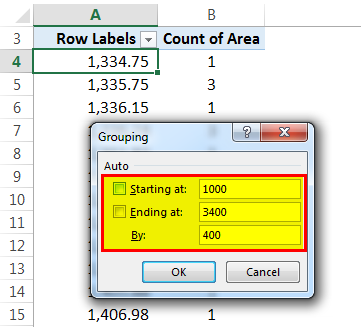
Now, we can see that the area category has been formed. There are 19 flats which got an area between 1,000-1,400 sq.ft, 5 flats with an area between 1,400-1,800 sq.ft., 41 flats with an area between 2,200-2,600 sq.ft., 2 flats with an area between 2,600-3,000 sq.ft. and 12 flats with an area between 3,000-3,400 sq.ft. So, here we can assume that we got the highest number of flats with 3 BHK configurations per area.

You can download this Pivot Table Examples Excel Template here - Pivot Table Examples Excel Template
- Pivot Table helps us analyse large dataset used in various fields such as gaming, finance, auditing, business projects etc.
- We can use statistical functions to create accurate Pivot Tables useful for the users.
- To select the entire sheet, remember that we need to click on the box next to "A" or above "1."
Pivot Tables can quickly point out essential data in our records/data that were first unnoticed, such as identifying any invoices before or after the date.
Yes. In finance, pivot tables are a critical tool for efficiency and accuracy in data analysis and financial reporting.
A Pivot Table consists of four areas where field names can be placed - Filters, Columns, Rows, and Values. These areas can help you to organize and analyze your data more effectively.
This article is a guide to PivotTable examples in Excel. Here, we provide practice exercises PivotTable in Excel with examples such as modifying PivotTable, statistical measures, and grouping fields. You may learn more about Excel from the following articles: -
- Excel Pivot Table Count Unique
- Create a Pivot Table From Multiple Sheets
- Use the Pivot Chart in Excel
- How to use a Pivot Table Filter?
101 Excel Pivot Tables Examples

Pivot Tables in Excel are one of the most powerful features within Microsoft Excel.
Pivot Tables in Excel are one of the most powerful features within Microsoft Excel. An Excel Pivot Table allows you to analyze more than 1 million rows of data with just a few mouse clicks, show the results in an easy to read table, “pivot”/change the report layout with the ease of dragging fields around, highlight key information to management and include Charts & Slicers for your monthly presentations. Pivot Tables are used by Project Managers, Finance Analysts, Auditors, Cost Controllers, Sales Analysts, Financial Controllers, Information Technology, Human Resources, Doctors and Statisticians just to name a few. You would be surprised on how widely used Excel Pivot Tables are!
We have over a hundred tutorials for you to learn and master Excel Pivot Tables ! So read on!
Analysis Calculated Fields & Items Conditional Formatting Customize Excel Pivot Tables Group
Pivot Charts Pivot Table Macros Slicers Sort & Filter Tips and Tricks
Click on any Excel Pivot Table link below and it will take you to the free example tutorial & downloadable Excel workbook for you to practice!
Table of Contents
Want to know learn Excel Pivot Tables in 5 minutes?
*** Watch our video and step by step guide below with free downloadable Excel workbook to practice ***
Watch it on YouTube and give it a thumbs-up!
download the youtube excel practice file PivotTable.xlsx
Want to master Excel Pivot Tables from scratch?
Analysis
Calculated fields & items , conditional formatting , customize , excel pivot tables , group , pivot charts , pivot table macros , slicers , sort & filter , tips and tricks .

Bryan Hong is an IT Software Developer for more than 10 years and has the following certifications: Microsoft Certified Professional Developer (MCPD): Web Developer, Microsoft Certified Technology Specialist (MCTS): Windows Applications, Microsoft Certified Systems Engineer (MCSE) and Microsoft Certified Systems Administrator (MCSA).
He is also an Amazon #1 bestselling author of 4 Microsoft Excel books and a teacher of Microsoft Excel & Office at the MyExecelOnline Academy Online Course .
#ez_toc_widget_sticky--1 .ez-toc-widget-sticky-container ul.ez-toc-widget-sticky-list li.active{ background-color: #ededed; } Steps To Follow
30+ excel & office courses.
$1 Trial for 30 days
Cancel Anytime
Related Articles
The Ultimate Excel Fix to Pivot Table Fields Not Showing
Month over Month Comparison Charts in Excel Pivot Tables
Excel Harvey Balls Made Easy: Step-by-Step Tutorial
30 Days - Full Access
$1 Trial for 30 days!

- Get FULL ACCESS to all our Excel & Office courses, bonuses, and support for just USD $1 today! Enjoy 30 days of learning and expert help.
- You can CANCEL ANYTIME — no strings attached! Even if it’s on day 29, you won’t be charged again.
- You'll get to keep all our downloadable Excel E-Books, Workbooks, Templates, and Cheat Sheets - yours to enjoy FOREVER!
- Practice Workbooks
- Certificates of Completion
- 5 Amazing Bonuses
Get Video Training
Advance your microsoft excel & office skills with the myexcelonline academy.
Dramatically Reduce Repetition, Stress, and Overtime! Exponentially Increase Your Chances of a Promotion, Pay Raise or New Job! Learn in as little as 5 minutes a day or on your schedule.
How to Make a Pivot Table in Excel (Easy Step-by-Step)
If you are reading this tutorial, there is a big chance you have heard of (or even used) the Excel Pivot Table. It’s one of the most powerful features in Excel (no kidding).
The best part about using a Pivot Table is that even if you don’t know anything in Excel, you can still do pretty awesome things with it with a very basic understanding of it.
This Tutorial Covers:
Let’s get started.
Click here to download the sample data and follow along.
What is a Pivot Table and Why Should You Care?
A Pivot Table is a tool in Microsoft Excel that allows you to quickly summarize huge datasets (with a few clicks).
Even if you’re absolutely new to the world of Excel, you can easily use a Pivot Table. It’s as easy as dragging and dropping rows/columns headers to create reports.
Suppose you have a dataset as shown below:
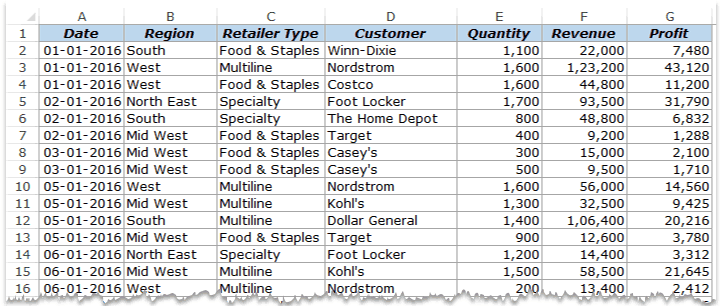
This is sales data that consists of ~1000 rows.
It has the sales data by region, retailer type, and customer.
Now your boss may want to know a few things from this data:
- What were the total sales in the South region in 2016?
- What are the top five retailers by sales?
- How did The Home Depot’s performance compare against other retailers in the South?
You can go ahead and use Excel functions to give you the answers to these questions, but what if suddenly your boss comes up with a list of five more questions.
You’ll have to go back to the data and create new formulas every time there is a change.
This is where Excel Pivot Tables comes in really handy.
Within seconds, a Pivot Table will answer all these questions (as you’ll learn below).
But the real benefit is that it can accommodate your finicky data-driven boss by answering his questions immediately.
It’s so simple, you may as well take a few minutes and show your boss how to do it himself.
Hopefully, now you have an idea of why Pivot Tables are so awesome. Let’s go ahead and create a Pivot Table using the data set (shown above).
Inserting a Pivot Table in Excel
Here are the steps to create a pivot table using the data shown above:
- Click anywhere in the dataset.
- Table/Range: It’s filled in by default based on your data set. If your data has no blank rows/columns, Excel would automatically identify the correct range. You can manually change this if needed.
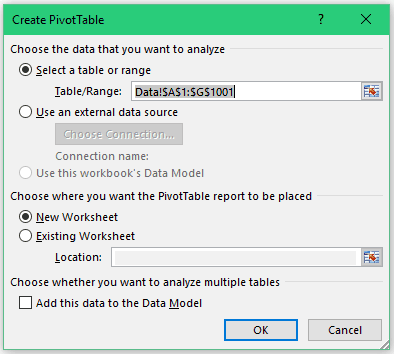
As soon as you click OK, a new worksheet is created with the Pivot Table in it.
While the Pivot Table has been created, you’d see no data in it. All you’d see is the Pivot Table name and a single line instruction on the left, and Pivot Table Fields on the right.
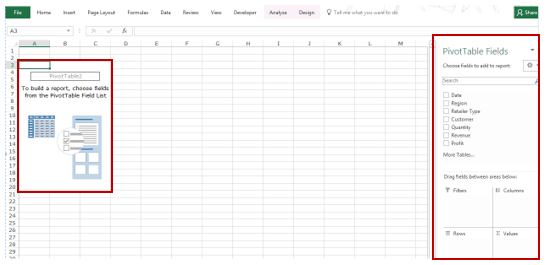
Now before we jump into analyzing data using this Pivot Table, let’s understand what are the nuts and bolts that make an Excel Pivot Table.
The Nuts & Bolts of an Excel Pivot Table
To use a Pivot Table efficiently, it’s important to know the components that create a pivot table.
In this section, you’ll learn about:
Pivot Cache
Values area, columns area, filters area.
As soon as you create a Pivot Table using the data, something happens in the backend. Excel takes a snapshot of the data and stores it in its memory. This snapshot is called the Pivot Cache.
When you create different views using a Pivot Table, Excel does not go back to the data source, rather it uses the Pivot Cache to quickly analyze the data and give you the summary/results.
The reason a pivot cache gets generated is to optimize the pivot table functioning. Even when you have thousands of rows of data, a pivot table is super fast in summarizing the data. You can drag and drop items in the rows/columns/values/filters boxes and it will instantly update the results.
Note: One downside of pivot cache is that it increases the size of your workbook. Since it’s a replica of the source data, when you create a pivot table, a copy of that data gets stored in the Pivot Cache.
The Values Area is what holds the calculations/values.
Based on the data set shown at the beginning of the tutorial, if you quickly want to calculate total sales by region in each month, you can get a pivot table as shown below (we’ll see how to create this later in the tutorial).
The area highlighted in orange is the Values Area.
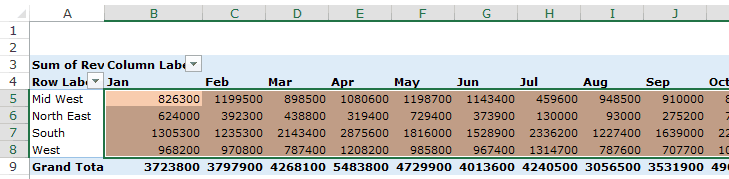
In this Pivot Table example, it has the total sales in each month for the four regions.
The headings to the left of the Values area makes the Rows area.
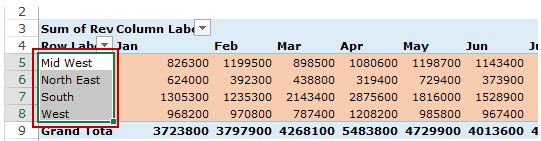
The headings at the top of the Values area makes the Columns area.
In the example below, Columns area contains the months (highlighted in red):
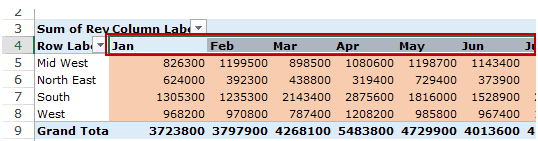
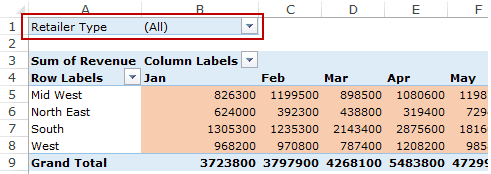
Filters area is an optional filter that you can use to further drill down in the data set.
For example, if you only want to see the sales for Multiline retailers, you can select that option from the drop down (highlighted in the image below), and the Pivot Table would update with the data for Multiline retailers only.
Analyzing Data Using the Pivot Table
Now, let’s try and answer the questions by using the Pivot Table we have created.
To analyze data using a Pivot Table, you need to decide how you want the data summary to look in the final result. For example, you may want all the regions in the left and the total sales right next to it. Once you have this clarity in mind, you can simply drag and drop the relevant fields in the Pivot Table.
In the Pivot Tabe Fields section, you have the fields and the areas (as highlighted below):
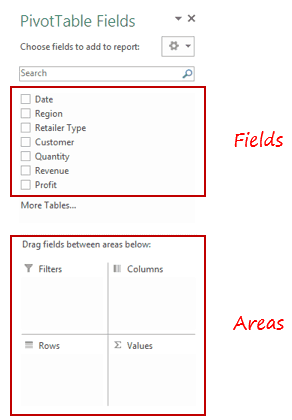
The Fields are created based on the backend data used for the Pivot Table. The Areas section is where you place the fields, and according to where a field goes, your data is updated in the Pivot Table.
It’s a simple drag and drop mechanism, where you can simply drag a field and put it in one of the four areas. As soon as you do this, it will appear in the Pivot Table in the worksheet.
Now let’s try and answer the questions your manager had using this Pivot Table.
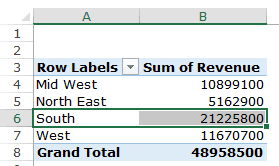
Q1: What were the total sales in the South region?
Drag the Region field in the Rows area and the Revenue field in the Values area. It would automatically update the Pivot Table in the worksheet.
Note that as soon as you drop the Revenue field in the Values area, it becomes Sum of Revenue. By default, Excel sums all the values for a given region and shows the total. If you want, you can change this to Count, Average, or other statistics metrics. In this case, the sum is what we needed.
The answer to this question would be 21225800.
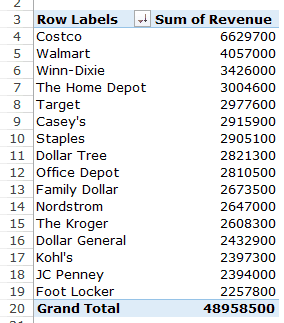
Q2 What are the top five retailers by sales?
Drag the Customer field in the Row area and Revenue field in the values area. In case, there are any other fields in the area section and you want to remove it, simply select it and drag it out of it.
You’ll get a Pivot Table as shown below:
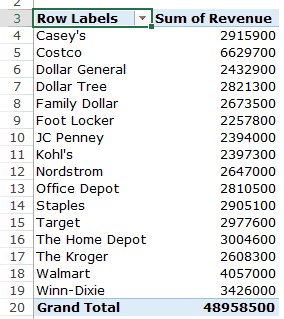
Note that by default, the items (in this case the customers) are sorted in an alphabetical order.
To get the top five retailers, you can simply sort this list and use the top five customer names. To do this:
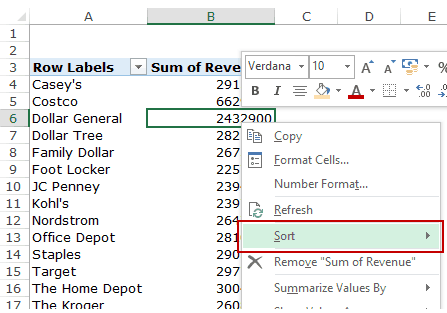
This will give you a sorted list based on total sales.
Q3: How did The Home Depot’s performance compare against other retailers in the South?
You can do a lot of analysis for this question, but here let’s just try and compare the sales.
Drag the Region Field in the Rows area. Now drag the Customer field in the Rows area below the Region field. When you do this, Excel would understand that you want to categorize your data first by region and then by customers within the regions. You’ll have something as shown below:
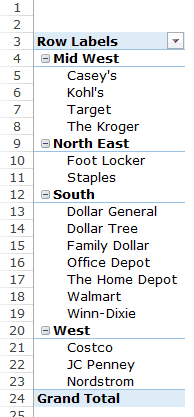
Now drag the Revenue field in the Values area and you’ll have the sales for each customer (as well as the overall region).
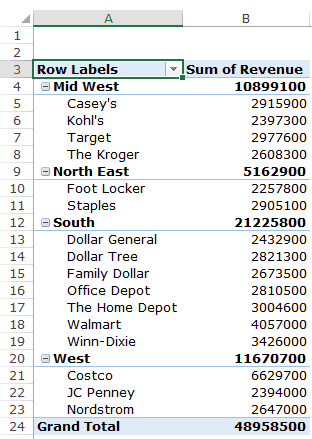
You can sort the retailers based on the sales figures by following the below steps:
- Right-click on a cell that has the sales value for any retailer.
- Go to Sort –> Sort Largest to Smallest.
This would instantly sort all the retailers by the sales value.
Now you can quickly scan through the South region and identify that The Home Depot sales were 3004600 and it did better than four retailers in the South region.
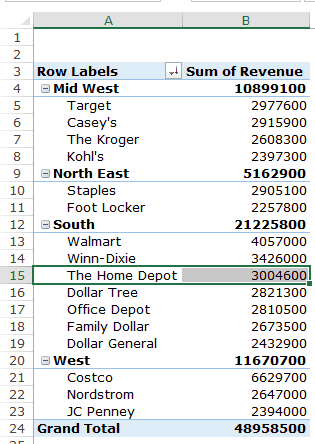
Now there are more than one ways to skin the cat. You can also put the Region in the Filter area and then only select the South Region.
Click here to download the sample data.
I hope this tutorial gives you a basic overview of Excel Pivot Tables and helps you in getting started with it.
Here are some more Pivot Table Tutorials you may like:
- Preparing Source Data For Pivot Table .
- How to Apply Conditional Formatting in a Pivot Table in Excel .
- How to Group Dates in Pivot Tables in Excel.
- How to Group Numbers in Pivot Table in Excel .
- How to Filter Data in a Pivot Table in Excel.
- Using Slicers in Excel Pivot Table.
- How to Replace Blank Cells with Zeros in Excel Pivot Tables.
- How to Add and Use an Excel Pivot Table Calculated Fields .
- How to Refresh Pivot Table in Excel .

FREE EXCEL BOOK
Get 51 Excel Tips Ebook to skyrocket your productivity and get work done faster
2 thoughts on “How to Make a Pivot Table in Excel (Easy Step-by-Step)”
I am not getting the excel tips free ebook
Just wanna say, thank you for sharing this it will help us, especially me as a beginner in this field.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
BEST EXCEL TUTORIALS
Best Excel Shortcuts
Conditional Formatting
Excel Skills
Creating a Pivot Table
Excel Tables
INDEX- MATCH Combo
Creating a Drop Down List
Recording a Macro
© TrumpExcel.com – Free Online Excel Training
Privacy Policy | Sitemap
Twitter | Facebook | YouTube | Pinterest | Linkedin

FREE EXCEL E-BOOK


- Description
- Data arrays
- Excel Formatted Tables
- Pivot tables
- Pivot Charts
- Slicers in tables
- Slicers In pivot tables
- P ivot Objects
Assignment Materials
Click next to start exploring excel tables.


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Jul 3, 2024 · Exercise 05 – Adding Slicers to the Pivot Table: Insert a slicer to the pivot table. Exercise 06 – Using a Calculated Field: You will need to find the sales tax which is 5% of the total sales using the calculated field. Remember, to import the pivot table as a data model. The following image shows the first three solutions.
Nov 9, 2019 · Existing Pivot Table – We will click on the “Analyze” tab and then on “Pivot Chart” in the “Tools” group (we have to select a cell in the Pivot Table before doing this) Creating a new Pivot Table – “Insert” tab -> “Pivot Chart” in the “Charts” group (we have to select the desired source data before doing this)
Basic tables (6) Formatting numbers and dates (4) Working with dates (1) Data validation (2) Protection (1) Advanced IFs (5) Lookup functions (10) Spill functions (1) Advanced lookup functions (4) Text functions (1) Advanced charts (4) Multiple worksheets (1) Advanced tables (2) Pivot tables / charts (7) Advanced pivot tables (3) Scenarios (2 ...
Note: Pivot Table tool will perform any required sorts. Part 2 – Genre Popularity 1. Select range A1-J17. 2. Insert, Pivot Table (leftmost selection on the Insert tab on the Ribbon). 3. The range should be filled in, if not select the range A1 – J17. Select New Worksheet for the Pivot table and hit OK. 4. Drag Genre to Row Labels box (this ...
ASSIGNMENT 3: SUBJECT Making the Pivot Table More Visual with Charts. Summarizing Data by Date and Time. Creating a Pivot Table from Multiple Spreadsheets. Study the course materials from pages 149 to 224. Complete the review questions at the end of each chapter. Answer the exam questions 20 to 32. Objectives:
Simple Pivot Table examples you can use for inspiration and learning. Includes screen shots, instructions, and video links.
Mar 17, 2019 · Pivot Table helps us analyse large dataset used in various fields such as gaming, finance, auditing, business projects etc. We can use statistical functions to create accurate Pivot Tables useful for the users. To select the entire sheet, remember that we need to click on the box next to "A" or above "1."
Pivot Tables in Excel are one of the most powerful features within Microsoft Excel. An Excel Pivot Table allows you to analyze more than 1 million rows of data with just a few mouse clicks, show the results in an easy to read table, “pivot”/change the report layout with the ease of dragging fields around, highlight key information to management and include Charts & Slicers for your monthly ...
Hopefully, now you have an idea of why Pivot Tables are so awesome. Let’s go ahead and create a Pivot Table using the data set (shown above). Inserting a Pivot Table in Excel. Here are the steps to create a pivot table using the data shown above: Click anywhere in the dataset. Go to Insert –> Tables –> Pivot Table.
A pivot table allows you to analyze data from a table or just an unformatted range of cells. With many features, a pivot table enables you to view the data in a variety of ways, calculate totals and other metrics, and even create a detailed report. You can create pivot charts using the data from your tables. There are a variety of chart types ...