Assignment Problem: Meaning, Methods and Variations | Operations Research
After reading this article you will learn about:- 1. Meaning of Assignment Problem 2. Definition of Assignment Problem 3. Mathematical Formulation 4. Hungarian Method 5. Variations.

Meaning of Assignment Problem:
An assignment problem is a particular case of transportation problem where the objective is to assign a number of resources to an equal number of activities so as to minimise total cost or maximize total profit of allocation.
The problem of assignment arises because available resources such as men, machines etc. have varying degrees of efficiency for performing different activities, therefore, cost, profit or loss of performing the different activities is different.
Thus, the problem is “How should the assignments be made so as to optimize the given objective”. Some of the problem where the assignment technique may be useful are assignment of workers to machines, salesman to different sales areas.
Definition of Assignment Problem:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Suppose there are n jobs to be performed and n persons are available for doing these jobs. Assume that each person can do each job at a term, though with varying degree of efficiency, let c ij be the cost if the i-th person is assigned to the j-th job. The problem is to find an assignment (which job should be assigned to which person one on-one basis) So that the total cost of performing all jobs is minimum, problem of this kind are known as assignment problem.
The assignment problem can be stated in the form of n x n cost matrix C real members as given in the following table:
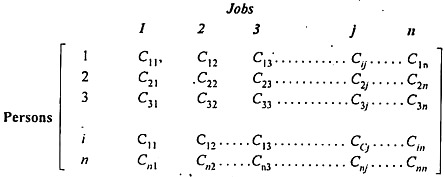

Introduction | Operations Research - Assignment Problem | 12th Business Maths and Statistics : Chapter 10 : Operations Research
Chapter: 12th business maths and statistics : chapter 10 : operations research, assignment problem.
Assignment Problem:
Introduction:
The assignment problem is a particular case of transportation problem for which more efficient (less-time consuming) solution method has been devised by KUHN (1956) and FLOOD (1956). The justification of the steps leading to the solution is based on theorems proved by Hungarian Mathematicians KONEIG (1950) and EGERVARY (1953), hence the method is named Hungarian Method.
Suppose that we have ‘ m ’ jobs to be performed on ‘ n ’ machines . The cost of assigning each job to each machine is C ij ( i =1,2,…, n and j = 1,2,…, n ).Our objective is to assign the different jobs to the different machines(one job per machine) to minimize the overall cost. This is known as assignment problem.
The assignment problem is a special case of transportation problem where the number of sources and destinations are equal. Supply at each source and demand at each destination must be one. It means that there is exactly one occupied cell in each row and each column of the transportation table . Jobs represent sources and machines represent destinations.
Related Topics
Privacy Policy , Terms and Conditions , DMCA Policy and Compliant
Copyright © 2018-2023 BrainKart.com; All Rights Reserved. Developed by Therithal info, Chennai.
MBA Knowledge Base
Business • Management • Technology
Home » Management Science » Transportation and Assignment Models in Operations Research
Transportation and Assignment Models in Operations Research
Transportation and assignment models are special purpose algorithms of the linear programming. The simplex method of Linear Programming Problems(LPP) proves to be inefficient is certain situations like determining optimum assignment of jobs to persons, supply of materials from several supply points to several destinations and the like. More effective solution models have been evolved and these are called assignment and transportation models.
The transportation model is concerned with selecting the routes between supply and demand points in order to minimize costs of transportation subject to constraints of supply at any supply point and demand at any demand point. Assume a company has 4 manufacturing plants with different capacity levels, and 5 regional distribution centres. 4 x 5 = 20 routes are possible. Given the transportation costs per load of each of 20 routes between the manufacturing (supply) plants and the regional distribution (demand) centres, and supply and demand constraints, how many loads can be transported through different routes so as to minimize transportation costs? The answer to this question is obtained easily through the transportation algorithm.
Similarly, how are we to assign different jobs to different persons/machines, given cost of job completion for each pair of job machine/person? The objective is minimizing total cost. This is best solved through assignment algorithm.
Uses of Transportation and Assignment Models in Decision Making
The broad purposes of Transportation and Assignment models in LPP are just mentioned above. Now we have just enumerated the different situations where we can make use of these models.
Transportation model is used in the following:
- To decide the transportation of new materials from various centres to different manufacturing plants. In the case of multi-plant company this is highly useful.
- To decide the transportation of finished goods from different manufacturing plants to the different distribution centres. For a multi-plant-multi-market company this is useful.
- To decide the transportation of finished goods from different manufacturing plants to the different distribution centres. For a multi-plant-multi-market company this is useful. These two are the uses of transportation model. The objective is minimizing transportation cost.
Assignment model is used in the following:
- To decide the assignment of jobs to persons/machines, the assignment model is used.
- To decide the route a traveling executive has to adopt (dealing with the order inn which he/she has to visit different places).
- To decide the order in which different activities performed on one and the same facility be taken up.
In the case of transportation model, the supply quantity may be less or more than the demand. Similarly the assignment model, the number of jobs may be equal to, less or more than the number of machines/persons available. In all these cases the simplex method of LPP can be adopted, but transportation and assignment models are more effective, less time consuming and easier than the LPP.
Related posts:
- Operations Research approach of problem solving
- Introduction to Transportation Problem
- Procedure for finding an optimum solution for transportation problem
- Initial Basic Feasible Solution of a Transportation Problem
- Introduction to Decision Models
- Transportation Cost Elements
- Modes of Transportation in Logistics
- Factors Affecting Transportation in Logistics
One thought on “ Transportation and Assignment Models in Operations Research ”
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Operations Research
Lesson 8. INTRODUCTION AND MATHEMATICAL FORMULATION
Current course
22 February - 28 February
1 March - 7 March
8 March - 14 March
15 March - 21 March
22 March - 28 March
29 March - 4 April
5 April - 11 April
12 April - 18 April
19 April - 25 April
26 April - 2 May

IMAGES
COMMENTS
After reading this article you will learn about:- 1. Meaning of Assignment Problem 2. Definition of Assignment Problem 3. Mathematical Formulation 4. Hungarian Method 5. Variations. Meaning of Assignment Problem: An assignment problem is a particular case of transportation problem where the objective is to assign a number of resources to an equal number of activities so as to minimise total ...
Definition and formulation. Consider the problem of assigning n jobs to n machines (one job to one machine). Let C ij be the cost of assigning i th job to the j th machine and x ij represents the assignment of i th job to the j th machine.
This is an unbalanced assignment problem. One way to solve it is to invent a fourth dummy task, perhaps called "sitting still doing nothing", with a cost of 0 for the taxi assigned to it. This reduces the problem to a balanced assignment problem, which can then be solved in the usual way and still give the best solution to the problem.
ASSIGNMENT PROBLEM Consider an assignment problem of assigning n jobs to n machines (one job to one machine). Let c ij be the unit cost of assigning ith machine to the jth job and,ith machine to jth job. Let x ij = 1 , if jth job is assigned to ith machine. x ij = 0 , if jth job is not assigned to ith machine. K.BHARATHI,SCSVMV. ASSIGNMENT ...
the objective is to maximise the effectiveness through Assignment, Hungarian Method can be applied to a revised cost matrix obtained from the original matrix. Balanced Assignment Problem: Balanced Assignment Problem is an assignment problem where the number of facilities is equal to the number of jobs. Unbalanced Assignment Problem:
The assignment problem is a particular case of transportation problem for which more efficient (less-time consuming) solution method has been devised by KUHN (1956) and FLOOD (1956). The justification of the steps leading to the solution is based on theorems proved by Hungarian Mathematicians KONEIG (1950) and EGERVARY (1953), hence the method ...
MODULE-3: Assignment Problem and Its Solution by Hungarian Method, and Travelling Salesman Problem 2.1 Assignment Problem The assignment problem is a special type of transportation problem where the objec-
Transportation and assignment models are special purpose algorithms of the linear programming. The simplex method of Linear Programming Problems(LPP) proves to be inefficient is certain situations like determining optimum assignment of jobs to persons, supply of materials from several supply points to several destinations and the like. More effective solution models have been evolved and these ...
8.2 Definition of Assignment Problem. Assignment problem is special class of the transportation problem in which the supply in each row represents the availability of a resource such as man, vehicle, product and demand in each column represents different activities to be performed, such as jobs, routes, milk plants respectively is required.
• The second problem: the transportation simplex method is a general method, it does not exploit the additional special structure in the assignment problem • Solution: Specialized method for assignment problems →Hungarian algorithm [1] • Description • Mathematical model • Solution procedures • Hungarian algorithm