SWOT Analysis: Assignment Overview
Discussion with students about the Week 2 SWOT assignment and other course questions (1 Hour)

Learning Objectives
At the end of this lesson you will learn:
- What electronic commerce is and how it has evolved in three waves of development
- Why companies concentrate on revenue models and the analysis of business processes instead of business models when they undertake electronic commerce initiatives
- How to identify opportunities for and barriers to electronic commerce initiatives
- How economic forces have led to the development and continued growth of electronic commerce
- How businesses use value chains and SWOT analysis to identify electronic commerce opportunities
- How the international nature of electronic commerce affects its growth and development
Electronic Commerce 12e: Chapter 1 Chapter Links
Chapter 1 Quiz on Canvas
Assignment/Discussion
SWOT Analysis Choose an e-commerce business that you might like to use for your course project this semester. This business can be real or fictitious, for-profit or nonprofit. To help you decide if your proposed business can be viable, you need to do a SWOT Analysis (SWOT stands for S trengths, W eaknesses, O pportunities, and T hreats).
See below for some great SWOT examples.
For this assignment you will be use an E-commerce Plan template. Download it here.
- After dowloading, change the file name by replacing "lastname" with your last name.
- You will be turning this completed E-Commerce Plan in at the end of the semester.
- Feel free to customize this plan in any way you like.
- For your final project you will be creating a Web site for an e-commerce business or non-profit (real or fictitious). Use that business or non-profit for this assignment. You are not stuck with this choice. You can change your mind later.
- Copy and paste the questions below into the E-commerce plan , and answer them to the best of your ability (1-2 sentences per question)
- After answering the questions, write a paragraph summarizing your analysis and explain why your analysis leads you to believe your e-commerce business would be viable -- or not
- Check your spelling and grammar
- Submit your full report in the E-commerce Plan Word Document the Week 2 Discussion on Canvas
- Paste your summary paragraph into a thread in Week 2 discussion.
- Provide thoughtful comments on two other student's summaries (3 sentence minimum).
Answer these questions in your SWOT Analysis
Type of Business: What kind of business or non-profit organization is this?
Strengths: 1. What does your business do well? 2. Is your business strong in its market? (do research and support with evidence) 3. Does your business have a strong sense of purpose and the culture to support that purpose?
Weaknesses: 1. What does your business do poorly? 2. What problems could be avoided? 3. Are there any potential financial difficulties?
Opportunities: 1. Are industry tends moving upward? (do research, support with evidence, provide sources) 2. Do new markets exist for your products or services? (do research, support with evidence, provide sources) 3. Are there any new technologies you can exploit? (think about web-based or computer-based technologies)
Threats: 1. Who are your competitors? (be specific for your marketplace) 2. What are competitors doing well? 3. What obstacles do you face? 4. Are there troubling changes in your business environment such as technologies, laws, and regulations? (do research, support with evidence, provide sources)
Example SWOT Assignments:
- Becky Plaza
Additional Reading:
- How to Choose a Business to Start
- What Is SWOT Analysis?
- Other SWOT examples
- SWOT Analysis Marketing Tools
- SWOT Template in MS Word
Rubric for SWOT Assignment = 30 pts.
Rubric for swot assignment.
23 Best Personal SWOT Analysis Examples for Students

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
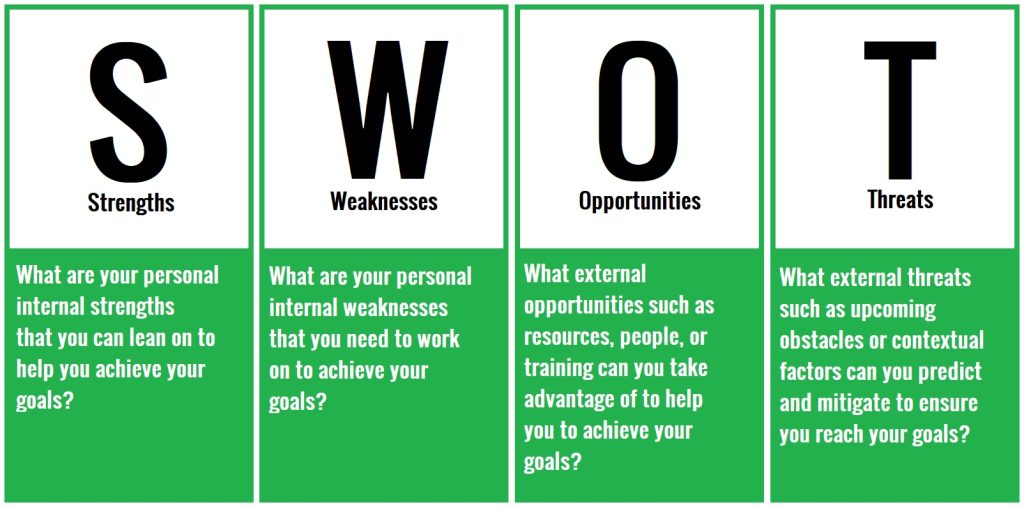
SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
It’s common for students to have a complete mind blank when asked to write a SWOT analysis. It can be hard to step back and objectively figure out what to place in each box in the analysis matrix.
However, by looking at some examples from other students, you can start to conceptualize what’s expected of you and even find yourself agreeing with some of their points.
Take a look at these personal SWOT analysis examples and see if you can cherrypick some key points that might resonate with you.
Pick and choose the points that resonate most with you so you can create your own unique SWOT chart.
Personal SWOT Analysis Examples for Students
1. swot analysis template.
Goal: Write down what your goal is.
2. Personal SWOT Analysis Example
Goal: To gain confidence at university.
Read Also: 42 US Colleges With Bear Mascots
3. Academic Writing Example
Goal: To get an A in an essay this semester.
4. New Student Example
Goal: To Get into a Routine and Comfortable on Campus.
5. College Student Example
Goal: To raise my GPA by 0.5 this year.
6. International Student Example
Goal: To gain confidence in a new society and develop cultural competencies.
7. Education Student Example
Goal: To develop skills and knowledge in teaching.
8. Sociology Student Example
Goal: To figure out how to use my sociology degree to get a career job.
9. Bachelor of Arts Student Example
Goal: To figure out what I want my major to be
10. High School Student Example
Goal: To develop the skills that I’ll need at college next year
11. Math and Science Example
Goal: To get a job in the science field following graduation.
12. Digital Marketing Example
Goal: To improve my skills in digital marketing while still at university.
13. Masters Degree Example
Goal: To complete my masters degree within 3 years
14. Business Student Example
Goal: To gain the skills I need to start my own business in the future.
15. Nursing Student Example
Goal: To get a job in nursing after I graduate with a good GPA.
16. Teacher Example
Goal: To gradually improve my pedagogical competencies in the next 12 months.
17. PhD Student Example
Goal: To make it through the first year of doing a PhD.
18. Internship or Practicum Example
Goal: To grow my confidence in a workplace situation and see if I like this career path.
19. Exchange Student Example
Goal: To broaden my horizons for an exchange semester.
20. Thesis or Dissertation Example
Goal: To get a high grade for my dissertation.
21. Teamwork and Groupwork Example
Goal: To complete our team project and get the best grade in the class.
22. Psychology Student Example
Goal: To get a career in clinical psychology.
23. Graduating Student Example
Goal: To smoothly transition into an entry-level position in my career choice
What does SWOT Analysis Stand For?
SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. These are the four key categories that you need to look at to develop an action plan for improving your skills as a student.
Under each column think about what you will write:
- Strengths: What are you aware that you’re good at right now? Make sure it’s relevant to your goal. For example, if your goal is to gain confidence at university, make it relevant to that and not something completely different (being really good at hotdog eating contexts is irrelevant to becoming a more confident student!)
- Weaknesses: What do you struggle with right now? Again, keep it relevant to your goal. If your goal is to get an A in your next paper, reflect on your weaknesses in essay writing.
- Opportunities: What can you think of that might be a valuable resource, support network, or another type of opportunity that can help you to meet your state goal?
- Threats: What can you think of that might make it hard to meet your goals? It’s good to know these so you can prepare ahead and minimize the chance that they will become major obstacles.
What is the Purpose of a SWOT Analysis?
The point of the SWOT analysis is to get you thinking about how you can prepare for improvement. If you know your weaknesses, opportunities, and potential challenges, you can work on the weaknesses, embrace the opportunities, and avert the threats. This will help you get closer to your goals.
Another alternative type of reflective analysis is the Johari Window , which is best completed in teams where your team members can provide input for you.
How to Do a SWOT Analysis
What to write for strengths.
When writing about strengths on a SWOT Analysis, you want to write about things that you’re personally good at.
These strengths are ‘internal’, meaning they’re features about you that make you good at things. They’re things under your direct control.
One problem students come across is that they don’t focus on strengths that are relevant to your goals . So, focus on strengths that can help you achieve your goals.
Key considerations when writing about strengths include:
- What do you do well (in relation to your goal)?
- What study skills do you currently have?
- What academic writing and research skills do you currently have?
- What workforce skills do you currently have?
- What soft skills do you currently have?
- What hard skills do you currently have?
We have a list of 110 strength examples for a SWOT analysis that you can browse to find ones that work for you.
What to Write for Weaknesses
When writing about weaknesses on a SWOT Analysis, you want to write about things that you’re personally not very good at.
These weaknesses are ‘internal’, meaning they’re features about you that you know are not your strongest trait. Like strengths, these weaknesses need to be things under your direct control.
Remember ot keep them relevant to your goals . So, focus on weaknesses that might prevent you from achieving your goals.
Key considerations when writing about weaknesses include:
- What do you think you’re not very good at (in relation to your goal)?
- What do you struggle with when studying?
- What are your weaknesses in regards to academic writing and researching?
- What workforce readiness skills do you lack?
- What soft skills do you lack?
- What hard skills do you lack?
We have a list of 79 weaknesses examples for a SWOT analysis that you can browse to find ones that work for you.
What to Write for Opportunities
When writing about opportunities on a SWOT Analysis, you want to write about things that you can rely on to help you reach your goals.
These opportunities are ‘external’, meaning they’re not personal features about you, but resources, people, or events that you turn to for help.
Again, remember to talk about opportunities that are relevant to your goals .
Key considerations when writing about opportunities include:
- Are there upcoming seminars, classes, or lectures that can help you improve?
- Do you have access to resources to help you improve?
- Do you have access to people or friends who can help you out?
We have a list of 61 opportunity examples for a SWOT analysis that you can browse to find ones that work for you.
What to Write for Threats
When writing about threats on a SWOT Analysis, you want to write about things that are outside of your direct control that might interfere with you achieving your goals.
These external threats are examined so you can predict them and think about ways to either avoid or mitigate their effects.
Remember to talk about threats that are relevant to your goals .
Key considerations when writing about threats include:
- What contextual factors might get in the way of your goals?
- What obstacles can you predict that might interfere with your plans?
- What resources do you lack that would otherwise be helpful?
A SWOT analysis is designed to get you thinking about how to use your personal strengths and opportunities to your advantage, while also improving your weaknesses and mitigating threats that you can predict.
While these examples can help get you mind turning, remember that your SWOT Analysis needs to be unique to you. So, use these personal SWOT analysis examples by students to get your mind turning, but write your own unique SWOT matrix that’s an honest reflection of your own situation.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
2 thoughts on “23 Best Personal SWOT Analysis Examples for Students”
Dr Chris… Excellent article and it was really helpful for me to set SWOT analysis for my students. The content of the article is highly useful and practical too to adopt for educational institutions. Thank You Dr Shyam prasad TS Asst Prof, RV Institute of legal studies , Bengaluru, India [email protected]
Thank you so much for the detailed SWOT for my learners.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- High School
- You don't have any recent items yet.
- You don't have any courses yet.
- You don't have any books yet.
- You don't have any Studylists yet.
- Information
SWOT Analysis - homework assignments
Microeconomics (eco201), southern new hampshire university.
Recommended for you
Students also viewed.
- ECO 201 Project Template (2)
- Module 3 discussion
- ECO 201 Project - Golightly
- Q19 - This is a question that you may run into while taking the microeconomics course
- Q4 - This is a question that you may run into while taking the microeconomics course
- Q8 - This is a question that you may run into while taking the microeconomics course

Related documents
- Q3 - This is a question that you may run into while taking the microeconomics course
- Q20 - This is a question that you may run into while taking the microeconomics course
- Q10 - This is a question that you may run into while taking the microeconomics course
- Q7 - This is a question that you may run into while taking the microeconomics course
- Q6 - This is a question that you may run into while taking the microeconomics course
- Q12 - This is a question that you may run into while taking the microeconomics course
Preview text
The SWOT analysis that I completed was the quiz. The hardest part for me was differentiating the threats from weaknesses. The scenarios to me that were presented to me could have gone in either direction. The two issues have very similar issues. I learned that a SWOT analysis is a useful tool for evaluating the internal and external factors that cand define the success or downfall of a company. It helps to identify the strengths and weaknesses of the business as well as the opportunities for growth. It also aids in the ability to overcome various weaknesses and threats that the company may face. I believe that marketers tend to overlook would be the threats. While they may identify a mass amount of them, sometimes I believe that because they fixate on specific threats, they can then overlook ones that they may not recognize as a threat. Overlooking this specific area can be detrimental to the growth of the company as well as keeping them relevant when they are pitted against the competition. When their guard is let down it gives the competition the upper hand on them and can lead to loss of revenue and could potentially leave the company susceptible to more weaknesses and threats.
- Multiple Choice
Course : Microeconomics (ECO201)
University : southern new hampshire university.

- More from: Microeconomics ECO201 Southern New Hampshire University 999+ Documents Go to course

SWOT Analysis
All business students are assigned to conduct SWOT analysis, usually at the earlier stages of their studies. This page focuses on the application of SWOT analysis in a business context as a part of academic assignments . This is a comprehensive SWOT resource and it contains an explanation of SWOT theory, an illustration of how to do a SWOT analysis and links to examples of SWOT analysis of major multinational brands. Moreover, SWOT analysis template further below can be used to generate SWOT tables of top multinational companies along a range of industries.
SWOT Analysis: Theory
SWOT is a strategic analytical tool for assessing strengths and weaknesses of a business, analyzing opportunities available to the business, as well as, threats faced by the business. SWOT analysis can be used at organizational and personal levels.
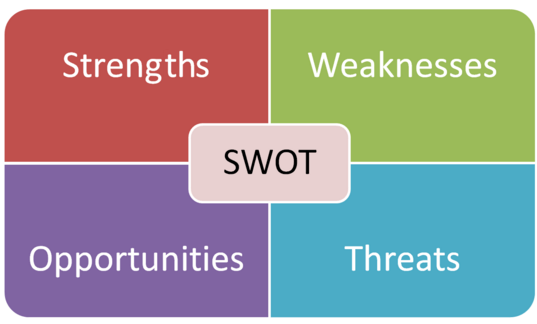
As it is illustrated below, strengths and weaknesses are internal, i.e. businesses are able to influence and to manipulate with their strengths and weaknesses. Opportunities and threats, on the other hand, are external. It means businesses can only react to opportunities and threats and they do not have any means to influence opportunities and threats.
SWOT analysis has important practical implications. Specifically, with findings of SWOT analysis in their hands, the senior level management identify and built upon their strengths, discover new opportunities and work upon eliminating or minimising threats to the business. Accordingly, SWOT can be a powerful aid for senior level management to develop appropriate strategy for the business.
As a strategic analytical tool, SWOT analysis has some weaknesses as well. Specifically, the application of this tool may encourage users to focus on quantity of factors, instead of focusing on a few, but the most powerful factors having the biggest impact on the business. In other words, SWOT analysis lacks guidance and provision in terms of differences in importance between factors. As a result weak strengths may appear to balance strong weaknesses.
The majority of sources explaining SWOT analysis assume that their audience is businesses aiming to improve their operational efficiency. This SWOT analysis resource is different. It explains SWOT analysis assuming that you a business student and you have been assigned to conduct SWOT analysis as a part of your assignment.
How to do SWOT Analysis
You can conduct a SWOT analysis with the following four steps:
Step 1: Selecting a company
If your assignment requires conducting a SWOT analysis, you are either given a case study company by your educational institution or you are free to analyze a company of your own choice. In the first scenario, you have no option but to conduct a SWOT analysis of the company named in your assignment instructions. However, the majority of educational institutions provide students the flexibility to conduct SWOT analysis of a company of their own choice.
Students are often tempted to conduct SWOT analysis of their employer. Choosing your employer as a case study can be a good strategy if you have an access to detailed relevant information. Please note that only descriptive information would not suffice and you will have to justify your arguments by referring to relevant quantitative data. Therefore, if you are not able to find relevant quantitative data about your employer, your best choice could be to conduct SWOT analysis of a multinational enterprise. This is due to the availability of data about the majority multinational enterprises. This portal offers up-to-date sample SWOT analyses of the most famous multinational enterprises as part of company reports .
Step 2: Finding information
If you are conducting a SWOT analysis of a small or medium sized organization such as your employer, family business or a company you are related to in some ways, approaching the company directly may prove to be an efficient strategy to obtain required information. You may try to secure a meeting with a senior level manager and explain practical implications of your SWOT analysis for the business. In other words, you may be able to convince a senior manager that results of your SWOT analysis may provide an important insight into the business and managers can act upon this knowledge to increase the efficiency of the business at various fronts.
Alternatively, if you are conducting SWOT analysis of a multinational enterprise, company annual report is usually the most comprehensive source of the relevant information. Note that annual reports highlight information about strengths of the business within the first few pages and you cannot find information about weaknesses of a company in its annual report for obvious reasons.
Information about Strengths in SWOT Analysis
Information about strengths of the company is easiest to find in your SWOT analysis. Strengths are competitive advantages of the business that made it successful in the first place. In case of small or medium sized organizations, the manager you are interviewing will be happy to discuss the strengths of the business.
In case of multinational companies, on the other hand, the first few pages of annual reports boast about competitive advantages of the business by referring to specific figures and charts. Using some of these charts in your assignment and properly referencing the source is going to increase the quality of your work.
You can determine strengths of businesses in answers to the following questions:
- What advantages does the company have?
- What does the company better than its competitors?
- What unique or low-cost resources are available to the company that are not available to its rivals?
- What Unique Selling Propositions (UPS) are associated with the company?
The following table illustrates the major strengths possessed by businesses and tips about how to discuss these strengths in your swot analysis:
Information about Weaknesses in SWOT Analysis
It may not be easy to find information about weaknesses of small and medium sized businesses. The manager you are interviewing may not want to discuss weaknesses of their business either intentionally, or they may not be aware of weaknesses. It is important for you to motivate your interviewee to discuss weaknesses of their company by asking relevant questions in a polite way.
It is easier with multinational organizations. An extensive online research can reveal relevant information about weaknesses associated with the company you are analyzing.The majority of big corporations have been involved in some kind of scandals during the past two years and you can discuss the damage of these scandals to the brand image as noteworthy weakness of the company.
For example, suppose you have chosen Coca Cola Company for your SWOT analysis assignment. If you google the term ‘Coca Cola scandal’, search results on the top relate to a scandal where the company funded obesity research that downplayed the negative health implications of Coca Cola products. Negative implications of this incident on Coca Cola brand image is brand’s weakness you can discuss in you SWOT analysis.
All arguments and numbers need to be referenced using referencing style required by your educational institution in an appropriate manner. Preference has to be given to online journals and magazines over online discussion forums and personal blogs.
Answers to the following questions can help to identify weaknesses of your case study company:
- What aspects of the business could the company improve?
- What should the company avoid?
- What factors are causing the company to lose sales?
- What aspects of products/services are customers are likely to see as weaknesses?
Major weaknesses of businesses and brief tips about discussing them in your assignment are illustrated in the following table:
Information about Opportunities in SWOT Analysis
Information about opportunities available to the business can be derived from its weaknesses in a way that businesses often have an opportunity to turn their weaknesses into strengths. At the same time, it is important that your SWOT analysis also identifies a set of opportunities that are not related to weaknesses. If you can’t think of any company-specific opportunities, you can discuss business opportunities that can be explored by any business in general, such as new product development, international market expansion and increasing the level of effectiveness of social media marketing. Interesting trends in the industry can also be opportunities for the business.
Opportunities can be identified through answering the following questions:
- What are interesting trends in the market that can be profitably explored by the company?
- What are the demographic and social changes that present new opportunities in the industry?
- Are there any government policies and regulations that can help the industry?
- Are there any opportunities for the company related to technological developments?
The following table illustrates the major opportunities available for businesses and tips about how to discuss these opportunities in your SWOT analysis:
Information about Threats in SWOT Analysis
Threats faced by the business can be classified into two categories. Firstly, there are company-specific threats that stem from company-specific factors such as the threat of losing market share due to ineffective cost structure or the threat of negative media coverage and damage to the brand image due to neglecting the importance of corporate social responsibility. Secondly, there are threats to the industry or to the economy on the whole, such as a threat of introducing tariffs to a certain range of products or the threat of a global economic and financial crisis. You will need to find information about threats belonging to both categories with more emphasis on the threats from the first category, i.e. company-specific threats.
You can identify the main threats to the business through answering the following questions:
- What are the main obstacles faced by the company?
- What are the latest developments in competitor Unique Selling Propositions?
- Does the company have substantial amount of bad debts or cash-flow problems?
- Was the company involved in any scandal recently?
Main threat facing the majority of businesses and brief tips about discussing them in your SWOT analysis are illustrated in the following table:
Step 3: Writing
You can structure your writing of SWOT analysis in the following way:
Firstly, you will need to discuss the company profile, its strategy and the most recent changes that have taken place in the company prior to presenting your SWOT analysis. The length of such a discussion depends on your assignment instructions and the total word count for your assignment.
Secondly, develop a SWOT Analysis Matrix for your chosen company. You can develop a table containing four sections headed strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. Major strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of your chosen company can be presented in bullet points under respective boxes. These should be precise and verifiable statements.
Using steps 1 and 2 above, you should have long list of factors related to strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats for the business. Now it is time to prioritize factors to be included in your SWOT analysis by focusing on the most significant factors. The numbers of factors that should be discussed under each category depends on the total word-count for your assignment.
Thirdly, you have to discuss bullet points in your SWOT table. Your analysis needs to contain statistical data and ideally graphs and tables as well. Do not forget to reference sources, using referencing system required by your university. Moreover, you can discuss how to address weaknesses and threats identified as a result of your SWOT analysis and get additional marks for your work.
SWOT Analysis Example
This portal contains example SWOT analysis of the following companies:

SWOT is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats related to organizations. The following table illustrates SWOT analysis:
SWOT Analysis Template
Please choose an industry and a company below to generate a SWOT table containing bullet points of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of your chosen company. In order to complete the SWOT analysis you will need to expand the bullet points into a couple of paragraphs with discussions and references from reliable sources to support your arguments.

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Related Articles
Critical Success Factors
What Is Strategy?
Porter's Five Forces - The Framework Explained
Pitfalls of Porter's Five Forces
Article • 17 min read
SWOT Analysis
Understanding your business, informing your strategy.
Written by Kevin Dunne
Reviewed by Keith Jackson
Key Takeaways:
SWOT stands for S trengths, W eaknesses, O pportunities, and T hreats.
A "SWOT analysis" involves carefully assessing these four factors in order to make clear and effective plans.
A SWOT analysis can help you to challenge risky assumptions, uncover dangerous blindspots, and reveal important new insights.
The SWOT analysis process is most effective when done collaboratively.
What Is a SWOT Analysis?
SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats, and so a SWOT analysis is a technique for assessing these four aspects of your business.
SWOT Analysis is a tool that can help you to analyze what your company does best now, and to devise a successful strategy for the future. SWOT can also uncover areas of the business that are holding you back, or that your competitors could exploit if you don't protect yourself.
A SWOT analysis examines both internal and external factors – that is, what's going on inside and outside your organization. So some of these factors will be within your control and some will not. In either case, the wisest action you can take in response will become clearer once you've discovered, recorded and analyzed as many factors as you can.
In this article, video and infographic, we explore how to carry out a SWOT analysis, and how to put your findings into action. We also include a worked example and a template to help you get started on a SWOT analysis in your own workplace.
Why Is SWOT Analysis Important?
SWOT analysis can help you to challenge risky assumptions and to uncover dangerous blindspots about your organization's performance. If you use it carefully and collaboratively, it can deliver new insights on where your business currently is, and help you to develop exactly the right strategy for any situation.
For example, you may be well aware of some of your organization's strengths, but until you record them alongside weaknesses and threats you might not realize how unreliable those strengths actually are.
Equally, you likely have reasonable concerns about some of your business weaknesses but, by going through the analysis systematically, you could find an opportunity, previously overlooked, that could more than compensate.
How to Write a SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis involves making lists – but so much more, too! When you begin to write one list (say, Strengths), the thought process and research that you'll go through will prompt ideas for the other lists (Weaknesses, Opportunities or Threats). And if you compare these lists side by side, you will likely notice connections and contradictions, which you'll want to highlight and explore.
You'll find yourself moving back and forth between your lists frequently. So, make the task easier and more effective by arranging your four lists together in one view.
A SWOT matrix is a 2x2 grid, with one square for each of the four aspects of SWOT. (Figure 1 shows what it should look like.) Each section is headed by some questions to get your thinking started.
Figure 1. A SWOT Analysis Matrix.
Swot analysis template.
When conducting your SWOT analysis, you can either draw your own matrix, or use our free downloadable template .
How to Do a SWOT Analysis
Avoid relying on your own, partial understanding of your organization. Your assumptions could be wrong. Instead, gather a team of people from a range of functions and levels to build a broad and insightful list of observations.
Then, every time you identify a Strength, Weakness, Opportunity, or Threat, write it down in the relevant part of the SWOT analysis grid for all to see.
Let's look at each area in more detail and consider what fits where, and what questions you could ask as part of your data gathering.
Strengths are things that your organization does particularly well, or in a way that distinguishes you from your competitors. Think about the advantages your organization has over other organizations. These might be the motivation of your staff, access to certain materials, or a strong set of manufacturing processes.
Your strengths are an integral part of your organization, so think about what makes it "tick." What do you do better than anyone else? What values drive your business? What unique or lowest-cost resources can you draw upon that others can't? Identify and analyze your organization's Unique Selling Proposition (USP), and add this to the Strengths section.
Then turn your perspective around and ask yourself what your competitors might see as your strengths. What factors mean that you get the sale ahead of them?
Remember, any aspect of your organization is only a strength if it brings you a clear advantage. For example, if all of your competitors provide high-quality products, then a high-quality production process is not a strength in your market: it's a necessity.
Weaknesses, like strengths, are inherent features of your organization, so focus on your people, resources, systems, and procedures. Think about what you could improve, and the sorts of practices you should avoid.
Once again, imagine (or find out) how other people in your market see you. Do they notice weaknesses that you tend to be blind to? Take time to examine how and why your competitors are doing better than you. What are you lacking?
Be honest! A SWOT analysis will only be valuable if you gather all the information you need. So, it's best to be realistic now, and face any unpleasant truths as soon as possible.
Opportunities
Opportunities are openings or chances for something positive to happen, but you'll need to claim them for yourself!
They usually arise from situations outside your organization, and require an eye to what might happen in the future. They might arise as developments in the market you serve, or in the technology you use. Being able to spot and exploit opportunities can make a huge difference to your organization's ability to compete and take the lead in your market.
Think about good opportunities that you can exploit immediately. These don't need to be game-changers: even small advantages can increase your organization's competitiveness. What interesting market trends are you aware of, large or small, which could have an impact?
You should also watch out for changes in government policy related to your field. And changes in social patterns, population profiles, and lifestyles can all throw up interesting opportunities.
Threats include anything that can negatively affect your business from the outside, such as supply-chain problems, shifts in market requirements, or a shortage of recruits. It's vital to anticipate threats and to take action against them before you become a victim of them and your growth stalls.
Think about the obstacles you face in getting your product to market and selling. You may notice that quality standards or specifications for your products are changing, and that you'll need to change those products if you're to stay in the lead. Evolving technology is an ever-present threat, as well as an opportunity!
Always consider what your competitors are doing, and whether you should be changing your organization's emphasis to meet the challenge. But remember that what they're doing might not be the right thing for you to do. So, avoid copying them without knowing how it will improve your position.
Be sure to explore whether your organization is especially exposed to external challenges. Do you have bad debt or cash-flow problems, for example, that could make you vulnerable to even small changes in your market? This is the kind of threat that can seriously damage your business, so be alert.
Use PEST Analysis to ensure that you don't overlook threatening external factors. And PMESII-PT is an especially helpful check in very unfamiliar or uncertain environments.
A SWOT Analysis Example
Imagine this scenario: a small start-up consultancy wants a clear picture of its current situation, to decide on a future strategy for growth. The team gathers, and draws up the SWOT Analysis shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. A Completed SWOT Analysis.
As a result of the team's analysis, it's clear that the consultancy's main strengths lie in its agility, technical expertise, and low overheads. These allow it to offer excellent customer service to a relatively small client base.
The company's weaknesses are also to do with its size. It will need to invest in training, to improve the skills base of the small staff. It'll also need to focus on retention, so it doesn't lose key team members.
There are opportunities in offering rapid-response, good-value services to local businesses and to local government organizations. The company can likely be first to market with new products and services, given that its competitors are slow adopters.
The threats require the consultancy to keep up-to-date with changes in technology. It also needs to keep a close eye on its largest competitors, given its vulnerability to large-scale changes in its market. To counteract this, the business needs to focus its marketing on selected industry websites, to get the greatest possible market presence on a small advertising budget.
Frequently Asked Questions About SWOT Analysis
1. who invented swot analysis.
Many people attribute SWOT Analysis to Albert S. Humphrey. However, there has been some debate on the originator of the tool, as discussed in the International Journal of Business Research .
2. What Does SWOT Analysis Stand For?
SWOT Analysis stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats.
3. What Can a SWOT Analysis Be Used For?
SWOT analysis is a useful tool to help you determine your organization's position in the market. You can then use this information to create an informed strategy suited to your needs and capabilities.
4. How Do I Write a SWOT Analysis?
To conduct a SWOT analysis, you first need to create a 2x2 matrix grid. Each square is then assigned to one of the four aspects of SWOT. You can either draw this grid yourself or use our downloadable template to get started.
5. How Do SWOT Analysis and the TOWS Matrix compare?
While SWOT analysis puts the emphasis on the internal environment (your strengths and weaknesses), TOWS forces you to look at your external environment first (your threats and opportunities). In most cases, you'll do a SWOT Analysis first, and follow up with a TOWS Matrix to offer a broader context.
6. What Are the Biggest SWOT Analysis Mistakes?
- Making your lists too long. Ask yourself if your ideas are feasible as you go along.
- Being vague. Be specific to provide more focus for later discussions.
- Not seeing weaknesses. Be sure to ask customers and colleagues what they experience in real life.
- Not thinking ahead. It's easy to come up with nice ideas without taking them through to their logical conclusion. Always consider their practical impact.
- Being unrealistic. Don't plan in detail for opportunities that don't exist yet. For example, that export market you've been eyeing may be available at some point, but the trade negotiations to open it up could take years.
- Relying on SWOT Analysis alone. SWOT Analysis is valuable. But when you use it alongside other planning tools (SOAR, TOWS or PEST), the results will be more vigorous.
How to Use a SWOT Analysis
Use a SWOT Analysis to assess your organization's current position before you decide on any new strategy. Find out what's working well, and what's not so good. Ask yourself where you want to go, how you might get there – and what might get in your way.
Once you've examined all four aspects of SWOT, you'll want to build on your strengths, boost your weaker areas, head off any threats, and exploit every opportunity. In fact, you'll likely be faced with a long list of potential actions.
But before you go ahead, be sure to develop your ideas further. Look for potential connections between the quadrants of your matrix. For example, could you use some of your strengths to open up further opportunities? And, would even more opportunities become available by eliminating some of your weaknesses?
Finally, it's time to ruthlessly prune and prioritize your ideas, so that you can focus time and money on the most significant and impactful ones. Refine each point to make your comparisons clearer. For example, only accept precise, verifiable statements such as, "Cost advantage of $30/ton in sourcing raw material x," rather than, "Better value for money."
Remember to apply your learnings at the right level in your organization. For example, at a product or product-line level, rather than at the much vaguer whole-company level. And use your SWOT analysis alongside other strategy tools (for example, Core Competencies Analysis ), so that you get a comprehensive picture of the situation you're dealing with.
SWOT Analysis Tips
Here are four tips for getting more out of a SWOT analysis:
- Be specific. The more focused and accurate you are about the points you write down, the more useful your SWOT analysis will be.
- Work backwards. Experiment with filling in the four sections of your SWOT analysis in a different order, to stimulate new ways of thinking. Working backwards, in particular, from threats to strengths, may cast new light on the situation.
- Get together. Highlight the most useful people to contribute to your SWOT analysis, then gather information and ideas from them all.
- SWOT your competition ! To stay ahead of your competitors, carry out a regular SWOT analysis on them . Use everything you know about them to evaluate their situation, and use SWOT analysis to plan your competitive strategies accordingly.
It's also possible to carry out a Personal SWOT Analysis . This can be useful for developing your career in ways that take best advantage of your talents, abilities and opportunities.
SWOT Analysis Infographic
See SWOT Analysis represented in our infographic :
SWOT Analysis helps you to identify your organization's Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
It guides you to build on what you do well, address what you're lacking, seize new openings, and minimize risks.
Apply a SWOT Analysis to assess your organization's position before you decide on any new strategy.
Use a SWOT matrix to prompt your research and to record your ideas. Avoid making huge lists of suggestions. Be as specific as you can, and be honest about your weaknesses.
Be realistic and rigorous. Prune and prioritize your ideas, to focus time and money on the most significant and impactful actions and solutions. Complement your use of SWOT with other tools.
Collaborate with a team of people from across the business. This will help to uncover a more accurate and honest picture.
Find out what's working well, and what's not so good. Ask yourself where you want to go, how you might get there – and what might get in your way.
Download Template Worksheet
This is your second and last free resource
Enjoy unlimited access to Mind Tools
Invest in Your Future – 35% Off Mind Tools Subscriptions!
This Black Friday, unlock expertly crafted courses and resources to boost your management skills and lead with confidence into 2025.
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Key Management Skills
Most Popular
Latest Updates

Strengths-Based Leadership

Hofstede's Cultural Dimensions in Today's Global Workplace
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Leading with humanity in the age of technology.
Building connections in a digital world
The EPRG Model and Global Business Strategy
Essential strategies for thriving in international markets
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
The soft edge: where great companies find lasting success.
Rich Karlgaard
Book Insights
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Women in Leadership
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
Member Newsletter
Introducing the Management Skills Framework
Transparent Communication
Social Sensitivity
Self-Awareness and Self-Regulation
Team Goal Setting
Recognition
Inclusivity
Active Listening
Coaching, Online Training Courses, Learning Resources and People Development Training to Train the Trainer
SWOT Analysis Assignment – the basics & method
05/08/2012 by Mike Morrison 13 Comments
SWOT Analysis Assignment – the basics
What is a SWOT analysis?

In simple terms a SWOT is a look at the factors and influences which may be considered a Strength , Weakness , Opportunity or Threat to an organization, its mission or goal or its current business plan/ objective.
Assignments on SWOT & Business
When studying management, marketing, business or human resources, it is not uncommon to be asked to complete a SWOT analysis assignment. What often makes this difficult is that it is also typically one of the first assignments students get assigned early on in the course so it is doubly difficult.
As you look around the web you are looking for an example to base your assignment on – for example you may have been asked to do a SWOT analysis on:
Amazon, American Airlines, Apple, ASDA, Best buy, BMW, Body Shop, Bose, British Airways, Burger King, Cadbury’s, Cafe Nero, Coca-Cola, Dell, EasyJet, EBay, English National Opera, Ericsson, Ford, French Connection (Fcuk), Google, Harley-Davidson, Heinz, Hewlett-Packard (HP), Home Depot, B & Q, HTC, IKEA, KFC, Krispy Kreme, Lenovo, LG, Marks and Spencer (M&S), McDonalds, Mercedes Benz, Microsoft, Morrisons, Nike, Nissan, Nokia, O2, Orange, Pepsi, Pizza Hut, RadioShack, Reebok, Renault, Rolls Royce, Ryanair, Samsung, Sony, Starbucks, Talktalk, Tata, Tesco, Three, T-Mobile, Toshiba, Toyota, Trebor Bassett, Vauxhall, Virgin, Vodafone, Walmart, Wella, Yumm Foods
….. or indeed 1000’s of other companies, colleges, groups, industries and sectors.
The one danger of looking for such “ready made” SWOT analysis is that before they get to the web they are out of date – and may indeed contain significantly out of date materials. For example a SWOT may have been done before the banks needed finance to survive, or on retail before the recession hit and changed many of their strengths.
Using the work of previous people may seem like it is giving you an advantage – it is not.
Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and threats of the SWOT analysis are very much transient. Some factors may well be stable for years, or at least financial quarters, other factors may be less predictable. For example HMV for the past 2 years have been developing and branching out into new areas to satisfy shareholder and customer expectations, however as I write this piece they are in discussions with banks regarding funding to manage a difficult cash-flow situation. n just 6 months HMV may not exists.
This means copying research from others done months if not years earlier is in fact one of the most dangerous things you could do – I hope that tutors penalise students for doing this. SWOT is a greatly undervalued and under-used management tool which deserves to be a core skill. the more you do (and dynamically) the better you will get at it.
A SWOT analysis just one of the tools available to managers and organizations to frovide a framework to help understand and analyise its market position or markets where it sells its products. SWOT can also be used to look at processes and product (or service) ranges it offers.
SWOT as we know stands for the Strengths and Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats which the organization perceives.
Strengths and weaknesses consider the internal (controllable) factors and Opportunities and Threats are external from the organization and to a greater or lesser extent are not controllable. They are the environment or context in which the organization operates.
Using the data gathered in the SWOT process, this information can be prioritised and a judgement made as to the likelihood and impact on the organization and its business.
SWOT is a tool to help structure the data collection to aid the decision making process. SWOT is actually an audit tool, rather than an analysis tool.
How to do a SWOT
Much like the saying – How do you eat an elephant – one bite at a time, a SWOT can be approached in much the same way:
Much like good practice brainstorming , the best way is for any individual involved in the SWOT to work on their own and to brainstorm Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities & Threats (use of the PRIMO-F & PESTLE frameworks can help). Then after researching on the internet, company accounts, industry reports etc – add more factors.
When this is done then a group activity should take each of the factors identified under Strengths , Weaknesses , Opportunities & Threats and build a complete table.

A SWOT review on SWOT:
Strengths – simple, flexible, quick, can be in-depth
Weaknesses – relies on those doing it to cover all factors, appears simplistic, too simple?, appears weak/ not robust
Opportunities – helps to see a business or organization from different perspectives, to review the “current state” on a regular basis
Threats – significant risks to the business, organization or plan may be ignored, Politically managers may not like what they see
For more information see our main page on SWOT Analysis
About Mike Morrison
Mike is a consultant and change agent specialising in developing skills in senior people to increase organizational performance. Mike is also founder & director of RapidBI, an organizational effectiveness consultancy. Check out his linkedin profile MikeMorrison LinkedIn Profile
SWOT Analysis Assignment – the basics & method http://t.co/JE5Lx2h3
SWOT Analysis Assignment – the basics & method http://t.co/wAqkpjSu
SWOT Analysis Assignment the basics & method – SWOT Analysis Assignment the basics What is a SWOT analysis? In sim… http://t.co/mp3AQOaO
RT: @rapidbi SWOT Analysis Assignment – the basics & method: SWOT Analysis Assignment – the basics What is a SWO… http://t.co/05Ot5zDR
New Blog post: SWOT Analysis Assignment – the basics & method http://t.co/e81HALm7
RT @RapidBI: New Blog post: SWOT Analysis Assignment – the basics & method http://t.co/xabzirIO
New Blog post: SWOT Analysis Assignment – the basics & method http://t.co/4HooaHUr
RT@rapidbi SWOT Analysis Assignment – the basics & method: SWOT Analysis Assignment – the basics What is a SWOT … http://t.co/Hwdlgiyo
SWOT Analysis Assignment [the basics] –
New Blog post: SWOT Analysis Assignment – the basics & method
SWOT Analysis Assignment – the basics & method: SWOT Analysis Assignment – the basics What is a SWOT analysis? I…
RT@rapidbi SWOT Analysis Assignment – the basics & method: SWOT Analysis Assignment – the basics What is a SWOT …
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

ARTICLE TAG CLOUD
Short cuts to some of our key content, free leadership resources.
- Management Training, Management Development and Business Articles and Resources
- Resource Zone
- Useful Links
- Cookie Policy
- Terms of Business and Site Terms


IMAGES
COMMENTS
SWOT Analysis Assignment 9/16/ Description: A personal SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis will give students an opportunity to reflect and identify their personal characteristics that helps them achieve and expand their Learning Objectives within the workplace.
SWOT analysis Assignments (Group assignments) Mini SWOT 3% • You will complete an analysis of one biotech company • The one that you discussed in the first workshop. • Living Carbon • Avantium • Lygenesis • You can also pick from the companies below that developed some of the top-selling biotechnology drugs • Due date: Oct 2
To help you decide if your proposed business can be viable, you need to do a SWOT Analysis (SWOT stands for S trengths, W eaknesses, O pportunities, and T hreats). See below for some great SWOT examples. For this assignment you will be use an E-commerce Plan template. Download it here.
What are the key strengths of the company? (Explain at least 2 strengths that enable the company to survive in a fast-changing environment) The two key strengths according to me are strong product portfolio and localization of products .which are giving them extra advantages against its competitors.
A SWOT analysis is designed to get you thinking about how to use your personal strengths and opportunities to your advantage, while also improving your weaknesses and mitigating threats that you can predict.
I learned that a SWOT analysis is a useful tool for evaluating the internal and external factors that cand define the success or downfall of a company. It helps to identify the strengths and weaknesses of the business as well as the opportunities for growth.
SWOT is a strategic analytical tool for assessing strengths and weaknesses of a business, analyzing opportunities available to the business, as well as, threats faced by the business. SWOT analysis can be used at organizational and personal levels.
SWOT Analysis helps you to identify your organization's Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It guides you to build on what you do well, address what you're lacking, seize new openings, and minimize risks.
In simple terms a SWOT is a look at the factors and influences which may be considered a Strength, Weakness, Opportunity or Threat to an organization, its mission or goal or its current business plan/ objective. Assignments on SWOT & Business.
How do we stand apart from others? What are our assets, and which are the strongest? What unique resources do we have? (Do we have any expertise or unique talents?) What do we offer to others? What do others think we do well? What is great about our team and our team culture? Do we have a sustainable competitive advantage? Other?