- USC Libraries
- Research Guides

Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Resources
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE: Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Silo!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: Dec 2, 2024 8:43 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

Literature Reviews in the Social Sciences
- Get started
- Search tips
- Select Databases
- Organize your sources
- Evaluate your sources
- Structure your literature review
This guide is designed to help you as you get started on a literature review in the social sciences. It contains search tips, advice on where to look for sources, and information on how to organize and evaluate the sources you find.
Doing a Literature Review
What's a Literature Review?
A literature review is the systematic written analysis of previously published research on a specific topic or subject. A literature review is not merely a summary of another scholar's articles or books. Instead, it provides a contextual analysis of the data, ideas, or theoretical concepts presented in the article, book, or other publication.
Why is a literature review important?
All scholars recognize the importance of the literature review. It provides the foundation for all scholarly research papers, theses, and dissertations. You can't write intelligently about a subject if you are unfamiliar with the existing literature. Therefore, the literature review is meant to showcase what has already been discussed or discovered in your topical area.
What types of resources should be used for a literature review?
A literature review should be written using "credible" academic sources of information. This means using peer-reviewed, scholarly articles, books, and other publications in your subject area. You should avoid using popular magazines, unpublished works, blogs, or other resources deemed non-scholarly.
What other things should I consider while reading the source material?
Take careful notes of important ideas, concepts, or facts you find that are relevant to your overall topic or thesis. Most importantly, keep track of all the sources used. This will keep you from needing to relocate them later. If your paper is large in scope, use electronic bibliographic tools such as Endnote or RefWorks to keep track of all your citations while you write.
What about writing the literature review itself?
When you are prepared to begin writing your literature review, you should not simply summarize the articles and books you find. You should carefully consider the research and the author's interpretation of the subject matter. Then show how their research relates to your specific topic, from your unique point of view.
Annual Reviews / Dissertations & Theses
Many scholarly journals, dissertations, and theses also publish long and extremely detailed literature reviews.
The Annual Reviews series of publications offer articles that analyze the most significant scholarly research published within the preceding year. Written by leading scholars and academics, the articles cover over 40 different subject disciplines in the social and hard sciences.
To search directly for a literature review, go to a library database and search for:
"literature review" AND [your research topic] .
- Annual Reviews This link opens in a new window Annual Reviews offers comprehensive, timely collections of critical reviews written by leading scientists. Annual Reviews volumes are published each year for 29 focused disciplines within the Biomedical, Physical, and Social Sciences.
- Dissertations & Theses Global This link opens in a new window Dissertations and Theses Global contains indexes, dissertations and some theses. Full-text is available for many dissertations and theses, including those from NYU.
Books on Writing Literature Reviews
Sage Research Methods - Videos on Doing Literature Reviews
- Sage Research Methods - Literature Reviews Professor Eric Jensen and Dr. Charles Laurie explain how to write a literature review, and why researchers need to do so. Literature reviews can be stand-alone research or part of a larger project. They communicate the state of academic knowledge on a given topic, specifically detailing what is still unknown.
- How to Conduct an Effective Literature Review Claire White, an Associate professor from California State University Northridge, explains how to conduct an effective literature review using a literature review sketch.
- Next: Get started >>
- Last Updated: Sep 17, 2024 10:25 AM
- URL: https://guides.nyu.edu/litreviews
15 Literature Review Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
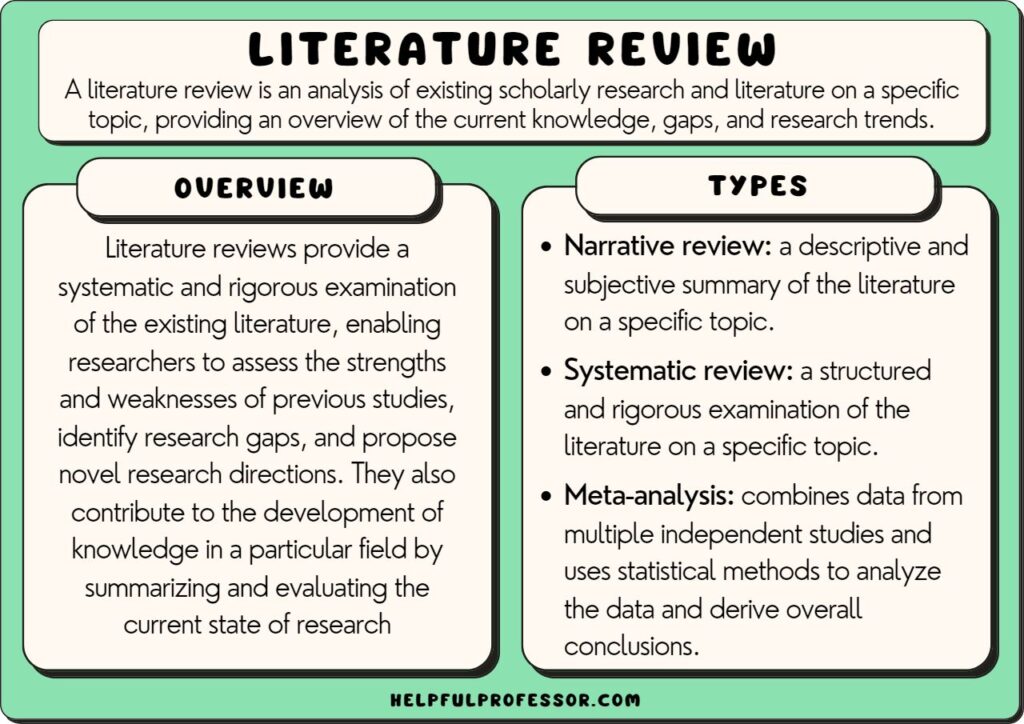
Literature reviews are a necessary step in a research process and often required when writing your research proposal . They involve gathering, analyzing, and evaluating existing knowledge about a topic in order to find gaps in the literature where future studies will be needed.
Ideally, once you have completed your literature review, you will be able to identify how your research project can build upon and extend existing knowledge in your area of study.
Generally, for my undergraduate research students, I recommend a narrative review, where themes can be generated in order for the students to develop sufficient understanding of the topic so they can build upon the themes using unique methods or novel research questions.
If you’re in the process of writing a literature review, I have developed a literature review template for you to use – it’s a huge time-saver and walks you through how to write a literature review step-by-step:
Get your time-saving templates here to write your own literature review.
Literature Review Examples
For the following types of literature review, I present an explanation and overview of the type, followed by links to some real-life literature reviews on the topics.
1. Narrative Review Examples
Also known as a traditional literature review, the narrative review provides a broad overview of the studies done on a particular topic.
It often includes both qualitative and quantitative studies and may cover a wide range of years.
The narrative review’s purpose is to identify commonalities, gaps, and contradictions in the literature .
I recommend to my students that they should gather their studies together, take notes on each study, then try to group them by themes that form the basis for the review (see my step-by-step instructions at the end of the article).
Example Study
Title: Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations
Citation: Vermeir, P., Vandijck, D., Degroote, S., Peleman, R., Verhaeghe, R., Mortier, E., … & Vogelaers, D. (2015). Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. International journal of clinical practice , 69 (11), 1257-1267.
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/ijcp.12686
Overview: This narrative review analyzed themes emerging from 69 articles about communication in healthcare contexts. Five key themes were found in the literature: poor communication can lead to various negative outcomes, discontinuity of care, compromise of patient safety, patient dissatisfaction, and inefficient use of resources. After presenting the key themes, the authors recommend that practitioners need to approach healthcare communication in a more structured way, such as by ensuring there is a clear understanding of who is in charge of ensuring effective communication in clinical settings.
Other Examples
- Burnout in United States Healthcare Professionals: A Narrative Review (Reith, 2018) – read here
- Examining the Presence, Consequences, and Reduction of Implicit Bias in Health Care: A Narrative Review (Zestcott, Blair & Stone, 2016) – read here
- A Narrative Review of School-Based Physical Activity for Enhancing Cognition and Learning (Mavilidi et al., 2018) – read here
- A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents (Dyrbye & Shanafelt, 2015) – read here
2. Systematic Review Examples
This type of literature review is more structured and rigorous than a narrative review. It involves a detailed and comprehensive plan and search strategy derived from a set of specified research questions.
The key way you’d know a systematic review compared to a narrative review is in the methodology: the systematic review will likely have a very clear criteria for how the studies were collected, and clear explanations of exclusion/inclusion criteria.
The goal is to gather the maximum amount of valid literature on the topic, filter out invalid or low-quality reviews, and minimize bias. Ideally, this will provide more reliable findings, leading to higher-quality conclusions and recommendations for further research.
You may note from the examples below that the ‘method’ sections in systematic reviews tend to be much more explicit, often noting rigid inclusion/exclusion criteria and exact keywords used in searches.
Title: The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review
Citation: Roman, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M., & Siegrist, M. (2017). The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends in food science & technology , 67 , 44-57.
Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092422441730122X
Overview: This systematic review included 72 studies of food naturalness to explore trends in the literature about its importance for consumers. Keywords used in the data search included: food, naturalness, natural content, and natural ingredients. Studies were included if they examined consumers’ preference for food naturalness and contained empirical data. The authors found that the literature lacks clarity about how naturalness is defined and measured, but also found that food consumption is significantly influenced by perceived naturalness of goods.
- A systematic review of research on online teaching and learning from 2009 to 2018 (Martin, Sun & Westine, 2020) – read here
- Where Is Current Research on Blockchain Technology? (Yli-Huumo et al., 2016) – read here
- Universities—industry collaboration: A systematic review (Ankrah & Al-Tabbaa, 2015) – read here
- Internet of Things Applications: A Systematic Review (Asghari, Rahmani & Javadi, 2019) – read here

3. Meta-analysis
This is a type of systematic review that uses statistical methods to combine and summarize the results of several studies.
Due to its robust methodology, a meta-analysis is often considered the ‘gold standard’ of secondary research , as it provides a more precise estimate of a treatment effect than any individual study contributing to the pooled analysis.
Furthermore, by aggregating data from a range of studies, a meta-analysis can identify patterns, disagreements, or other interesting relationships that may have been hidden in individual studies.
This helps to enhance the generalizability of findings, making the conclusions drawn from a meta-analysis particularly powerful and informative for policy and practice.
Title: Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s Disease Risk: A Meta-Meta-Analysis
Citation: Sáiz-Vazquez, O., Puente-Martínez, A., Ubillos-Landa, S., Pacheco-Bonrostro, J., & Santabárbara, J. (2020). Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease risk: a meta-meta-analysis. Brain sciences, 10(6), 386.
Source: https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060386
O verview: This study examines the relationship between cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Researchers conducted a systematic search of meta-analyses and reviewed several databases, collecting 100 primary studies and five meta-analyses to analyze the connection between cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease. They find that the literature compellingly demonstrates that low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels significantly influence the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
- The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback research (Wisniewski, Zierer & Hattie, 2020) – read here
- How Much Does Education Improve Intelligence? A Meta-Analysis (Ritchie & Tucker-Drob, 2018) – read here
- A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling (Geiger et al., 2019) – read here
- Stress management interventions for police officers and recruits (Patterson, Chung & Swan, 2014) – read here
Other Types of Reviews
- Scoping Review: This type of review is used to map the key concepts underpinning a research area and the main sources and types of evidence available. It can be undertaken as stand-alone projects in their own right, or as a precursor to a systematic review.
- Rapid Review: This type of review accelerates the systematic review process in order to produce information in a timely manner. This is achieved by simplifying or omitting stages of the systematic review process.
- Integrative Review: This review method is more inclusive than others, allowing for the simultaneous inclusion of experimental and non-experimental research. The goal is to more comprehensively understand a particular phenomenon.
- Critical Review: This is similar to a narrative review but requires a robust understanding of both the subject and the existing literature. In a critical review, the reviewer not only summarizes the existing literature, but also evaluates its strengths and weaknesses. This is common in the social sciences and humanities .
- State-of-the-Art Review: This considers the current level of advancement in a field or topic and makes recommendations for future research directions. This type of review is common in technological and scientific fields but can be applied to any discipline.
How to Write a Narrative Review (Tips for Undergrad Students)
Most undergraduate students conducting a capstone research project will be writing narrative reviews. Below is a five-step process for conducting a simple review of the literature for your project.
- Search for Relevant Literature: Use scholarly databases related to your field of study, provided by your university library, along with appropriate search terms to identify key scholarly articles that have been published on your topic.
- Evaluate and Select Sources: Filter the source list by selecting studies that are directly relevant and of sufficient quality, considering factors like credibility , objectivity, accuracy, and validity.
- Analyze and Synthesize: Review each source and summarize the main arguments in one paragraph (or more, for postgrad). Keep these summaries in a table.
- Identify Themes: With all studies summarized, group studies that share common themes, such as studies that have similar findings or methodologies.
- Write the Review: Write your review based upon the themes or subtopics you have identified. Give a thorough overview of each theme, integrating source data, and conclude with a summary of the current state of knowledge then suggestions for future research based upon your evaluation of what is lacking in the literature.
Literature reviews don’t have to be as scary as they seem. Yes, they are difficult and require a strong degree of comprehension of academic studies. But it can be feasibly done through following a structured approach to data collection and analysis. With my undergraduate research students (who tend to conduct small-scale qualitative studies ), I encourage them to conduct a narrative literature review whereby they can identify key themes in the literature. Within each theme, students can critique key studies and their strengths and limitations , in order to get a lay of the land and come to a point where they can identify ways to contribute new insights to the existing academic conversation on their topic.
Ankrah, S., & Omar, A. T. (2015). Universities–industry collaboration: A systematic review. Scandinavian Journal of Management, 31(3), 387-408.
Asghari, P., Rahmani, A. M., & Javadi, H. H. S. (2019). Internet of Things applications: A systematic review. Computer Networks , 148 , 241-261.
Dyrbye, L., & Shanafelt, T. (2016). A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents. Medical education , 50 (1), 132-149.
Geiger, J. L., Steg, L., Van Der Werff, E., & Ünal, A. B. (2019). A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling. Journal of environmental psychology , 64 , 78-97.
Martin, F., Sun, T., & Westine, C. D. (2020). A systematic review of research on online teaching and learning from 2009 to 2018. Computers & education , 159 , 104009.
Mavilidi, M. F., Ruiter, M., Schmidt, M., Okely, A. D., Loyens, S., Chandler, P., & Paas, F. (2018). A narrative review of school-based physical activity for enhancing cognition and learning: The importance of relevancy and integration. Frontiers in psychology , 2079.
Patterson, G. T., Chung, I. W., & Swan, P. W. (2014). Stress management interventions for police officers and recruits: A meta-analysis. Journal of experimental criminology , 10 , 487-513.
Reith, T. P. (2018). Burnout in United States healthcare professionals: a narrative review. Cureus , 10 (12).
Ritchie, S. J., & Tucker-Drob, E. M. (2018). How much does education improve intelligence? A meta-analysis. Psychological science , 29 (8), 1358-1369.
Roman, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M., & Siegrist, M. (2017). The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends in food science & technology , 67 , 44-57.
Sáiz-Vazquez, O., Puente-Martínez, A., Ubillos-Landa, S., Pacheco-Bonrostro, J., & Santabárbara, J. (2020). Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease risk: a meta-meta-analysis. Brain sciences, 10(6), 386.
Vermeir, P., Vandijck, D., Degroote, S., Peleman, R., Verhaeghe, R., Mortier, E., … & Vogelaers, D. (2015). Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. International journal of clinical practice , 69 (11), 1257-1267.
Wisniewski, B., Zierer, K., & Hattie, J. (2020). The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback research. Frontiers in Psychology , 10 , 3087.
Yli-Huumo, J., Ko, D., Choi, S., Park, S., & Smolander, K. (2016). Where is current research on blockchain technology?—a systematic review. PloS one , 11 (10), e0163477.
Zestcott, C. A., Blair, I. V., & Stone, J. (2016). Examining the presence, consequences, and reduction of implicit bias in health care: a narrative review. Group Processes & Intergroup Relations , 19 (4), 528-542

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Literature Reviews
- General overview of Literature Reviews
- What should a Literature Review include?
- Examples of Literature Reviews
- Research - Getting Started
Online Resources
- CWU Learning Commons: Writing Resources
- Purdue OWL: Writing a Literature Review
Literature Reviews Examples
Social Sciences examples
- Psychology study In this example, the literature review can be found on pages 1086-1089, stopping at the section labeled "Aims and Hypotheses".
- Law and Justice study In this example, the literature review can be found on pages 431-449, stopping at the section labeled "Identifying and Evaluating the Impacts of the Prisoners' Rights Movement". This article uses a historical literature review approach.
- Anthropology study The literature review in this article runs from page 218 at the heading "Between Critique and Enchantment" and ends on page 221 before the heading "The Imagination as a Dimension of Reality".
Hard Science examples
- Physics article The literature review in this paper can be found in the Introduction section, ending at the section titled "Experimental procedure".
- Health Science article The literature review in this article is located at the beginning, before the Methods section.
Arts and Humanities examples
- Composition paper In this example, the literature review has its own dedicated section titled "Literature Review" on pages 2-3.
- Political geography paper The literature review in this paper is located in the introduction section.
Standalone Literature Review examples
- Project-based learning: A review of the literature
- Mental health and gender dysphoria: A review of the literature
- Academic engagement and commercialisation: A review of the literature on university–industry relations
- << Previous: What should a Literature Review include?
- Next: Research - Getting Started >>
- Last Updated: Sep 18, 2024 9:14 AM
- URL: https://libguides.lib.cwu.edu/LiteratureReviews

- EMU Library
- Research Guides
Social Research Methods
- Literature Reviews
- Welcome. Start Here.
- Social Problem Topics
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources
- Reference Works for Sociology
- Search for News Articles
- Find Articles by tracking citations
- Locating Full Text
- Citing Sources in Sociology
What is a Literature Review?
Literature reviews in the social sciences take a slightly different approach than in the humanities (literature, philosophy, history, etc.) or the sciences (biology, physics, etc.). This guide focuses ONLY on the social sciences (anthropology, criminology, political science, sociology, etc.).
'literature' - commonly people use this word for creative written works like novels; but in academics the word 'literature' is also used to mean any collection or body of written work, including research articles and books.
'review' - commonly people use the word review for evaluations, like a movie review; but in academics the word is used broadly to mean a paper or section of a paper that summarizes and synthesizes literature to give an overview of theory and research on a topic.
Putting it together:
In the social sciences, a literature review is a paper or section of a paper that summarizes and synthesizes. To summarize is to describe the main arguments and conclusions. To synthesize is to compare, contrast, highlight relevant points, relate to ongoing trends or problems, and generally to draw out an argument or position based on the literature being reviewed.
A literature review is not a book review! Book reviews are articles that review a single book title. A literature sums up and analyzes a set of books or articles on a theme.
Literature reviews can be a section of a longer paper or book, or they can stand alone. Social scientists generally include a short review of relevant literature in their research papers to demonstrate how their own research fits into ongoing debates. Longer stand-alone review papers are published to give a picture of the current state of research. The Annual Reviews publication series are classic examples of stand-alone reviews.
- Annual Reviews This link opens in a new window Critical reviews of primary research literature in the sciences and social sciences. EMU access does not include the most recent 5 years.
- example of lit review articles
Guides on writing literature reviews:
- Literature Reviews - UNC Writing Center
- The Literature Review - USC Libraries
- Literature Reviews: An Overview - NCSU libraries
More kinds of review articles
Review articles are generally a kind of secondary source. That is, they are not presenting empirical findings from a single research project. They are, however, original , in the sense that the author is using skill, knowledge and creativity to compile and write something new about the material (books, articles) under review.
There are several kinds of review articles. Book Reviews are a special case, because sometimes they are written by experts but sometimes they are written by journalists or just fans of the book. Typically, a book review describes the main contents of the book, how it relates to existing ideas or works, and gives a judgment as to its value to various readers. Some book reviews are just a paragraph, but the reviews in scholarly journals can be several pages. In Esearch, you can limit search results to book reviews only, or screen book reviews out of the results, by clicking into the left-hand column under Content Type .
Stand-alone Review Articles or Literature Reviews are common in the social sciences. The authors of these articles are experts, usually scholars. The review articles will address a current topic, lay out the main theories or ideas, recent developments in research, and suggest where further research is needed. Typical review articles are published in series such as:
In the health fields, Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses are articles that go a step further. Not only do they summarize and research on a topic, but they carefully analyze the research and may attempt to draw conclusions based on the compiled studies. For more on these kinds of reviews, see:
- What is a systematic review? (Cochrane)
- Systematic Reviews (EPPI centre)
Finding related articles
Whether for a literature review or a research paper, the analysis is much easier if it is based on a cluster of related articles and not a random assortment. Finding articles that are related rarely happens just by doing a single search, but it is not hard. Here are some approaches:
- Start with a textbook, reference book, dissertation or review article and collect the citations of the authors who are mentioned or cited as part of the debate. Make sure to collect works from all points of view.
- Use citation tracking to see how scholars mention each others' work, whether as examples, evidence or in order to debate. See below for more on citation tracking.
- << Previous: Social Problem Topics
- Next: Selecting sources >>
- Last Updated: Nov 1, 2024 3:43 PM
- URL: https://guides.emich.edu/c.php?g=188066

Writing a Systematised Review in Social Sciences
- Introduction
- Choosing your research question
- Searching for Literature
- Searching for Literature (part 2)
- Extracting Information
- Writing your review: Analysis and Synthesis:
- Reference Management
- Finding Material Beyond the Library
- Still Need Help?
Contact your Academic Subject Librarian for help and advice on systematic reviews. They can advise on:
- Which databases and other resources to search
- The use of keywords and subject headings in your search strategy
- How to translate your search across different databases
- Glossary Key terminology explained.
- Sponsorship in Grassroots Football by Matthew Russell Hindmarsh, Liverpool John Moores University (United Kingdom), 2020. An example of a thesis with an excellent systematic literature review section.
- The Development, Deployment, and Redeployment of Business Solutions – A Systematic Review by Katharina Windler, Cranfield University (United Kingdom), 2012. An example of a systemic literature review thesis.
T his guide provides an overview of the process of writing a systematised literature review within a social science related degree or discipline . There are many ways of approaching your systematised review, and it is important to understand that a literature review is not a “single definable product” (Booth et al., 2021, 1) — it may perform a variety of different purposes depending on the nature of your project and research goals.
Who this guide is for:
This guide is for students undertaking a systematised literature review as a form of secondary research either as a dissertation or as a standalone piece of work.
Who this guide is not for:
If you are collecting primary data for your dissertation, you may need to include one chapter reviewing literature, typically called the “literature review”. This chapter is at the beginning of a dissertation, sitting between your aims and objectives and your methodology. This review is normally a narrative review with literature selected based on judgement (rather than a systematised review).
Booth et al., (2021, 2) define a systematised literature review as “a form of research synthesis that seeks to systematically search for, appraise and synthesize research evidence, using strategies to limit bias often adhering to guidelines on the conduct of a review”
Unlike a narrative literature review, a systematic review attempts to incorporate “transparent and well-defined steps”, answering a specific question.
What makes a literature review systematised?
A systematised literature review differs from a traditional narrative review by including a transparent methodology that explains to the reader exactly what you did to get your search results and how you refined those results to produce your final sample. A key term here is reproducibility. A good systematised gives the reader all the information necessary to reproduce your results using your search strategy, inclusion criteria and analysis.
A systematised review should include most of the below:
- Step by step methodology – including search terms, database selection, and inclusion /exclusion criteria.
- Reports the number of hits retrieved from database searching
- Reports results using a specified framework (such as PRISMA)
- Coordinated analysis (such as narrative synthesis)
- Systematic approaches to presentation (tables etc.)
The rest of this guide provides an overview of the review process . Navigate the menu on the left hand side to find out more
1.Choosing your research question
2.Finding Literature
3.Screening and reporting your results
4.Extracting your data
5.Analysis and synthesis
The below table outlines some of the differences between a systematised review and a (traditional) narrative literature review.

Advantages of doing a systematised review for your dissertation:
- Removes difficulties involved in collecting data
- Removes time consuming ethics forms
- Gain a rigorous understanding of a topic
- Large and rich pool of data
- Facilitates connections between different areas of literature.
Despite this, a systematised literature review is not an easy option! It is a time-consuming process that is often challenging (yet rewarding).
The words “systematic literature review” have been used in a variety of different ways, often interchangeably to mean subtly different things. Strictly speaking, a systematic review is an exhaustive search for evidence. This kind of review, prominent within healthcare, is conducted by large teams of researchers and can take many months (or even years) to complete. To take a look at some examples, you can visit the Cochrane library here
For an undergraduate or postgraduate dissertation, however, you may wish to carry out a review with systematic features. Grant et al. (2009), refer to this kind of review as a “ systematised review ” which attempts “to include elements of systematic review process while stopping short of systematic review. Typically conducted as postgraduate student assignment.”
A systematised review (the terminology favoured in this guide) acknowledges that your project will have time constraints and that you will be the sole researcher (thus falling short of a systematic review in the strict sense). Despite this, your lecturer or fellow students may still refer to your review as systematic, as terminology is used flexibly throughout the literature. You may also hear your review referred to as a structured review .
The pages on the left-hand side talk you through each stage of your review, from scoping searches and planning your methodology, right through to the write up.
Booth, A, Papaioannou, D., Sutton, A. Clowns, M and Booth, A. (2021) Systematic approaches to a successful literature review , 3rd edition. London: SAGE
- Next: Choosing your research question >>
- Last Updated: Sep 2, 2024 10:28 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.lincoln.ac.uk/c.php?g=721643
- Admin login
- ICT Support Desk
- Policy Statement
- www.lincoln.ac.uk
- Accessibility
- Privacy & Disclaimer

- Meriam Library
Literature Reviews
- What's a literature review?
Literature Review Examples
Articles (free for csuc users), additional how-to guides and help.
- Resources for Educators
- Evaluating Info
- Empirical Research This link opens in a new window
- Annotated Bibliography This link opens in a new window
Books On Literature Reviews in the Meriam Library
- Conducting Research Literature Reviews : From the Internet to Paper Call Number: Main Collection - Q180.55.M4 F56 2014
- Literature Reviews Made Easy: A Quick Guide to Success Call Number: Main Collection - PN98.B7 D37 2010
- Preparing Literature Reviews: Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches Call Number: Main Collection - Q180.55.E9 P36 2008
- Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review Call Number: Main Collection - LB1047.3 .B66 2012
- The Literature Review: Six Steps to Success Call Number: Main Collection - LB1047.3 .M33 2009
- Writing Literature Reviews: A Guide for Students of the Social and Behavioral Sciences Call Number: Reference H61.8 .G34 2013
Books on Research Methodology in the Meriam Library
- Doing Case Study Research : A Practical Guide for Beginning Researchers Call Number: Main Collection - LB1028 .H313 2006
- Evaluating Research Articles from Start to Finish Call Number: Main Collection - Q180.55.E9 G57 2011
- How to do a Research Report: A Guide for Undergraduate Students Call Number: Main Collection - LB2369 .R575 2007
- How to Write a Master's Thesis Call Number: Main Collection - LB2369 .B75 2014
- Understanding Research Methods: An Overview of the Essentials Call Number: Main Collection - Q180.55.M4 P38 2018
- Master's Theses Database of master's theses written by CSU, Chico students, from 2009 on. Many of these will contain published examples of literature reviews.
- Proquest Dissertations and Theses: The Humanities and Social Sciences Collection Containes over 2 million dissertations and theses with abstracts, 24 page free previews, and full-text PDF, if available, for dissertations and theses dating back to 1637.
- Sample APA Paper (lit. review begins page 3) Purdue University Online Writing Lab (OWL)
- A Commentary on Literature Reviews Rhodes, E.A. (2011). A commentary on literature reviews. Volta Reviews, 111(3), 353-368.
- A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review Randolph, J.J. (2009). A guide to writing the dissertation literature review. Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation, 14(13), 1-13.
- The Value and Purpose of the Traditional Qualitative Literature Review Rozas, L.W. & Klein, W.C. (2010). The value and purpose of the traditional qualitative literature review. Journal of Evidence-Based Social Work, 7(5), 382-399.
- Undertaking a Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Approach Cronin, P., Ryan, F., & Coughlan, M. (2008). Undertaking a literature review: a step-by-step approach. British Journal of Nursing, 17(1), 38-43.
- Undertaking a Structured Literature Review or Structuring a Literature Review: Tales from the Field Armitage, A. & Keeble-Allen, D. (2008). Undertaking a structured literature review or structuring a literature review: tales from the field. Electronic Journal of Business Research Methods, 6(2), 103-114.
- CSU, Chico Office of Graduate Studies - Thesis Assistance Instructions, policies, and guidelines for graduate studies theses/projects.
- CSU, Chico Writing Center Make a one-on-one appointment with a writing tutor to help with your writing assignments.
- Learn How to Write a Review of the Literature University of Wisconsin-Madison
- Literature Review: An Overview for Graduate Students Video overview by North Carolina State University Libraries
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide University of Connecticut University Libraries
- Social Work Literature Review Guidelines Purdue University Online Writing Lab (OWL)
- << Previous: What's a literature review?
- Next: Resources for Educators >>
- Last Updated: Sep 2, 2020 12:43 PM
- URL: https://libguides.csuchico.edu/LiteratureReviews
Meriam Library | CSU, Chico

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
This guide is designed to help you as you get started on a literature review in the social sciences. It contains search tips, advice on where to look for sources, and information on how to organize and evaluate the sources you find.
Get your time-saving templates here to write your own literature review. For the following types of literature review, I present an explanation and overview of the type, followed by links to some real-life literature reviews on the topics. 1. Narrative Review Examples.
The review of literature identifies that there is lack of research examining factors associated with treatment lies. The findings presented here suggest that runaway youth and their families are amenable to treatment efforts and that treatment attendance may be enhanced through providing
Designed to help support your academic journey and enhance your research skills, this guide can help you better understand literature reviews before you plan, conduct, and write one of your own. A few samples of literature reviews for you to reference!
In the social sciences, a literature review is a paper or section of a paper that summarizes and synthesizes. To summarize is to describe the main arguments and conclusions. To synthesize is to compare, contrast, highlight relevant points, relate to ongoing trends or problems, and generally to draw out an argument or position based on the ...
purpose of the literature review is the same: to briefly summarize and evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each source, while pointing out overall trends, contradictions, or gaps between sources.
A systematised literature review differs from a traditional narrative review by including a transparent methodology that explains to the reader exactly what you did to get your search results and how you refined those results to produce your final sample.
Many of these will contain published examples of literature reviews. Proquest Dissertations and Theses: The Humanities and Social Sciences Collection Containes over 2 million dissertations and theses with abstracts, 24 page free previews, and full-text PDF, if available, for dissertations and theses dating back to 1637.
Today we’ll focus on the INTEGRATIVE review, the most common type in the social sciences. Other types are: Argumentative; Historical; Methodological; Theoretical. NOTE: Be sure you are clear on expectations such as how many sources to use, what formats, the organization of the review (headings, etc.) and length. Typology from